Summary
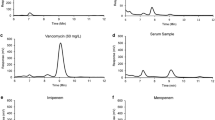
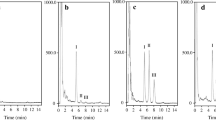
The purpose of this study was to develop a simple and fast analytical method for quantitation of ampicillin in rabbit plasma, suitable for analysis of large numbers of samples collected from experimental animals. The concentration of ampicillin in rabbit plasma was determined utilizing ion-pair reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection and a column switching technique. Plasma samples were treated with a perchloric acid solution to precipitate proteins and centrifuged to pellet the precipitated proteins. Cephalexin was used as an internal standard. The C18 precolumn was placed in the injector loop of the Rheodyne injector. Samples were injected with the injector in the load position and the precolumn was washed free from interfering compounds. When the injector was switched to the inject position, the mobile phase was passed through the precolumn taking relatively pure compounds onto the analytical column. The limit of quantitation was established to be 400 ng mL−1 of plasma. The standard curves were linear over the range of ampicillin concentrations assayed, 400 to 10,000 ng mL−1 of rabbit plasma, and had a mean regression coefficient of 0.9962 (±0.0043). Intra-day variability was determined using six replicates of controls (low and high) analyzed on a single assay. The percent of relative accuracy for low and high controls were 5.67 and 1.12, respectively. Inter-day variability was determined over a four day period analyzing replicates of each control. The percent of relative accuracy for low and high controls were 4.33 and 1.63, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. A. Bloom, R. K. Kohli, N. J. Harrison, J. J. Schentag, Antimicrob. Angets. Chemother.33, 1470 (1989).
J. Haginaka, J. Wakai, H. Yasuda, T. Uno, K. Takahashi, T. Katagi, J. Chromatogr.400, 101 (1987).
S. Suwanrumpha, R. B. Freas, Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom.18, 983 (1989).
Y. Akimoto, K. Kaneko, A. Fujii, H. Yamamoto, J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg.50, 11 (1992).
U. Meetschen, M. Petz, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem.73, 373 (1990).
A. O. Akanni, J. S. K. Ayim, J. Pharmac. Biomed. Anal.10, 43 (1992).
A. Marzo, N. Monti, M. Ripamonti, E. Arrigoni Martelli, M. Picari, J. Chromatogr.507, 235 (1990).
M. J. Akhtar, S. Khan, M. A. S. Khan, J. Pharmac. Biomed. Anal.11, 375 (1993).
H. J. Nelis, J. Vandenbranden, B. Verhaeghe, A. De Kruif, D. Mattheeuws, P. De Leenheer, Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother.36, 1606 (1992).
T. B. Vree, Y. A. Hekster, A. M. Baars, E. Van Der Kleijn, J. Chromatogr.145, 496 (1978).
J. Haginaka, J. Wakai, Analyst110, 1277 (1985).
B. R. Meyers, P. Wilkinson, M. H. Mendelson, S. Walsh, C. Bournazos, S. Z. Hirschman, Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother.35, 2098 (1991).
K. Lundbeck-Vallen, J. Carlqvist, T. Nordgren, J. Chromatogr. Biomed. Appl.567, 121 (1991).
K. Miyazaki, K. Ohtani, K. Sunada, T. Arita, J. Chromatogr. Biomed. Appl.276, 478 (1983).
J. P. Rho, A. Jones, M. Woo, S. Castle, K. Smith, R. E. Bawdon, D. C. Norman, J. Antimicrob. Chemother.24, 573 (1989).
T. Nakagawa, A. Shibukawa, T. Uno, J. Chromatogr.239, 695 (1982).
F. Nachtmann, K. Gstrein, Int. J. Pharmac.7, 55 (1980).
K. Tsuji, J. H. Robertson, J. Pharmac. Sci.64, 1542 (1975).
M. A. Sheikh Salem, H. N. Alkaysi, Drug Devel. Industr. Pharm.13, 2771 (1987).
R. F. Straub, R. D. Voyksner, J. Chromatogr.647, 167 (1993).
J. M. Anderson, S. W. Kim, “Recent Advantages in Drug Delivery Systems”, Plenum Press, New York and London, 1984, p. 185.
I. R. Tebbett, A. Negrusz, A. K. Larsen Jr., R. C. Jensen, Chromatographia34, 143 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolhurst, T.A., Negrusz, A., Libelt, B. et al. Determination of ampicillin in New Zealand white rabbit plasma using column switching technique and HPLC. Chromatographia 42, 223–226 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02269657
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02269657