Summary
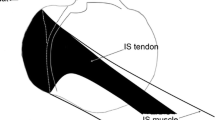
Axial MR images of the shoulder joint reveal a central linear band within the supraspinatus muscle void of signal which seems not to represent the only tendon of this muscle. Due to the importance of the supraspinatus muscle for the painful impingement syndrome of the shoulder we studied the fibrous architecture of this muscle comparing 30 MR images and 49 cadaver dissections. We found the supraspinatus muscle to be composed of two distinct portions. The mean length of the ventral portion is 88 mm and of the dorsal portion 106 mm. The angle of the central tendon which is formed by fibers of both muscle portions relative to the frontal plane is 50°. Both muscle portions probably act differently in moving the arm. This finding seems to be important for the pathophysiology of rotator cuff tears which are mainly located anteriorly within the ventral muscle portion and the eccentric central tendon.
Résumé
Les coupes axiales d'épaule obtenues en IRM montrent une bande linéaire centrale à l'intérieur du m. supra-épineux, vide, qui ne semble pas représenter uniquement le tendon de ce muscle. En raison de l'importance du m. supraépineux dans les syndrômes douloureux de l'épaule, nous avons étudié l'architecture fibreuse de ce muscle, en comparant 30 imageries par résonnance magnétique nucléaire et 49 dissections cadavériques. Nous avons trouvé que le m. supra-épineux était composé de deux parties distinctes. La longueur moyenne de la partie ventrale est de 88 mm et celle de la partie dorsale de 106 mm. L'angle du tendon central qui est formé par les fibres des deux parties musculaires, fait 50° avec le plan frontal. Les deux parties musculaires agissent probablement différemment dans les mouvements du bras. Ces constatations semblent être importantes pour la physiopathologie des ruptures de la coiffe des rotateurs, qui sont principalement situées en avant, dans la partie ventrale du muscle et dans le tendon central excentrique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Codman EA (1934) The shoulder, rupture of the supraspinatus tendon and other lesions in or about the subacromial bursa. Thomas Todd, Boston
Farley TE, Neumann CH, Steinbach LS, Jahnke AJ, Petersen SS (1992) Full-thickness tears of the rotator cuff of the shoulder: Diagnosis with MR imaging. AJR 158: 347–351
Gagey N, Gagey O, Bastian G, Lassau JP (1990) The fibrous frame of the supraspinatus muscle. Surg Radiol Anat 12: 291–292
Gray H 1827–1861 (1989) Myology. In: PL Williams (eds) Gray's anatomy. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 560–566
Kolts I (1992) A note on the anatomy of the supraspinatus muscle. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 111: 247–249
Neer CS (1990) Shoulder reconstruction. WB Saunders, PHiladelphia
Ozaki J, Fujimoto S, Nakagawa Y, Masuhara K, Tamai S (1988) Tears of the rotator cuff of the shoulder associated with pathological changes in the acromion. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 70-A: 1224–1230
Seeger LL, Ruszowski JT, Bassett LW, Kay SP, Kathmann RD, Ellman H (1987) MR imaging of the normal shoulder: anatomic correlation. AJR 148: 83–91
Vahlensieck M, Pollack M, Lang P, Grampp S, Genant HK (1993) Two segments of the supraspinatus muscle: cause of high signal in the supraspinatus critical zone on MRI? Radiology 186: 449–454
Vahlensieck M, Resendes M, Genant HK (1992) MRI of the shoulder. Imaging 59: 123–132
Zlatkin MB, Bjorkengren AG, Gylys-Morin V, Resnick D, Sartoris DJ (1988) Cross-sectional imaging of the capsular mechanism of the glenohumeral joint. AJR 150: 151–158
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vahlensieck, M., Haack, K.a. & Schmidt, HM. Two portions of the supraspinatus muscle: a new finding about the muscles macroscopy by dissection and magnetic resonance imaging. Surg Radiol Anat 16, 101–104 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01627931
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01627931