Abstract
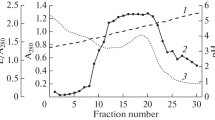
Mast cells were isolated from the bovine liver capsule by treatment with collagenase. The extract from the mast cells contained aprotinin. The concentrations of aprotinin, heparin and histamine in these mast cells were (196±42) pg/cell, (1.6±0.2)×10−4 IU/cell and (32±3) pg/cell (mean±S.E.M. of 8–11 experiments), respectively, determined by an enzyme immunoassay, spectrophotometrically and fluorometrically.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Vogel andG. Zickgraf-Rüdel, Evaluation of the role of kinins in experimental, pathological, and clinical conditions; the therapeutic use of kallikrein inhibitor. InBradykinin Kallidin and Kallikrein, pp. 550–578 (Ed.E.G. Erdös). Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1970.
H. Fritz, J. Kruck, I. Rüsse andH.G. Liebich,Immunofluorescence studies indicate that the basic trypsin-kallikrein-inhibitor of bovine organs (Trasylol) orig-inates from mast cells, Hoppe-Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem.360, 437–444 (1979).
T. Shikimi andT. Kobayashi,Production of antibody to aprotinin and location of this compound in bovine tissue, J. Pharmacobiodyn.3 400–406 (1980).
T. Kobayashi andT. Shikimi,Histological studies of aprotinin-containing cells, Japan. J. Pharmacol.30, Suppl. 87P (1980).
M.M. Simlot andR.E. Feeney,Relative reactivities of chemically modified turkey ovomucoids, Arch. Biochem. Biophys.113, 64–71 (1966).
T. Shikimi,Sandwich enzyme immunoassay of aprotinin, J. Pharmacobiodyn.5, 708–715 (1982).
N. Zöllner andW. Kaiser, Heparin. InMethods of Enzymatic Analysis, 2nd English Edition. pp. 1151–1156 (Ed.H.U. Bergmeyer). Academic Press, New York 1974.
M. Takagi, A. Ichikawa, K. Esumi, K. Yatsunami, M. Negishi andK. Tomita,Effect of adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate on growth and several functions of cultured mastocytoma P-815 cells, J. Pharmacobiodyn.3, 136–148 (1980).
P.A. Shore, A. Burkhalter andV.H. Cohn Jr,A method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.127, 182–186 (1959).
J.C. Houck,The inhibition of ribonuclease, Biochim. Biophys. Acta,26, 649–651 (1957).
H.T. Graham, O.H. Lowry, N. Wahl andM.K. Priebat,Mast cells as sources of tissue histamine, J. Exp. Med.102, 307–318 (1955).
J.F. Riley, The Mast Cells pp. 73–74, E. & S. Livingstone, Edinburgh 1959.
U. Lindahl,Attempted isolation of a heparin proteoglycan from bovine liver capsule, Biochem. J.116, 27–34 (1970).
R.W. Stoddart andJ.A. Kiernan,Aprotinin, a carbohydrate-binding protein, Histochemie34, 275–280 (1973).
B. Uvnäs, C-H. Åborg andA. Bergendorff,Storage of histamine in mast cells. Evidence for an ionic binding of histamine to protein carboxyls in the granule heparin-protein complex, Acta Physiol. Scand.78 Suppl. 336 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shikimi, T., Kobayashi, T. Contents of aprotinin, heparin and histamine in mast cells from bovine liver capsule. Agents and Actions 18, 325–328 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01964992
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01964992