Summary
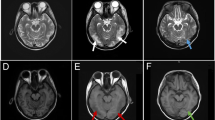
We present the unusual case of 16-year-old girl who developed intractable convulsions five days after the onset of a cold. Meningeal signs, lymphopenia, proteinuria, and lupus anticoagulant were also present. Treatment with anticonvulsants, antituberculous agents, and adenine arabinoside were ineffective. The initiation of methylprednisolone pulse therapy immediately resolved convulsions and fever. The diagnosis, suggested by the clinical course and the marked improvement of the meningoencephalitis by pulse therapy, was an encephalitic form of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Clinical and laboratory findings indicated that an immune disorder may have triggered an abnormal response to a viral infection leading to this patient's neurologic disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner, B., Tavori, S., Lerner, M., Tatarsky, I., Lorber, M. Association of lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies with thrombosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, primary antiphospholipid syndrome and other disorders. Isr J Med Sci 1992, 28, 9–15.
Asherson, R.A., Khamashta, M.A., Gil, A., et al. Cerebrovascular disease and antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus-like disease, and the primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Am J Med 1989, 86, 391–399.
Love, P.E., Santoro, S.A. Antiphospholipid antibodies: anticardiolipin and the lupus anticoagulant in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and in non-SLE disorders. Ann Intern Med 1990, 112, 682–698.
Nonomiya, C., Taniguchi, O., Kato, T., Hirano, T., Hashimoto, H., Hirose, S. Distribution and clinical significance of lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibody in 349 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus Intern Med 1992, 32, 194–199.
Gold, J.E., Haubenstock, A., Zalusky, R. Lupus anticoagulant and AIDS. N Engl J Med 1986, 314, 1252–1253.
Jeffrey, R.F. Transient lupus anticoagulant and fansidar therapy Postgrad Med J 1986, 62, 893–894.
Canoso, R.T., Oliveira, R.M. Chlorpromazine-induced anticardiolipin antibodies and lupus anticoagulant: absence of thrombosis. Am J Hematol 1988, 27, 272–275.
Behan, P.O. Post-infectious encephalomyelitis: some aetiological mechanisms. Postgrad Med J 1978, 54, 755–759.
Murphy, J., Austin, J. Spontaneous infection or vaccination as cause of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neuroepidemiology 1985, 4, 138–145.
Hsiung, G.D. Yale. In: Diagnostic Virology an Illustrated Handbook University Press, New Haven and London, 1973, p. 3.
Kutt, H., Winters, W., Kokenge, R., McDowell, F. Diphenylhydantoin metabolism blood levels, and toxicity. Arch Neurol 1964, 11, 642–648.
Kuroiwa, Y. Clinical features of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Rinshoshinkeigaku (Clinical Neurol) 1966, 6, 683–689. (in Japanese, Abstract in English).
Sirridge, M.S., Shannon, R. Detection of circulating coagulation inhibitor. In: Laboratory Evaluation of Hemostasis and Thrombosis. 3rd ed. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, 1983, p. 158.
Kesselring, J., Miller, D.H., Robb, S.A. et al. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Brain 1990, 113, 291–302.
Zarrabi, M.H., Zucker, S., Miller, F. et al. Immunologic and coagulation disorders in chlorpromazine-treated patients. Ann Intern Med 1979, 91, 194–199.
Asherson, R.A., Khamashta, M.A., Ordi-Ros, J. et al. The “primary” antiphospholipid syndrome: major clinical and serological features. Medicine 1989, 68, 366–374.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsukawa, Y., Mizutani, T., Kitamura, N. et al. Patient with both lupus anticoagulant and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Clin Rheumatol 15, 501–503 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02229651
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02229651