Summary
The enzyme monoamine oxidase was labelled in the rat striatum or substantia nigra with locally injected radioactive pargyline. The binding was prevented by a pretreatment with non-radioactive pargyline, or with a combination of clorgyline and deprenyl. Most of the MAO labelled with3H-pargyline was of the B-type, but also some MAO-A was labelled, as shown in rats pretreated with clorgyline or deprenyl separately.
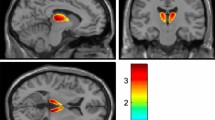
Seven days after the injection of (3H)-pargyline into the striatum a significant labelling was observed in the substantia nigra. This labelling was clorgyline sensitive, indicating type A MAO, and was not present when striatal neurons were destroyed with kainic acid. Labelling of the striatum following3H-pargyline injection into the substantia nigra was also less in kainate intoxicated striata. Damage of nigral dopamine neurons with 6-hydroxydopamine did not influence the distribution of the label.
Thus by using3H-pargyline, specific labelling and axonal transport of type A MAO in striatal neurons projecting to the substantia nigra was demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Callingham BA, Parkinson D (1979) Tritiated pargyline binding to rat liver mitochondrial MAO. In: Singer TP, Von Korff RW, Murphy DL (eds.) Monoamine oxidase: structure, function and altered functions. Academic Press, London, pp 81–86
Chéramy A, Leviel V, Glowinski J (1981) Dendritic release of dopamine in the substantia nigra. Nature 289: 537–542
Dahlström A (1972) The axonal transport of monoamine oxidase. In: Costa E, Sandler M (eds.) Monoamineoxidases: New Vistas, Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol., Vol. 5. Raven Press, New York, pp 293–305
Del Zompo A, Pintus S, Zuddas A, Corsini GU (1985) Deprenyl selectively inhibits (3H)MPTP binding sites in monkey brain. Eur J Pharmacol 107: 285–286
Demarest KT, Smith DJ, Azzaro AJ (1980) The presence of the type A form of MAO within the nigrostriatal dopamine containing neurons. J Pharmacol ExpTher 215: 461–468
Erwin VG, Deitrich RA (1971) The labellingin vivo of monoamine oxidase by14C-pargyline: a tool for studying the synthesis of the enzyme. Mol Pharmacol 7: 219–228
Fowler CJ, Callingham BA, Mantle TJ, Tipton KF (1978) Monoamine oxidase A and B: a useful concept? Biochem Pharmacol 27: 97–101
Fuller RW (1972) Selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase. In: Costa E, Sandler M (eds) Monoamine oxidases: New Vistas, Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol, Vol. 5. Raven Press, New York, pp 339–354
Fuller RW, Wasser BJ, Molloy BB (1970) Selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase in rat brain mitochondria. Biochem Pharmacol 19: 2934–2936
Glover V, Sandler M, Owen F, Riley GJ (1977) Dopamine is a monoamine oxidase B substrate in man. Nature 265: 80–81
Goridis C, Neff NH (1971) Monoamine oxidase and approximation of turnover rates. J Neurochem 18: 1673–1682
Grafstein B, Forman DS (1980) Intracellular transport in neurons. Physiol Rev 60: 1167–1283
Hall DWR, Logan BW, Parsons GH (1969) Further studies on the inhibition of monoamine oxidase by M & B 9302 (clorgyline)-I. substrate specificity in various mammalian species. Biochem Pharmacol 18: 1447–1454
Hattori T, McGeer EG (1977) Fine structural change in the rat striatum after local injections of kainic acid. Brain Res 129: 174–180
Heikkila RE, Manzino L, Cabbat FS, Duvoisin RC (1984) Protection against the dopaminergic neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1.2.5.6-tetrahydropyridine by monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nature 311: 467–469
Johnston JP (1968) Some observations upon a new inhibitor of monoamine oxidase in brain tissue. Biochem Pharmacol 46: 295–297
Koe BK (1975) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors antagonize the acceleration of brain synthesis induced by neuroleptic drugsin vivo: implications for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia. Experienta 31: 669–671
Knoll J, Magyar K (1972) Some puzzling pharmacological effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. In: Costa E, Sandler M (eds.) Monoamine Oxidase: New Vistas, Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol, Vol 5. Raven Press, New York, pp 393–409
König JFR, Klippel RA (1963) The Rat Brain. A Stereotaxic Atlas of the Forebrain and Lower Parts of the Brainstem. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Korf J, Postema F (1984) Regional calcium accumulation and cation shifts in rat brain by kainate. J Neurochem 43: 1052–1060
Korf J, Venema K (1983) Aminoacids in the substantia nigra of rats with striatal lesions produced with kainic acid. J Neurochem 40: 1171–1173
Langston JW, Irwin I, Langston EB, Forno LS (1984) Pargyline prevents MPTP-induced parkinsonism in primates. Science 225: 1480–1482
