Summary
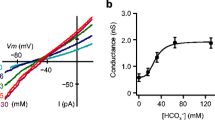
Using whole-cell patch-clamp techniques, we demonstrate that sheep parotid secretory cells have both inwardly and outwardly rectifying currents. The outwardly rectifying current, which is blocked by 10 mmol/liter tetraethylammonium (TEA) applied extracellularly, is probably carried by the 250 pS Ca2+-and voltage-activated K+ (BK) channel which has been described in previous studies. In contrast, the inwardly rectifying current, which is also carried by K+ ions, is not sensitive to TEA. It is similar to the inwardly rectifying currents observed in many excitable tissues in that (i) its conductance is dependent on the square root of the extracellular K+, (ii) the voltage range over which it is activated is influenced by the extracellular K+ concentration and (iii) it is blocked by the addition of Cs+ ions (670 µmol/liter) to the bathing solution. Our previously published cell-attached patch studies have shown that the channel type most commonly observed in the basolateral membrane of unstimulated sheep parotid secretory cells is a K+ channel with a conductance of 30 pS and, in this study, we find that its conductance also depends on the square root of the extracellular K+ concentration. It thus seems likely that it carries the inwardly rectifying K+ current seen in the whole-cell studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry, P.H., Lynch, J.W. 1991. Liquid junction potentials and small cell effects in patch clamp analysis.J. Membrane Biol. 121:101–117
Bechem, M., Glitsch, H.G., Pott, L. 1983. Properties of an inward rectifying K channel in the membrane of guinea-pig atrial cardioballs.Pfluegers Arch. 399:186–193
Bezanilla, F. 1985. A high capacity data recording device based on a digital audio processor and a video cassette recorder.Biophys. J. 47:437–441
Brismar, T., Collins, V.P. 1989. Inward rectifying potassium channels in human malignant glioma cells.Brain Res. 480:249–258
Burgen, A.S.V. 1956. The secretion of potassium in saliva.J. Physiol. 132:20–39
Coats, D.A., Denton, D.A., Goding, J.R., Wright, R.D. 1956. Secretion by the parotid gland of the sheep.J. Physiol. 131:13–31
Compton, J.S., Nelson, J., Wright, R.D., Young, J.A. 1980. A micropuncture investigation of electrolyte transport in the parotid glands of sodium-replete and sodium-depleted sheep.J. Physiol. 309:429–446
Cook, D.I., Young, J.A. 1989. Effect of K+ channels in the apical plasma membrane on epithelial secretion based on secondary active Cl− transport.J. Membrane Biol. 110:139–146
Cook, D.I., Young, J.A. 1989. Fluid and electrolyte secretion by salivary glands.In: Handbook of Physiology. The Gastrointestinal System. Salivary, Pancreatic, Gastric and Hepatobiliary Secretion. J.G. Forte, editor. Section 6, Volume III, pp. 1–23. American Physiological Society, Bethesda.
Cook, D.I., Young, J.A. 1990. Cation channels and secretion.In: Epithelial Secretion of Water and Electrolytes. J.A. Young and P.Y.D. Wong, editors. pp. 15–38. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg.
Cook, D.I., Wegman, E.A., Ishikawa, T., Young, J.A. 1990. Cation channels in the parotid and mandibular glands of the sheep.In: Exocrine Secretion II. P.Y.D. Wong, J.A. Young, editors. pp. 35–38. ISES, Hong Kong.
