Summary
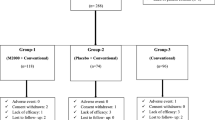
The efficacy and tolerability of sulphasalazine (SASP) was examined in a double blind, placebo-controlled 24-week study of 32 patients with rheumatoid factor (RF)-negative RA. Twelve patients (75%) of the SASP group completed the study; 4 patients were withdrawn because of an adverse event. Ten patients (62.5%) in the placebo group completed the study; 5 dropped out because of lack of response and one because of an adverse reaction.
Efficacy was demonstrated by a significant and sustained improvement in the indices of disease activity in the SASP group. It was confirmed by significant intergroup differences in favour of SASP over placebo in the changes in ESR, Ritchie index, number of painful joints and clinical score. There was also a significant difference in favour of SASP in the number of responders and the number of withdrawals due to inefficacy. The character, frequency and timing of side-effects were similar to those previously reported. All were reversible on stopping therapy.
This study shows that SASP is an effective second-line drug for treating patients with RF-negative RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McConkey, B., Amos, R.S., Durham, S. Sulphasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ 1980, 280, 442–444.
Bird, H.A., Dixon, J.S., Pickup, M.E., Wright, V. A biochemical assessment of sulphasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1982, 9, 36–45.
Neumann, V.C., Grindulis, K.A., Wright, V., McConkey, B. Comparison between penicillamine and sulphasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis: Leeds-Birmingham trial. BMJ 1983, 287, 1099–1102.
Pullar, T., Hunter, J.A., Capell, H.A. Sulphasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis: a double blind comparison of sulphasalazine with placebo and sodium aurothiomalate. BMJ 1983, 287, 1102–1104.
Farr, M., Tunn, E., Crockson, A.P., Bacon, P.A. The long-term effects of sulphasalazine and a comparative study with penicillamine. Clin Rheumatol 1984, 473–482.
Bax, D.E., Amos, R.S. Sulphasalazine: a safe, effective agent for prolonged control of rheumatoid arthritis. A comparison with aurothiomalate. Ann Rheum Dis 1985, 44, 194–198.
Pinals, R.S., Kaplan, S.B., Lawson, J.G., Hepburn, B. Sulphasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis; a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 1986, 29, 1427–34.
Nuver-Zwart, I.H., Van Riel, P.L.C.M., Van de Putte, L.B.A., Gribnau, F.W.J. A double-blind comparative study of sulphasalazine and hydroxychloroquine in rheumatoid arthritis: evidence of an earlier effect of sulphasalazine. Ann Rheum Dis 1989, 48, 389–395.
Porter, D., Madhok, R., Hunter, J.A., Capell, H.A. Prospective trial confirming the use of sulphasalazine and auranafin as second line drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1992, 51, 461–464.
Feltelius, N., Hallgren, R. Sulphasalazine in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 1986, 45, 396–399.
Dougados, M., Boumier, P., Amor, B. Sulphasalazine in ankylosing spondylitis: a double-blind controlled study in 60 patients. BMJ 1986, 293, 911–914.
Farr, M., Kitas, G.D., Waterhouse, L., Felix-Davies, D.D., Bacon, P.A. Sulphasalazine in psoriatic arthritis: a double-blind placebo controlled study. Br J Rheumatol 1990, 29, 46–49.
Mielants, H., Veys, E.M., Joos, R. Sulphasalazine (salazopyrin) in the treatment of enterogenic reactive synovitis ankylosing spondylitis with peripheral arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 1986, 5, 80–83.
van der Heijde, D.M., van Riel, P.L., Nuver-Zwart, I.H., Gribnau, F.W., van de Putte, L.B. Effects of hydroxychloroquine and sulphasalazine on progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1989, 1, 1036–1038.
van der Heijde, D.M., van Riel, P.L.C.M., van de Putte, L.B.A. Sulphasalazine versus hydroxychloroquine in rheumatoid arthritis (letter): 3 year follow-up. Lancet 1990, 1, 539.
Buchanan, W.W., Singal, D.P. Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis: Tell it as it is. J Rheumatol 1994, 21, 391–392.
