Summary
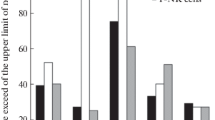
Thirty-one patients with classical or definite rheumatoid arthritis (RA), on treatment with azathioprine and sodium aurothiomalate in combination were studied. Absolute lymphocyte counts and IgA levels were reduced but this did not reach statistical significance. Lymphocyte transformation with phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) showed no significant difference from a control group. However, antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity was significantly impaired compared to rheumatoid controls (p<0.001). There was no relation to the degree of impairment of ADCC and the current dose of azathioprine nor to the total dose or duration of therapy. Inhibiting material to cell-mediated cytotoxicity was present in the sera of 23 patients but its presence showed no relation to the degree of cytotoxicity exhibited by cells in the same patient. Our studies of cellular cytotoxicity have revealed alterations in cellular function possibly attributable to azathioprine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Silva M. and Hazleman B. Long term azathioprine in rheumatoid arthritis. A double-blind study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1981, 40, 560–563.
Haegert D.G., Hallberg T.D. and Coombs R.R.A. B and T lymphocyte subpopulations in human peripheral blood. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol 1974, 46, 525–538.
Hallberg T., Guru B.W. and Coombs R.R.A. Opsonic Adherence of sensitised red cell to human lymphocytes as easured by rosette formation. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol 1973, 44, 500–513.
Pellegrino M.A. Ferrone S., Dierich H.P. and Reisfeld R.A. Enhancement of sheep red blood cell human lymphocyte rosette formation by the sulphydryl compound 2 — aminoethylisothiouronium bromide. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol 1975, 3, 324–333.
Franks D., Kelly N.M. and Sanderson C.J. Inhibition of xenogeneic cell-mediated cytotoxicity in the rat by antiglobulin sera. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immonol. 1975, 48, 621–631.
Sanderson C.J. and Taylor G.A. The kinetics of51Cr release from target cells in cell mediated cytotoxicity and the relationship to the kinetics of killing. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1975, 8, 23–32.
Denman E.J., Denman A.M., Greenwood B.M., Gall D. and Heath R.B. Failure of cytotoxic drugs to suppress immune responses of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1970, 29, 220–2316.
Micheli A. and Bron J. Studies on Blood T and B lymphocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1974, 33, 435–436.
Eremin O. Personal communication.
Campbell A.C., Skinner J.M., Maclennan C.M. Hersey P., Waller C.A., Wood J., Jewell D.P. and Truelove S.C. Immunosuppression in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. II the effects of azathioprine on lymphoid cell populations in a double-blind trial in ulcerative colitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol 1976, 24, 249–258.
Rosenberg J.N. and Currey H.L.F. Antibody dependent and PHA induced cellular cytotoxicity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1979, 38, 347–350.
Cooke L.A., Hay F.C. and Perumal R. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1979, 38, 252–256.
Wisloff F., Froland S.S. and Natvig J.B. Deficient lymphoid cell mediated, PHA-induced cytotoxicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Scand. J. Immunol. 1975, 4, 303–307.
Froland S.S., Natvig J.B. and Wisloff F. Lymphocyte sub-populations in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 1975, 6, 231–241.
Feldman J.L., Becker M.I., Moutsopoulos H., Fye K., Blackman M., Epstein W.V. and Talal N. Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity in selected autoimmune diseases. J. Clin. Invest. 1976, 58, 173–179.
Panayi G.S., and Corrigall V. Functional assay of cytotoxic lymphocytes involved in antibody-mediated cytotoxicity in normal and rheumatoid subjects. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1977, 36, 257–260.
Sany J., Clot J., Frietas M., Charmasson E., and Serre H. Antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) of rheumatoid arthritis blood lymphocytes. Rev. Rheum. Mal. Osteoartic 1976, 43, 333–338.
Isturiz M.A., de Bracco M.M., de E., Pizzi A.M. and Manni J.A. Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976, 19, 725–730.
McGill P.E. and Twinn I. Antibody-mediated cytotoxicity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1977, 36, 268–270.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis, P., Hazleman, B.L., Park, J.R. et al. Immunological studies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving azathioprine and myocrisin in combination. Clin Rheumatol 1, 168–175 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02042770
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02042770