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1979) Interconnection of dopamine systems. In: Horn AS, Korf J, Westerink BHC (eds.) The neurobiology of dopamine. Academic Press, London, pp 381–392
O'Caroll AM, Fowler CJ, Phillips JP, Tobbia J, Tipton KF (1983) The deamination of dopamine by human brain monoamine oxidase. Specificity for the two enzyme forms in seven brain regions. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 322: 178–202
Parsons B, Rainbow T (1984) High-affinity binding sites for (3H)MPTP may correspond to monoamine oxidase. Eur J Pharmacol 102: 375–377
Reubi JC, Iversen LL, Jessel TM (1977) Dopamine selectively increases3HGABA release from slices of rat substantia nigrain vitro. Nature 268: 652–654
Sahgal A, Andrews JS, Biggins JA, Candy JM, Edwardson JA, Keith AB, Turner JD, Wright C (1984) N-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) affects locomotor activity without producing a nigrostriatal lesion in the rat. Neurosci Lett 48 (2): 179–185
Schmidt RE, McDougal jr DB (1978) Axonal transport of selected particlespecific enzymes in rat sciatic nervein vivo and its response to injury. J Neurochem 30: 527–535
Schmidt RE, Ross CD, McDougal Jr DB (1978) Effects of sympathectomy on axoplasmic transport of selected enzymes including MAO and other mitochondrial enzymes. J Neurochem 30: 537–541
Schoepp DD, Azzaro AJ (1981 a) Alteration of dopamine synthesis subsequent to selective type A monoamine oxidase inhibition. J Neurochem 37: 527–530
Schoepp DD, Azzaro AJ (1981 b) Specificity of endogenous substrates for types A and B monoamine oxidase in rat striatum. J Neurochem 36: 2025–2031
Schoepp DD, Azzaro AJ (1983) Effects of intrastriatal kainic acid injection on (3H)dopamine metabolism in rat striatal slices: evidence for postsynaptic glial cell metabolism by both the type A and B forms of monoamine oxidase. J Neurochem 40: 1340–1348
Schwartz JH (1979) Axonal transport: components, mechanisms and specificity. Ann Rev Neurosci 2: 467–504
Schwarcz R, Coyle JT (1977) Striatal lesions with kainic acid: neurochemical characteristics. Brain Res 41: 245–248
Siegel S (1956) Non-parametric statistics for the behavioral sciences. McGraw Hill, Kogakasha
Student AK, Edwards DJ (1977) Subcellular localization of type A and type B MAO in the rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 26: 2337–2342
Tipton KF, Houslay MD, Garrett NJ (1973) Allotopic properties of human brain monoamine oxidase. Nature New Biology (Lond) 246: 213–214
Van der Heyden JAM, Venema K, Korf J (1980 a) Biphasic and opposite effects of dopamine and apomorphine on endogenous GABA release in the rat substantia nigra. J Neurochem 34: 119–125
Van der Heyden JAM, Venema K, Korf J (1980 b)In vivo release of endogenous GABA from rat striatum: inhibition by dopamine. J Neurochem 34: 1338–1341
Van der Krogt JA, Koot-Gronsveld E, Van den Berg CJ (1983 a) Subcellular fractionation of striatum: sedimentation properties of dopaminergic synaptosomes. Life Sci 33: 605–613
Van der Krogt JA, Koot-Gronsveld E, Van den Berg CJ (1983 b) Localization of rat striatal monoamine oxidase activities towards dopamine, serotonine and kynuramine by gradient centrifugation and nigro-striatal lesions. Life Sci 33: 615–623
Van der Werf JF, Sebens JB, Vaalburg W, Korf J (1983)In vivo binding of N-n-propylnorapomorphine in the rat brain: regional localization, quantification in striatum and lack of correlation with dopamine metabolism. Eur J Pharmacol 87: 259–270
Waldmeier PC, Maître L (1976) Comparison of short and long-lasting effects of pargyline on cerebral dopamine metabolism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 294: 133–140
Waldmeier PC, Delim-Stula A, Maître L (1976) Preferential deamination of dopamine by an A type monoamine oxidase in rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 292: 9–14
Waldmeier PC, Felner AE, Maître L (1981) Long-term effects on selective MAO inhibitors on MAO activity and amine metabolism. In: Youdim MBH, Paykel ES (eds.) Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. The state of the art, Chichester
Westerink BHC, Korf J (1976) Turnover of acid dopamine metabolites in striatal and mesolimbic tissue of the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 37: 249–255
Young HYT, Neff NH (1974) The monoamine oxidase of brain: selective inhibition with drugs and the consequences for the metabolism of the biogenic amines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 189: 733–740
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gramsbergen, J.B.P., Sebens, J.B. & Korf, J. In vivo labelling and axonal transport of monoamine oxidase in the rat basal ganglia using radioactive pargyline. J. Neural Transmission 66, 21–36 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01262955
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01262955