Abstract
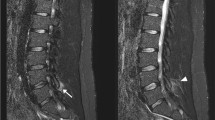
We report the cases of two patients with the very uncommon clinical finding of two noncontiguous spinal epidural abscesses, which were located in the cervical and lumbar spine. In each case the diagnosis of the second spinal abscess was made by MRI only after the appearance of a new neurological deficit. Decompressive spinal surgery and intravenous antibiotic therapy led to complete recovery in one patient; the other patient was moderately disabled. As epidural spinal abscesses can occur at noncontiguous sites, MRI of the entire spine may be necessary in selected cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker AS, Ojemann RG, Swartz MN, Richardson EP Jr (1975) Spinal epidural abscess. N Engl J Med 293:463–468
Corboy JR, Price RW (1993) Myelitis and toxic, inflammatory, and infectious disorders. Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg 6:564–570
Curling OD, Gower DJ, McWhorter JM (1990) Changing concepts in spinal epidural abscess: a report of 29 cases. Neurosurgery 27:185–192
Danner RL, Hartman BJ (1987) Update of spinal epidural abscess: 35 cases and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis 9:265–274
Gellin BG, Weingarten K, Gamache FW Jr, Hartman BJ (1991) Epidural abscess. In: Scheld WM, Whitley RJ, Durack DT (eds) Infections of the central nervous system. Raven Press, New York, pp 499–514
Heusner AP (1948) Nontuberculous spinal epidural infections. N Engl J Med 239:845–854
Hlavin ML, Kaminski HJ, Ross JS, Ganz E (1990) Spinal epidural abscess: a ten-year perspective. Neurosurgery 27:177–184
Lange M, Tiecks F, Schielke E, Yousry T, Haberl R, Oeckler R (1993) Diagnosis and results of different treatment regimens in patients with spinal abscesses. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 125:105–114
Mampalam TJ, Rosegay H, Andrews BT, Rosenblum ML, Pitts LH (1989) Nonoperative treatment of spinal epidural infections. J Neurosurg 71:208–210
Nussbaum ES, Rigamonti D, Standiford H, Numaguchi Y, Wolf AL, Robinson WL (1992) Spinal epidural abscess: a report of 40 cases and review. Surg Neurol 38:225–231
Post MJD, Quencer RM, Montalvo BM, Katz BH, Eismont FJ, Green BA (1988) Spinal infection: evaluation with MR imaging and intraoperative US. Radiology 169:765–771
Pfister HW (1994) Spinal abscesses. In: Hacke W (ed) Neurocritical care. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 446–454
Sadato N, Numaguchi Y, Rigamonti D, Kodama T, Nussbaum E, Sato S, Rothman M (1994) Spinal epidural abscess with gadolinium-enhanced MRI: serial follow-up studies and clinical correlations. Neuroradiology 36:44–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfister, HW., von Rosen, F. & Yousry, T. MRI detection of epidural spinal abscesses at noncontiguous sites. J Neurol 243, 315–317 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868404
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868404