Abstract
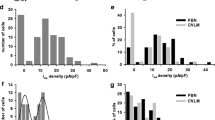
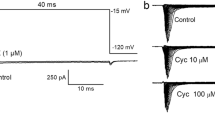
Helothermine, a recently isolated toxin from the venom of the Mexican beaded lizard Heloderma horridum horridum was tested on K+ currents of newborn rat cerebellar granule cells. In whole-cell voltageclamp experiments, cerebellar granule neurons exhibited at least two different K+ current components: a first transient component which is similar to an I A-type current, is characterized by fast activating and inactivating kinetics and blocked by 4-aminopyridine; a second component which is characterized by noninactivating kinetics, is blocked by tetraetylammonium ions and resembles the classical delayed-rectifier current. When added to the standard external solution at concentrations ranging between 0.1 and 2 μm helothermine reduced the pharmacologically isolated I A-type current component in a voltage- and dose-dependent way, with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 0.52 μm. A comparison between control and nelothermine-modified peak transient currents shows a slowdown of activation and inactivation kinetics. The delayed-rectifier component inhibition was concentration dependent (IC50 = 0.86 μm) but not voltage dependent. No frequency-or use-dependent block was observed on both K+ current types. Perfusing the cells with control solution resulted in quite a complete current recovery. We conclude that helothermine acts with different affinities on two types of K+ current present in central nervous system neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blatz, A.L., Magleby, K.L. 1987. Calcium-activated potassium channels. Trends Neurosci. 10:463–467
Brayden, J.E., Nelson, M.T. 1992. Regulation of arterial tone by activation of calcium-dependent potassium channels. Science 256:532–535
Carbone, E., Lux, H.D. 1984. A low voltage-activated calcium conductance in embryonic chick sensory neurons. Biophys. J. 46:413–418
Carbone, E., Prestipino, G., Spadavecchia, L., Franciolini, F., Possani, L.D. 1987. Blocking of the squid axon K+ channel by noxiustoxin: a toxin from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides noxius. Pfluegers Arch. 408:423–431
Carignani, C., Robello, M., Marchetti, C., Maga, L. 1991. A transient outward current dependent on external calcium in rat cerebellar granule cells. J. Membrane Biol. 122:259–265
Catterall, W.A. 1979. Binding of scorpion toxin to receptor sites associated with sodium channels in frog muscle. J. Gen. Physiol. 74:375–391
Cull-Candy, S.G., Marshall, C.G., Ogden, D. 1989. Voltage-activated membrane currents in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J. Physiol. 414:179–199
Fagni, L., Bossu, L., Bockaert, J. 1991. Activation of a large-conductance Ca2+-dependent K+ channel by stimulation of glutamate phosphoinositide-coupled receptors in cultured cerebellar granule cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 3:778–789
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recordings from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pfluegers Arch. 91:81–100
Hendon, R.R., Tu, A.T. 1981. Biochemical characterization of the lizard Gilatoxin. Biochemistry 20:3517–3522
Hille, B. 1992. Modifiers of gating. In: Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, pp. 445–471. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Jalonen, T., Johansson, S., Holopainen, I., Oja, S.S., Arhen, P. 1990. Single-channel and whole-cell currents in rat cerebellar granule cells. Brain Res. 535:33–38
Komori, Y., Nikai, T., Sugihara, H. 1988. Purification and characterization of a lethal toxin from the venom of Heloderma horridum horridum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 154:613–619
Levi, G., Aloisi, F., Ciotti, M.T., Gallo, V. 1984. Autoradiographic localization and depolarization-induced release of acidic amino acids in differentiating granule cells cultures. Brain Res. 290:77–86
Miller, C., Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R., Phillips, M. 1985. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature 313:316–318
Mochca-Morales, J., Martin, B.M., Possani, L.D. 1990. Isolation and characterization of helothermine, a novel toxin from Heloderma horridum horridum (Mexican beaded lizard) venom. Toxicon 28:299–309
Mozhayeva, G.N., Naumov, A.P., Nosyreva, E.D., Grishin, E.V. 1980. Potential-dependent interaction of toxin from venom of the scorpion Buthus eupeus with sodium channels in myelinated fibre. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 597:587–602
Nikai, T., Imai, K., Sugihara, H., Tu, A.T. 1988. Isolation and characterization of Horridum toxin with arginine esterhydrolase activity from Heloderma horridum (beaded lizard) venom. Archs. Biochm. Biophis. 264:270–280
Possani, L.D., Mochca-Morales, J., Amezcua, J., Martin, B.M., Prestipino, G., Nobile, M. 1992. Anionic currents of chick sensory neurons are affected by a phospholipase A2 purified from the venom of the taipan snake. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1134:210–216
Sosa, B., Alagon, A.C., Martin, B.M., Possani, L.D. 1986. Phospholipase B activity of a purified phospholipase A2 from Vipera Palaestinae. J. Lipid Res. 14:267–278
Strichartz, G., Rando, T., Wang, G.K. 1987. An integrated view of the molecular toxinology of sodium channel gating in excitable cells. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 10:237–267
Wang, G.K., Strichartz, G. 1982. Simultaneous modifications of sodium channel gating by two scorpion toxins. Biophys. J. 40:175–179
Weller, U., Bernhardt, U., Siemen, D., Dreyer, F., Vogel, W., Habermann, E. 1985. Electrophysiological and neurobiochemical evidence for the blockade of a potassium channel by dendrotoxin. Arch. Pharmacol. 330:77–83
Yatani, A., Kirsch, G.E., Possani, L., Brown, A.M. 1988. Effects of New World scorpion toxins on single-channel and whole-cell cardiac sodium currents. Am. J. Physiol. 254:H443-H451
Yeh, J.Z., Oxford, G.S., Wu, C.H., Narahashi, T. 1976. Dynamics of aminopyridine block of potassium channels in squid axon membrane. J. Gen. Physiol. 68:519–535
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nobile, M., Magnelli, V., Lagostena, L. et al. The toxin helothermine affects potassium currents in newborn rat cerebellar granule cells. J. Membarin Biol. 139, 49–55 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232674
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232674