Abstract
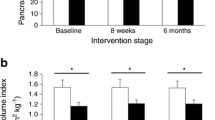
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus are associated with reduced pancreatic size. This could be caused by insulinopenia with loss of a trophic insulin effect and/or other factors associated with a diabetic state. To investigate the role of long-term moderate insulinemia per se, we compared the pancreatic size in healthy subjects with documented low (n=5) and high (n=5) insulin secretion. Insulin responses to a glucose clamp (11 mM) procedure were threefold higher in the high insulin responders (HIR) than low insulin responders (LIR). Age, body mass index (BMI), and blood glucose were similar between groups. Computed tomography showed no difference in total pancreatic size (total pancreas volume 84.8±29.4 ml in LIR, 79.8±8.4 ml in HIR; NS) nor in the size of various parts (caput, corpus, or cauda). We conclude that moderate hypoinsulinemia of long duration does not affect the pancreatic size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fonesca V, Berger LA, Beckett AG, Dandona P, Size of pancreas in diabetes mellitus: a study based on ultrasound. Br Med J 291:1240–1241, 1985
Gilbeau JP, Poncelet V, Libon E, Derue G, Heller FR The density, contour, and thickness of the pancreas in diabetics: CT findings in 57 patients. Am J Radiol 159:527–531, 1992
Brunova E, Bruna J, Bartos V et al, Pancreatic and renal size and density determined by computed tomography in patients with type I (insulin dependent) diabetes. Radiol Diagn (Berl) 27:737–744, 1986
Hill DJ, Milner RD, Insulin as a growth factor. Pediatr Res 19:879–886, 1985
Adler G, Kern HF, Regulation of exocrine pancreatic secretory process by insulin in vivo. Horm Metab Res 7:290–296, 1975
Henderson JR, Daniel PM, Fraser PA, The pancreas as a single organ: the influence of the endocrine upon the exocrine part of the gland. Gut 22:158–167, 1981
Efendic S, Luft R, Wajngot A, Aspects of the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocrine Rev 5:395–408, 1984
Alvarsson M, Grill V, Wajngot A, Cerasi E, Efendic S, Long term stability of low insulin responses to glucose in non-diabetic subjects. Acta Endocrinol 127:33–37, 1992
World Health Organization Expert Committee on Diabetes Mellitus, Technical report series 727, Geneva, 1985
DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R, Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol 237:E214–E223, 1979
Grill V, Pigon J, Hartling SG, Binder C, Efendic S, Effects of dexamethasone on glucose-induced insulin and pro-insulin release in low and and high insulin responders. Metabolism 39:251–258, 1990
Herbert V, Lau KS, Gottlieb CW, Bleicher SJ, Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 25: 1375–1384, 1965
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nyrén, S., Blomqvist, L., Efendic, S. et al. Pancreas size and insulin secretion: lack of association in non-diabetic subjects. Acta Diabetol 33, 274–276 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571563
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571563