Abstract
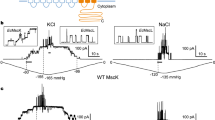
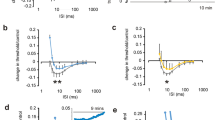
ONE important supporting fact for the concept of the membrane potential of muscle and nerve being a diffusion potential1 was the demonstration of a rectilinear relationship between the logarithm of the external potassium concentration and the measured membrane potential, according to the Nernst equation:  This was shown to be approximately true by Cowan2 for the injury potential of crab nerve and by Shanes3 for the ‘anaerobic’ fraction of the injury potential of frog nerve. Doubts as to the significance of the rectilinearity of their curves4,5 seem to be met, at least in the case of squid giant axon, by the work of Curtis and Cole6, although these authors hesitated to ascribe the membrane potential completely to the potassium concentration gradient. Using the classical injury potential technique, a similar relationship has been demonstrated in frog muscles by Steinbach7 and by Boyle, Conway and co-workers8,9. Thus a potential v. log [K+] relation has been found for both nerve and muscle.
This was shown to be approximately true by Cowan2 for the injury potential of crab nerve and by Shanes3 for the ‘anaerobic’ fraction of the injury potential of frog nerve. Doubts as to the significance of the rectilinearity of their curves4,5 seem to be met, at least in the case of squid giant axon, by the work of Curtis and Cole6, although these authors hesitated to ascribe the membrane potential completely to the potassium concentration gradient. Using the classical injury potential technique, a similar relationship has been demonstrated in frog muscles by Steinbach7 and by Boyle, Conway and co-workers8,9. Thus a potential v. log [K+] relation has been found for both nerve and muscle.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein, J., Arch. f. d. ges. Physiol., 92, 521 (1902).
Cowan, S. L., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 115, 216 (1934).
Shanes, A. H., J. Cell. and Comp. Physiol., 23, 193 (1944).
Lorente de Nó, R., “A Study of Nerve Physiology”, Rockefeller Institute for Med. Res., Vol. 131 (1947).
Steinbach, H. B., J. Cell. and Comp. Physiol., 15, 373 (1940).
Curtis, H. J., and Cole, K. S., J. Cell. and Comp. Physiol., 19, 135 (1942).
Steinbach, H. B., Cold Spring Harbor Symposium, 8, 242 (1940).
Boyle, P. J., and Conway, E. J., J. Physiol., 100, 1 (1941).
Conway, E. J., and Kane, F., unpublished, cited by E. J. Conway, Irish J. Med. Science, 1 (1947).
Ling, G., and Gerard, R. W., J. Cell. and Comp. Physiol. (in the press).
Hodgkin, A. L., and Nastuk, W. L., J. Physiol., 108, 42P (1949).
Osterhout, W. J. V., and Harris, E. S., J. Gen. Physiol., 12, 761 (1929).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LING, G., GERARD, R. External Potassium and the Membrane Potential of Single Muscle Fibres. Nature 165, 113–114 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1038/165113a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/165113a0
This article is cited by
-
Effect of Extracellular Potassium Accumulation on Muscle Fiber Conduction Velocity: A Simulation Study
Annals of Biomedical Engineering (2009)
-
Transport of electrolytes in muscle
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1982)
-
Sodium dependence of the inotropic effect of a reduction in extracellular potassium concentration
Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archiv f�r Pharmakologie (1971)
-
Adsorption of ions at charged sites and phase boundary potentials
The Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics (1964)
-
Membranpotentialmessungen am Skeletmuskel mit der ?Saccharose-Trennwand?-Methode
Pfl�gers Archiv f�r die Gesamte Physiologie des Menschen und der Tiere (1962)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.