Abstract
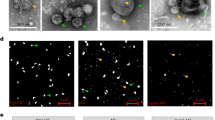
USING the methods of Safferman and Morris1, who isolated the first phycovirus, strain LPP-1, and propagated it on the blue green alga, Plectonema boryanum, five strains of cyanophages2 have been isolated from local polluted pond waters. Two of these differ in host range and plaque morphology wrhile the remaining three bring about lysis of LPP-1 host, P. boryanum, although showing variation in growth behaviour and plaque size. The first two strains infect either spore forming and/or heterocystous blue green algae and are inactive on. P. boryanum. One of these which has been isolated on a species of Cylindrospermum, forming heterocysts at both ends of its filaments and subterminal chains of spores, has a restricted host range. It does not infect other strains of Cylindrospermum with a similar morphology or Andbaena doliolum, another heterocystous and spore forming blue green alga. The second isolate causes lysis of three spore forming blue green algae, Anabaenopsis raciborskii, A. circularis and Raphidiopsis indica., of which the first two are also heterocystous. Tho first isolate is designated C-1 and the second AR-1 following the terminology of Safferman and Morris1 for LPP-1, which is based on the first letter of the genus name of the host algao. Strain C-1 causes fast lysis of the host in liquid medium and on agar plates. Plaques appear late but their size increases very fast and the entire algal growth on the plate is lysed within a few days. AR-1 plaques are irregular in comparison with LPP-1. Their size increases with longer incubation. After 16 days plaque size varies from 5 mm to 14 mm (Fig. 1). The margin of the plaque is frayed because of the filamentous nature of the host algae. The notable characteristic of strains C-1 and AR-1 is that they do not lyse spores and heterocysts which remain unaffected in plaques or lysates (Figs. 3 and 4). The gas vacuoles of the algae possessing them also remain unaffected by the strain AR-1, leaving trails of gas vacuoles behind (Figs. 2, 3.and 4).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Safferman, R. S., and Morris, M. E., Science, 140, 679 (1963).
Luftig, R., and Haselkorn, R., J. Virol., 1, 344 (1967).
Safferman, R. S., and Morris, M. E., J. Amer. Water Works Assoc., 56, 1217 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SINGH, R., SINGH, P. Isolation of Cyanophages from India. Nature 216, 1020–1021 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/2161020a0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2161020a0
This article is cited by
-
Occurrence and distribution of cyanophages in ponds, sewage and rice fields
Archiv f�r Mikrobiologie (1973)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.