Summary
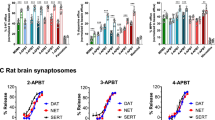
The diastereomers of 3,N,N′-trimethyl-2-phenyl-1,4-piperazine dihydrochloride (TPP) were tested for their effects on NA, DA and 5-HT uptake in synaptosomes prepared from hypothalamus, corpus striatum, and frontal cortex, respectively. The diastereomers differed with respect to their inhibitory properties. (2R, 3R)-TPP was more potent than the other diastereomers on NA and DA uptake, whereas (2S, 3S)-TPP was least potent. In contrast, the (2S, 3S)- and (2 S, 3R)-diastereomers of TPP were more potent than (2R, 3R)- and (2R, 3S)-TPP as inhibitors of 5-HT uptake. None of the diastereomers affected monoamine oxidase activity. The findings show that the diastereomers of TPP interact stereoselectively with neuronal mechanisms for monoamine uptake, and that the (S)-configuration at the 2 carbon is important for inhibitory actions of TPP on 5-HT uptake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horn AS, Snyder SH (1972) Steric requirements for catecholamine uptake by rat brain synaptosomes: studies with rigid analogs of amphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 180: 523–530
Koe BK (1976) Molecular geometry of inhibitors of the uptake of catecholamines and serotonin in synaptosomal preparations of rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 199: 649–661
Magnussen I, Tønder K, Engbaek F (1982) Paroxetine, a potent selective long-acting inhibitor of synaptosomal 5-HT uptake in mice. J Neural Transm 55: 217–226
Maxwell RA, Ferris RM, Burcsu JE (1976) Structural requirements for inhibition of noradrenaline uptake by phenethylamine derivatives, desipramine, cocaine and other compounds. In: Paton DM (ed) The mechanism of neuronal and extraneuronal transport of catecholamines. Raven Press, New York, pp 95–153
Norusis MJ (ed) (1988) SPSS/PC+TM V 2.0 Base Manual for the IBM PC/XT-/AT and PS/2. SPSS Inc., Chicago, 1ll
Patil PN, Miller DD, Trendelenburg U (1975) Molecular geometry and adrenergic drug activity. Pharmacol Rev 26: 323–392
Richelson E, Pfenning M (1984) Blockade by antidepressant and related compounds of biogenic amine uptake into rat brain synaptosomes: most antidepressants selectively block norepinephrine uptake. Eur J Pharmacol 104: 277–286
Rutledge CO, Walters DE, Grunewald GL (1984) Noradrenergic drugs: conformational preferences in uptake mechanisms. In: Smith DF (ed) CRC Handbook of stereoisomers. Drugs in psychopharmacology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 79–92
Smith DF (1984) CRC Handbook of stereoisomers. Drugs in psychopharmacology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Smith DF (1986) The stereoselectivity of serotonin uptake in brain tissue and blood platelets: the topography of the serotonin uptake area. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 10: 37–46
Smith DF (1989a) Psychotropic drugs. In: Smith DF (ed) Handbook of stereoisomers. Therapeutic drugs. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 323–393
Smith DF (1989b) Lithium alters the stereoselectivity of monoamine oxidase in rat brain. J Neural Transm 76: 205–210
Smith DF, Jensen PN, Poulsen SH, Mikkelsen EO, Elbaz E, Glaser R (1991) Effects of pyrroloisoquinoline enantiomers ((+)- and (−) McN-5652-Z) on behavioral and pharmacological serotonergic mechanisms in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 196: 85–92
Tenne M, Youdim MBH (1984) Mao-inhibiting drugs: stereochemical aspects. In: Smith DF (ed) Handbook of stereoisomers. Drugs in psychopharmacology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 285–296
Tuomisto J (1978) Some structural features of amine uptake mechanisms. In: Simon P (ed) Adv Pharmacol Therapeutics, vol 2. Neurotransmitters. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 231–248
Tuomisto J, Smith DF (1986) Effects of tranylcypromine enantiomers on monoamine uptake and release and imipramine binding. J Neural Transm 65: 135–145
Tuomisto J, Walaszek EJ, Smissman EE, Pazdernik TL (1974) Decalin analogs of phenethylamines as inhibitors of amine uptake by rabbit platelets. II. Uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Pharm Sci 63: 1714–1718
Tuomisto J, Tuomisto L, Pazdernik TL (1976) Conformationally rigid amphetamine analogs as inhibitors of monoamine uptake by brain synaptosomes. J Med Chem 19: 725–727
Tytgat D (1991) Synthèses de phénylpropanediamines isostères de l'éphédrine: étude configurationnelle et conformationnelle par R.M.N. et essais pharmacologiques preliminaires. Ph. D. thesis, Faculté de Médicine et de Pharmacie, Université Libre de Bruxelles
Tytgat D, Gelbcke M, Smith DR (1990) Convenient synthesis of 1-phenyl-1,2-propane-diamines. Preliminary pharmacological results. Pharmazie 45: 835–836
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, D.F., Jensen, P.N., Gelbcke, M. et al. Effects of 3,N,N′-trimethyl-2-phenyl-1,4-piperazine diastereomers on monoamine uptake and monoamine oxidase in rat brain. J. Neural Transmission 88, 177–185 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01244731
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01244731