Abstract:
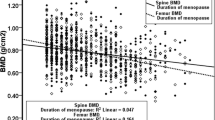
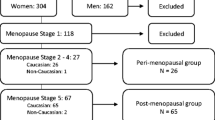
To determine the effects of menopause on bone loss in different parts of the skeleton, bone mineral density (BMD) values were measured longitudinally in 85 healthy women. BMD values included the lumbar spine measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and quantitative CT (QCT) and the distal and midradius measured by DXA obtained over 5 years. BMD at the calcaneus was measured using DXA for 3 years, and the BMD values of the distal metaphyses and diaphyses of radius and tibia were measured using peripheral QCT (pQCT) for 4 years. The subjects were 19 premenopausal, 17 perimenopausal, 12 early postmenopausal and 38 late postmenopausal women with the respective average ages of 39.1 ± 7.1 (SD), 51.9 ± 2.9, 55.8 ± 1.8 and 61.9 ± 3.9 years at the start of measurement. Average years since menopause were 1.4 ± 1.8, 3.3 ± 1.3 and 12.7 ± 5.3 years, respectively. In the perimenopausal group, the annual rate of bone loss for lumbar trabecular bone measured by QCT, and for the calcaneus, and metaphyseal trabecular bone at the radius and tibia by pQCT were higher than the respective values in the premenopausal group. These values in the late postmenopausal group became significantly lower compared with those in the perimenopausal group, coming down to the level of the premenopausal group. While the annual rates of bone loss at the tibial diaphysis in the perimenopausal group were also higher than those in the premenopausal group, the values at the radial diaphysis by DXA or pQCT did not differ significantly. The reductions in the annual rates of bone loss with the passage of time after menopause were not marked in these cortical bone dominated sites. These data indicated that the annual rates of bone loss at trabecular bone dominated sites were accelerated in both axial and appendicular skeletons. Diaphyseal cortical bone, however, seemed to be less sensitive to estrogen withdrawal. Other factors, such as genetics and calcium/vitamin D metabolism, would also affect the age-dependent bone loss at the cortical bone dominated sites after menopause.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 October 1998 / Accepted: 6 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, M., Nakamura, T., Tsurusaki, K. et al. Effects of Menopause on Age-Dependent Bone Loss in the Axial and Appendicular Skeletons in Healthy Japanese Women . Osteoporos Int 10, 377–383 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980050243
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980050243