Abstract.
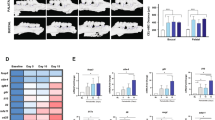
The purpose of this study was to clarify the involvement of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells on bone resorption induced by Escherichia coli endotoxin. Two kinds of monoclonal antibodies, anti-CD4 and/or anti-CD8, were employed for the depletion of each or both T cell subsets. E. coli endotoxin was injected into mouse mesial gingiva of the first molar of the left mandible every 48 hours for up to 14 days (7 injections). The mice were divided into four groups: CD4-depleted, CD8-depleted, T cell-depleted, and normal. The mice were sacrificed on the day after the 1st, 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 7th injection and alveolar bone was examined histopathologically and histomorphometrically. Bone surface in contact with osteoclasts was defined as the site of active resorption and the ratios of active resorption were compared among the four groups. In addition, sections obtained after the 1st, 4th, and 7th injection were immunohistologically stained in order to confirm the presence or absence of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. Alveolar bone resorption gradually increased in normal mice as the number of injections increased. In contrast, alveolar bone resorption was significantly weaker in each or both subset-depleted mice. For the duration of the experimental period, the number of CD4+ T cells in CD8-depleted and normal mice significantly increased with increasing bone resorption. Considering the function of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, these results suggest that each subset preferentially acts as a macrophage activator in the early period of bone resorption induced by E. coli endotoxin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 May 1997 / Accepted: 14 November 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hara, Y., Ukai, T., Yoshimura, A. et al. Histopathological Study of the Role of CD4- and CD8-Positive T Cells on Bone Resorption Induced by Escherichia coli Endotoxin. Calcif Tissue Int 63, 63–66 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002239900490
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002239900490