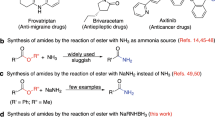
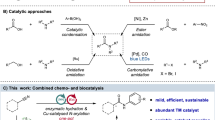
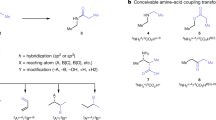
Abstract
PREVIOUS work on acid-catalysed amide hydrolysis has indicated that the reaction is bimolecular: in the rate-determining step the conjugate acid of the amide is attacked by a water molecule1. This conclusion is derived from three types of evidence. It has been shown that in concentrated aqueous acid solutions the rate of hydrolysis of a number of simple amides increases with the proportion of water in the solvent2; that polar substituents in the acyl part of the amide molecule have very little effect on the rate3; and that the rate is substantially diminished by groups, for example, ortho substituents in benzamides, which shield the reaction centre from attack by other molecules3 4.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ingold, C. K., “Structure and Mechanism in Organic Chemistry”, 784 (Bell, 1953).
See, for example, Taylor, J. W. J., J. Chem. Soc., 2741 (1930).
Reid, E. E., Amer. Chem. J., 21, 284 (1899); 24, 397 (1900). Meloche, I., and Laidler, K. J., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 73, 1712 (1951).
de Roo and Bruylants, A., Bull. Soc. chim. Belges., 63, 140 (1954).
Leisten, J. A., J. Chem. Soc., 298 (1955); 1572 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DUFFY, J., LEISTEN, J. A New Mechanism for Amide Hydrolysis. Nature 178, 1242–1243 (1956). https://doi.org/10.1038/1781242b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1781242b0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.