Abstract
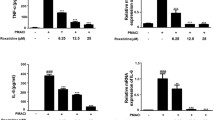
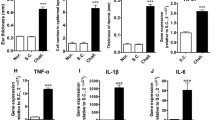
Protein kinase C (PKC) mediates a number of intracellular signal transduction pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammation, including phospholipase A2-dependent arachidonic acid release and eicosanoid production. Recent studies demonstrate that the PKC inhibitor GF109203X significantly reduces a number of inflammatory processes resulting from PKC activation by the topical application of phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) to mouse ears. In this model, GF109203X significantly reduced edema at doses similar to the PKC inhibitor staurosporine, and more effectively than indomethacin, zileuton, or sodium meclofenamate. Histological and biochemical analysis of biopsies from control and drug-treated ears revealed a marked reduction in edema, infiltrating neutrophils, and levels of the neutrophil-specific marker, myeloperoxidase, in GF109203X-treated mice. Prostaglandin E2 levels were also reduced in ears treated with GF109203X. These data suggest that GF109203X is an effective antiinflammatory agent as evaluated in the PMA model of edema, and implicates PKC as a potential target in the development of novel anti-inflammatory agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Nishizuka,Studies and prospectives of the protein kinase family for cellular regulation. Cancer63, 1892–1903 (1989).
J. M. Young, B. M. Wagner and D. A. Spires,Tachyphylaxis in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbolacetate- and arachidonic acid-induced ear edema. J. Invest. Dermatol.80, 48–52 (1983).
C. R. Loomis and R. M. Bell,Sangivamycin, a nucleoside analogue, is a potent inhibitor of protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem.263, 1682–1692 (1988).
H. Hidaka, M. Inagaki, S. Kawamoto and I. Sasaki,Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitor of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry23, 5036–5041 (1984).
T. Tamaoki, H. Nomoto, I. Takahashi, Y. Kato, M. Morimoto and F. Tomita,Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca ++ dependent protein kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.135, 397–402 (1986).
D. Toullec, P. Pianetti, H. Coste, P. Bellevergue, T. Grand-Perret, M. Ajakane, V. Baudet, P. Boissin, E. Boursier, F. Loriolle, L. Duhamel, D. Churon and J. Kirilousky,The bisindolylmaleimide GF109203X is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem.266, 15771–15781 (1991).
R. P. Carlson, L. O'Neill-Davis, J. Chang and A. Lewis,Modulation of mouse ear edema by cyclooxygenase and lipooxygenase inhibitors and other pharmacologic agents. Agents and Actions17, 198–204 (1985).
R. R. Harris, W. M. Mackin, D. G. Batt, S. M. Rakich, R. J. Collins, E. M. Bruin and N. R. Ackerman,Cellular and biochemical characterization of the antiinflammatory effects of Dup 654 in the arachidonic acid murine skin inflammation model. Skin Pharmacol.3, 29–40 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuchera, S., Barth, H., Jacobson, P. et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of the protein kinase C inhibitor, 3-[1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-1H-indol-3-yl]-4(1H-indol-3-yl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione monohydrochloride (GF109203X) in the PMA-mouse ear edema model. Agents and Actions 39 (Suppl 1), C169–C173 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972756
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972756