Summary.
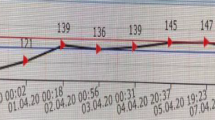
Extrapontine myelinolysis (EPM) is a demyelinating process of the brain. We report the case of an 11-year-old girl who developed EPM with parkinsonism. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed demyelinating patterns in the basal ganglia without central pontine lesions. The cerebrospinal fluid levels of homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid were high at the time of onset and normalized upon complete recovery from extrapyramidal symptoms after a dopaminergic treatment.
We speculated that demyelination of nerve fibers containing dopamine receptors in the striatum might be a main cause of these symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received December 2, 1998; accepted May 6, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagamitsu, S., Matsuishi, T., Yamashita, Y. et al. Extrapontine myelinolysis with parkinsonism after rapid correction of hyponatremia: high cerebrospinal fluid level of homovanillic acid and successful dopaminergic treatment. J Neural Transm 106, 949–953 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050215
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050215