Summary
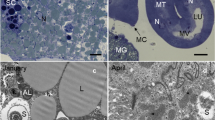
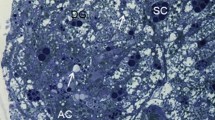
Spherites in the digestive and secretory cells of the midgut gland of the agelenid spiderCoelotes terrestris were studied by electron microscopy and histochemical methods. Spherites measured 1–6 μm in diameter and were characterized by alternating layers of electron dense and electron lucent material. The main-components of spherites were calcium phosphates and calcium carbonates. Guanine and barium, as well as aminopeptidase and alkaline phosphatase were also present. The matrix consisted of proteins and carbohydrates. Numerous spherites were found together with excretory products within the excretory vacuoles of the digestive cells.
Spiders fed with food containing lead, showed deposition of the metall in the spherites. It is then proposed that spherites, aside from their role in storing calcium and other ions, may function in detoxification of heavy metals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolins-Krogis A (1970) Electron microscope studies of intracellular origin and formation of calcifying granules and calcium spherites in the hepatopancreas of the snail,Helix pomatia. L. Z Zellforsch mikrosk Anat 108: 501–515
Alberti G, Storch V (1983) Zur Ultrastruktur der Mitteldarmdrüsen von Spinnentieren (Scorpiones, Araneae, Acari) unter verschiedenen Ernährungsbedingungen. Zool Anz Jena 211: 145–160
André J, Fauré-Fremiet E (1967) Formation et structure des concrétions calcaires chezPorodon morgani Kahl. J Microscopie 6: 391–398
Becker A, Peters W (1985) Fine structure of the midgut gland ofPhalangium opilio (Chelicerata, Phalangida). Zoomorphology 105: 317–325
Becker GL, Chen CH, Greenawalt JW, Lehninger AL (1974) Calcium phosphate granules in the hepatopancreas of the blue crabCallinectes sapidus. J Cell Biol 61: 316–326
Brown BE (1982) The form and function of metal-containing “granules” in invertebrate tissues. Biol Rev 57: 621–667
Burton R (1972) The storage of calcium and magnesium phosphates and of calcite in the digestive glands of thePulmonata (Gastropoda). Comp Biochem Physiol 43 a: 655–663
Carasso N, Favard P (1966) Mise en evidence du calcium dans les myonemes pedonuclaires de cilies peritriches. J Microscopie 5: 759–770
Chayen L, Bitensky R, Butcher G (1975) Histochemie, Grundlagen und Methoden. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim
Erhardt P (1965) Magnesium und Calcium enthaltende Einschluß- körper in den Mitteldarmzellen von Aphiden. Experientia 21/6: 337–338
Fausser V (1909) Über Guaninablagerungen bei Spinnen. Zool Anz 35: 65–75
Feigl F (1924) Qualitative Microanalysis. Mikrochemie 2: 186–188
Gouranton J (1968) Composition, structure et mode de formation des concretions minerales dans l'intestin moyen des homoptères cercopides. J Cell Biol 37: 316–328
Goyffon M, Martoja R (1983) Cytophysiological aspects of digestion and storage in the liver of a scorpion,Androctonus australis (Arachnida). Cell Tissue Res 228: 661–675
Guary JC, Negrel R (1981) Calcium phosphate granules: a trap for transuranics and iron in crab hepatopancreas. Comp Biochem Physiol 68 A: 423–427
Hausmann K (1982) Kristalle in Wimpertierchen. Mikrokosmos 2: 33–39
Hubert M (1978) Données histophysiologiques complémentaires sur les bioaccumulations minérales et puriques chezCylindroiulus londinensis (Leach 1814) (Diplopode, Iuloidea). Arch Zool Exp Gen 119: 669–683
Hugon JS, Borgers M(1966) A direct lead method for the electron microscopic visualisation of alkaline phosphatase activity. J Histochem Cytochem 14: 429–431
Humbert W (1974) Localisation, structure et genèse des concrétions minérales dans le mésentéron des collembolesTomoceridae (Insecta, Collembola). Z Morph Tiere 78: 93–109
— (1977) The mineral concretions in the midgut ofTomocerus minor (Collembola): microprobe analysis and physioecological significance. Rev Ecol Biol Sol 14 (1): 71–80
Janssen HH (1985) Some histophysiological findings on the midgut gland of the common garden snail,Arion rufus (L.) [Syn.A. ater (L.),A. empiricorum Ferrusac],Gastropoda: Stylommatophora. Zool Anz 215: 33–51
Kanungo MS, Bohidar SC, Patnaik BK (1962) Excretion in the scorpionPalamnaeus bengalensis C. Koch. Physiol Zool 35: 201–203
McGhee-Russel SM (1958) Histochemical methods for calcium. J Histochem Cytochem 6: 22–42
Miller F, Palade G (1964) Lytic activities in renal protein absorbtion droplets. J Cell Biol 23: 519–552
Pearse AGE (1961) Histochemistry: 2nd edition. J. + A. Churchill Ltd, London
Richardson KC, Jarett L, Finke EH (1960) Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol 35: 313–323
Romeis B (1948) Mikroskopische Technik. R. Oldenbourg, München
Seligman AM, Wasserkrug HL, Plapinger RE, Seito T, Hanker JS (1970) Membraneous ultrastructural demonstration of aminopeptidase and γ-glutamyltranspeptidase activities with a new diazonium salt, that yields a lipophobic, osmiophilic azo dye. J Histochem Cytochem 18: 542–551
Simkiss K (1981) Calcium, pyrophosphate and cellular pollution. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 6: 3–5
Sminia T, de With WD, Bos JL, van Nieumwegen ME, Witter MP, Wondergem J (1985) Structure and function of the calcium cells of the freshwater pulmonate snail,Lymnea stagnalis. Netherl J Zool 27: 195–208
Storch V, Welsch U (1977) Elektronenmikroskopische und enzymhistochemische Untersuchungen der Mitteldarmdrüse der landlebenden DekapodenCoenobita rugosa undOcypode ceratophthalma. Zool Jb Anat 97: 25–39
Thiery JP (1967) Mise en evidence des polysaccharides sur coupes fines en microscopie electronique. J Microscopie 6: 987–1018
Timm F (1958) Zur Histochemie der Schwermetalle. Das Silbersulfidverfahren. Dt Z gerichtl Med 46: 706–711
Triebskorn R (1986)Pomatias elegans: Zur Ernährungsbiologie einer prosobranchen Landschnecke. Diplomarbeit, Heidelberg
Turbeck B (1974) A study of the concentrically laminated concretions, “Spherites”, in the regenerative cells of the midgut of lepidopterous larvae. Tissue and Cell 6: 627–640
Van Herb F (1970) Study of the influence of sinus gland extirpation on the alkaline phosphatase in the hepatopancreas of the crayfishAstacus leptodactylus. Comp Biochem Physiol 34: 439–445
Wieser W (1979) Schwermetalle im Blickpunkt ökologischer Forschung. Biol in unserer Zeit 3: 80–89
Wright KA, Newell JM (1964) Some observations on the finestructure of the midgut of the miteAnystis spec. Ann Entomol Soc Am 57: 684–693
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ludwig, M., Alberti, G. Mineral congregations, “spherites” in the midgut gland ofCoelotes terrestris (Araneae): Structure, composition and function. Protoplasma 143, 43–50 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01282958
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01282958