Summary
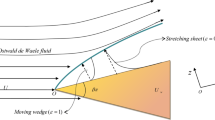
A pseudo-similarity solution has been obtained for the flow of an incompressible fluid of second grade past a wedge. The numerical method developed for this purpose enables computation of the flow characteristics for any value of the parametersK anda, whereK is the dimensionless normal stress modulus of the fluid, anda is related to the wedge angle. Results computed forKx wa varying from 0 to 200 show a marked decrease or increase in wall shear, depending upon the wedge angle, asx −2a /K increases from 0 to about 1; thereafter the change in wall shear stress is small. The present results match exactly with those from an earlier perturbation analysis forKx 2a≦0.01 but differ significantly asKx 2a increases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajeswari, G. K., Rathna, S. L.: Flow of a particular class of non-Newtonian visco-elastic and visco-inelastic fluids near a stagnation point. Z. Angew. Math. Phys.13, 43–57 (1962).
Beard, D. W., Walters, K.: Elastico-viscous boundary layer flows. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc.60, 667–674 (1964).
Astin, J., Jones, R. S., Lockyer, P.: Boundary layers in non Newtonian fluids J. Mec.12, 527–539 (1973).
Srivastava, A. C.: The flow of a non-Newtonian liquid near a stagnation point Z. Angew. Math. Phys.9, 80–84 (1958).
Rajagopal, K. R., Gupta, A. S., Wineman, A. S.: On a boundary layer theory for non-Newtonian fluids. Lett. Appl. Sci. Engng.18, 875–883 (1980).
Rajagopal, K. R., Gupta, A. S., Na, T. Y.: A note on the Falkner-Skan flows of a non-Newtonian fluid. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech.18, 313–319 (1983).
Rivlin, R. S., Ericksen, J. L.: Stress deformation relation for isotropic materials. J. Rational Mech. Analysis4, 323–425 (1955).
Oldroyd, J. G.: On the formulation of rheological equations of state Proc. Roy. Soc. LondonA 200 523–541 (1950).
Garg, V. K., Rajagopal, K. R.: Stagnation point flow of a non-Newtonian fluid. Mech. Res. Comm.17, 415–421 (1990).
Beard, D. W.: Ph. D. Thesis, University of Wales, Aberystwyth, U.K.(1978).
Dunn, J. E., Rajagopal, K. R.: A critical review and thermodynamic analysis of fluids of the differential type. Submitted (1990).
Fosdick, R. L., Rajagopal, K. R.: Uniqueness and drag for fluids of second grade in steady motion. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech.13, 131–137 (1978).
Bellman, R. E., Kalaba, R. E.: Quasilinearization and non-linear boundary value problems, Chap. 4. New York: Elsevier 1965.
Garg, V. K.: Improved shooting techniques for linear boundary value problems Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engng.22, 87–99 (1980).
Scott, M. R., Watts, H. A.: Computational solution of linear two-point boundary value problems via orthonormalization. SIAM J. Num. Analysis14 40–70 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, V.K., Rajagopal, K.R. Flow of a non-Newtonian fluid past a wedge. Acta Mechanica 88, 113–123 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01170596
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01170596