Abstract
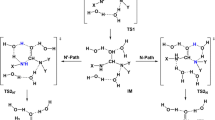
The hydrolysis of amides is a model reaction to study peptide hydrolysis. This process has been previously considered in the literature at the ab initio level. In this work, we revisit different reaction mechanisms (water-assisted, non-assisted, neutral and acid-catalyzed) with various theoretical methods : semiempirical, ab initio and Density Functional. The ab initio calculations are carried out at a computational level which is substantially higher than in previous studies. We describe the structure of the transition states and discuss the influence of the catalyst. We also compute the activation free energies for these processes at the Density Functional Theory level. Comparison of the methods allows to outline the main trends of these theoretical approaches which may be useful to design new computational strategies for investigating biological reaction mechanisms through the use of combined Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 July 1997 / Accepted: 21 October 1997 / Published: 30 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonczak, S., Ruiz-López, M. & Rivail, JL. The Hydrolysis Mechanism of Formamide Revisited: Comparison Between ab initio, Semiempirical and DFT Results. J Mol Med 3, 434–442 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s008940050061
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s008940050061