Cook, D.I., Wegman, E.A., Ishikawa, T., Poronnik, P., Read, A.M., Titchen, D.A., Allen, D.G., Young, J.A. 1992. TEA blocks muscarinically evoked secretion in the sheep parotid gland by a mechanism additional to its blockade of BK channels.Pfluegers Arch. 420:167–171
Cooper, K., Rae, J.L., Dewey, J. 1991. Inwardly rectifying potassium current in mammalian lens epithelial cells.Am. J. Physiol. 261:C15-C23
Hagiwara, S., Takahashi, K. 1974. The anomalous rectification and cation selectivity of the membrane of a starfish egg cell.J. Membrane Biol. 18:61–80
Halliwell, J.V., Adams, P.R. 1982. Voltage-clamp analysis of muscarinic excitation in hippocampal neurons.Brain Res. 250:71–92
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, A., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F. S. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high resolution current recording from cells and cell free membrane patches.Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Henderson, S., Graf, J., Boyer, J.L. 1989. Inward-rectifying potassium channels in rat hepatocytes.Am. J. Physiol. 256:G1028-G1035
Hirst, G.D.S., Edwards, F.R. 1989. Sympathetic neuroeffector transmission in arteries and arterioles.Physiol. Rev. 69:546–604
Hume, J.R., Uehara, A., 1985. Ionic basis of the different action potential configurations of single guinea-pig atrial and ventricular myocytes.J. Physiol. 368:525–544
Hunter, M., Oberleithner, H., Henderson, R.M., Giebisch, G. 1988. Whole-cell potassium currents in single early distal tubule cells.Am. J. Physiol. 255:F699-F703
Iwatsuki, N., Petersen, O.H. 1985. Action of tetraethylammonium on calcium-activated potassium channels in pig pancreatic acinar cells studied by patch-clamp single-channel and whole-cell current recording.J. Membrane Biol. 86:139–144
Kurachi, Y. 1985. Voltage-dependent activation of the inward-rectifier potassium channel in the ventricular cell membrane of guinea-pig heart.J. Physiol. 366:365–385
Maruyama, Y., Petersen, O.H., Flanagan, P., Pearson, G.T. 1983. Quantification of Ca2−-activated K+ channels under hormonal control in pig pancreas acinar cells.Nature 305:228–232
Matsuda, H. 1991. Magnesium gating of the inwardly rectifying K+ channel.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 53:289–298
McKinney, L.C., Gallin, E.K. 1988. Inwardly rectifying whole-cell and single-channel K currents in the murine macrophage cell line J774. 1.J. Membrane Biol. 103:41–53
McLarnon, J.G., Kim, S.U. 1989. Single channel potassium currents in cultured adult bovine oligodendrocytes.Glia 2:298–307
Ohmori, H., Yoshida, S., Hagiwara, S., 1981. Single K+ channel currents of anomalous rectification in cultured rat myotubes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78:4960–4964
Petersen, O.H., Gallacher, D.V. 1988. Electrophysiology of pancreatic and salivary acinar cells.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 50:65–80
Sakai, H., Okada, Y., Morii, M., Takeguchi, N. 1989. Anion and cation channels in the basolateral membrane of rabbit parietal cells.Pfluegers Arch. 414:185–192
Sakmann, B., Trube, G. 1984. Conductance properties of single inwardly rectifying potassium channels in ventricular cells from guinea-pig heart.J. Physiol. 347:641–657
Sepulveda, F.V., Fargon, F., McNaughton, P.A. 1991. K+ and Cl− currents in enterocytes isolated from guinea-pig small intestinal villi.J. Physiol. 434:351–3677
Sims, S.M., Dixon, S.J. 1989. Inwardly rectifying K+ current in osteoclasts.Am. J. Physiol. 256:C1277-C1282
Takahashi, T. 1990. Inward rectification in neonatal rat spinal motoneurones.J. Physiol. 423:47–62
Wright, R.D., Blair-West, J.R. 1990. The effects of K+ channel blockers on ovine parotid secretion depend on the mode of stimulation.Exp. Physiol. 75:339–348
Wright, R.D., Blair-West, J.R., Nelson, J.F. 1986. Effects of ouabain, amiloride, monensin, and other agents on ovine parotid saliva.Am. J. Physiol. 250:F503-F510
Yanagihara, K., Irisawa, H. 1980. Inward current activated during hyperpolarization in the rabbit sinoatrial node cell.Pfluegers Arch. 385:11–19
Young, J.A., Cook, D.I., Van Lennep, E.W., Roberts, M.L. 1987. Secretion by the major salivary glands.In: Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. L. Johnson, J. Christensen, M. Jackson, E. Jacobson, J. Walsh, editors. Volume 2, 2nd Edition, pp. 773–815. Raven, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa, T., Wegman, E.A. & Cook, D.I. An inwardly rectifying potassium channel in the basolateral membrane of sheep parotid secretory cells. J. Membrain Biol. 131, 193–202 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02260108
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02260108