Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to assess the diagnostic value of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and intraductal ultrasound (IDUS) in the detection of small pancreatic tumors.
Methods: EUS was performed in 166 patients with verified pancreatic disease. IDUS was performed in 46 patients. A microprobe was introduced into the main pancreatic duct through the papilla of Vater using the duodenoscope.
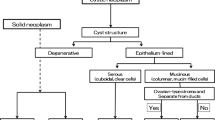
Results: EUS was valuable in the detection of small pancreatic tumors. Ductal adenocarcinomas smaller than 1 cm were demonstrated as a hypoechoic mass with a central irregular hyperechoic area. EUS and IDUS were useful in the characterization of intraductal paillary tumors (ductectatic mucinous tumors). EUS demonstrated nodular excrescences, and IDUS depicted papillary proliferation of the duct epithelium, which are characteristic of carcinomas and adenomas but not of hyperplasia. Internal architecture of cystic neoplasms was clearly depicted by EUS, and differentiation of serous and mucinous tumors was readily achieved. A tumor as small as a 5-mm islet cell was demonstrated on EUS because islet cell tumors are very hypoechoic.
Conclusion: EUS and IDUS are relatively noninvasive procedures and are useful in the detection of small tumors and differentiation of pancreatic diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ariyama, J., Suyama, M., Satoh, K. et al. Endoscopic ultrasound and intraductal ultrasound in the diagnosis of small pancreatic tumors. Abdom Imaging 23, 380–386 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002619900365
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002619900365