Masi, A.T., Feigenbaum, S.L. Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis: fact or fiction? Arch Intern Med 1983, 143, 2167–2172.
Scott, D.L., Huskisson, E.C. The course of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Clinical Rheumatology. Ed.: Scott, D.L. The course and outcome of rheumatoid arthritis. Bailliere Tindall Press 1992, 6 (1), 1–21.
Isömaki, H.A. An epidemiologically based follow-up study of recent arthritis. Incidence, outcome and classification. Clin Rheumatol 1987, (suppl 2), 53–59.
Reilly, P.A., Elswood, J., Calin, A. Therapeutic intervention in rheumatoid arthritis: a case-controlled comparison of seronegative and seropositive disease. Br J Rheumatol 1988, 27, 102–105.
Edelman, J., Russell, A.S. A comparison of patients with seropositive and seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 1983, 3, 47–48.
Burns, T.M., Calin, A. The hand radiograph as a diagnostic discriminant between seropositive and seronegative rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled study. Ann Rheum Dis 1983, 42, 605–612.
Griffin, J., Celinska, E., Panayi, G.S., Gibson, T., Graham R. A radiological study of seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 1985, 24, 92.
McCarty, D.J., O'Duffy, J.D., Pearson, C., Hunter, J.B. Remitting seronegative symmetrical synovitis with pitting oedema (PS3 PE) syndrome. J Am Med Assoc 1985, 254, 2763–2767.
Arnett, F.C., Edworthy, S.M., Black, D.A. et al. The American Rheumatology Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988, 31, 315–323.
Gran, J.T., Husby, G. Editorial. Rheumatoid factor (RF)-negative arthritis and HLA-DR4. Proposal for criteria. J Rheumatol 1987; 14: 1079–1082.
Ritchie, D.M., Boyle, J.A., McInnes, J.M. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med 1968, 37, 393–406.
Farr, M., Scott, D.G.I., Bacon, P.A. Side-effect profile of 200 patients with inflammatory arthritis treated with sulphasalazine. Drugs 1986, 32 (suppls.), 49–53.
Amos, R.S., Pullar, T., Bax, D.E., Situnayake, D., Capell, H.A., Sulphazalazyne for rheumatoid arthritis: toxicity in 114 patients monitored for one to 11 years. BMJ 1986, 293, 420–423.
Multicentre Trial Group. A prospective 5-year comparison of treatment which included penicillamine and that excluding penicillamine in early rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 1986, 25, 184–192.
Nielsen, O.H. Sulphasalazine intolerance: a retrospective survey of the reasons for discontinuing treatment in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 1992, 17, 389–393.
Khan, A.K.A., Howes, D.T., Piris, J., Truelove, S.C. Optimum dose of sulphasalazine for maintenance treatment in ulcerative colitis. Gut 1980, 21, 232–240.
Pullar, T., Hunter, J.A., Capell, H.A. Sulphasalazine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: relationship of dose and serum levels in efficacy. Br J Rheumatol 1985, 24, 269–276.
Farr, M., Tunn, E.J., Symmons, D.P.M., Scott, D.G.I., Bacon, P.A. Sulphasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis: Haematological problems and changes in haematological indices associated with therapy. Br J Rheumatol 1989, 28, 134–138.
Prouse, P.J., Shawe, D., Gumpel, J.M. Macrocytic anaemia in patients treated with sulphasalazine for rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ 1986, 293, 1407.
Butler, R.C. Gold in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Rheumatoid arthritis: The Treatment Controversy. Eds.: Goddard, D.H., Butler, R.C. London and Basingstoke. Macmillan Press, 1984, 8–36.
Scott, D.L. Penicillamine. In: Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Treatment Controversy. Eds.: Goddard, D.H., Butler, R.C. London and Basingstoke, Macmillan Press 1984, 8–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farr, M., Waterhouse, L., Johnson, A.E. et al. A double-blind controlled study comparing sulphasalazine with placebo in rheumatoid factor (RF)-negative rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 14, 531–536 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02208150
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02208150