Abstract
Migration inhibitory (MI) activity in exudates, and ‘migration’ and ‘inhibition of migration’ of exudate cells was investigated in the delayed hypersensitivity (DH) reaction induced by intrapleural injection of PPD into complete Freund's adjuvant(CFA)-sensitized guinea-pigs. During the initial reaction (6-hour), two types of antigen-dependent MI activity were detected in serum and cell free exudate. One was a high molecular weight material associated with immunoglobulin, and the other was a low molecular weight material and appeared to be so-called antigen-dependent migration inhibitory factor (MIF). As the reaction progressed (i.e. 12–24-hour), two types of antigen-independent MI activity were revealed in exudate, but not in serum. One of these was a high molecular weight material, and the other was a low molecular weight material and thought to be socalled antigen-independent MIF.
Similar experiments were performed on the reversed passive Arthus (RPA) reaction in the pleural cavity of guinea-pigs. A high molecular weight substance having MI activity was detected in 6-hour cell free exudate and was found to be antigen-independent. So-called MIF was not found in this reaction.
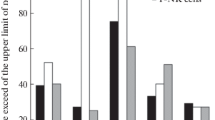
Migration of unseparated exudate cells from the 18-hour DH reaction was less extensive than that of 6-hour unseparated cells. Addition of antigen caused further inhibition, the effect on 18-hour exudate cells being more pronounced. These results were further examined, using mononuclear cells separated on a Ficoll-Isopaque gradient. The migration area of the mononuclear cells was reduced as the DH reaction progressed. Mononuclear cells from the DH reaction gave a smaller migration area throughout the reaction in comparison with blood mononuclear cells. The migration area of the RPA exudate mononuclear cells was also reduced as the reaction progressed. However 6-hour RPA exudate mononuclear cells gave a larger migration area than blood mononuclear cells.
The migration of mononuclear cells from DH exudate was inhibited by addition of antigen. A greater degree of inhibition of migration was induced by addition of antigen to mononuclear cells from 18- and 24-hour exudate cells in comparison with 6- and 12-hour exudates. The migration of mononuclear cells from normal blood (i.e. unsensitized animals) and RPA exudate (6- and 18-hour) was unaffected by addition of antigen. Similar results were obtained for blood of complete Freund's adjuvant sensitized animals from 0- to 18-hour.
Adherent (A) and nonadherent (NA) mononuclear cells from 18-hour DH exudate were separated through a glass bead column. The migration of adherent cells from 6-hour exudates was not significantly inhibited whereas that of 18-hour mononuclear cells was markedly inhibited. The effect on migration of each mononuclear cell fraction was detected by mixing with peritoneal exudate cells (used as indicator cells). The effect of the A cells from 18-hour mononuclear cell exudates on peritoneal exudate cells was strong, whereas that of 6-hour exudates was less marked. A similar effect was observed with NA cells, from 6- and 18-hour exudate, on the migration of peritoneal mononuclear cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Boughton and W. G. Spector,Histology of the tuberculin reaction in guinea-pigs, J. Path. Bact.85, 371 (1963).
S. Yamamoto, C. J. Dunn, F. Capasso, D. A. Deporter and D. A. Willoughby,Quantitative studies on cell-mediated immunity in the pleural cavity of guinea-pigs, J. Path. (in press).
S. Yamamoto, C. J. Dunn, D. Deporter D. A. Willoughby and E. Huskisson,A model for the quantitative study of immediate hypersensitivity in rats, Agents and Actions (submitted for publication).
J. J. Scheidegger,Une micro-methode d'immunoelectrophorese, Int. Arch. Allergy7, 103 (1955).
J. Porath, R. Axén and S. Ernback,Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose, Nature215, 1491 (1967).
F. C. Greenwood, W. M. Hunter and J. S. Glover,The preparation of 131 I-labelled human growth hormone of high specific radioactivity, Biochem. J.89, 114 (1963).
A. Bøyum,Separation of leucocytes from blood and bone marrow, Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest.21, Suppl., 97 (1968).
K. Shortman, N. Williams, H. Jackson, P. Russel, P. Byrt and E. Diener,The separation of lymphocytes from phagocytes on a glass bead column, and its effect on subpopulation of lymphocytes and antibody-forming cells, J. Cell. Biol.48, 566 (1971).
Y. Rabinowitz,Separation of lymphocytes, polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes on glass columns including tissue culture observations, Blood23, 811 (1964).
J. R. David, S. Al-Askari and H. S. Lawrence,Delayed hypersensitivity in vitro. The specificity of inhibition of cell migration by antigen, J. Immun.93, 264 (1964).
T. Yoshida and S. Cohen,Lymphokine activity in vivo in relation to circulating monocyte levels and delayed skin reactivity, J. Immun.112, 1540 (1974).
E. R. Heise, S. Han and R. S. Weiser,In vitro studies on the mechanism of macrophage migration inhibition in tuberculin sensitivity, J. Immun.101, 1004 (1968).
H. E. Amos, R. J. Gurner, R. J. Olds and R. R. A. Coombs,Passive sensitization of tissue cells. II. Ability of cytophilic antibody to render the migration of guineapig peritoneal exudate cells inhibitable by antigen, Int. Arch. Allergy32, 496 (1967).
B. R. Bloom and B. Benett,Mechanism of reaction in vitro associated with delayed type hypersensitivity, Science 153, 80 (1966).
J. R. David,Delayed hypersensitivity in vitro, its mediation by cell-free substances formed by lymphoid cell antigen interaction, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci.56, 72 (1966).
B. Benett and B. R. Bloom,Studies on the migration inhibition factor associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity; cytodynamics and specificity, Transplantation5, 996 (1967).
J. Sveicar, J. Pekárek and J. Johanovsky,Studies on production of biologically active substances which inhibit cell migration in supernatants and extracts of hypersensitive lymphoid cells incubated with specific antigen in vitro, Immunology15, 1 (1968).
H. E. Amos and P. J. Lachmann,The immunological specificity of a macrophage inhibition factor, Immunology18, 269 (1970).
T. Yoshida, C. A. Janeway and W. E. Paul,Activity of migration inhibitory factor in the absence of antigen, J. Immun.109, 201 (1972).
D. Zucker-Franklin,The percentage of monocytes among ‘mononuclear’ cell fractions obtained from normal human blood., J. Immun.112, 234 (1974).
T. Yoshida, H. Sonozaki and S. Cohen,The production of migration inhibition factor by B and T cells of the guinea-pig, J. exp. Med.138, 784 (1973).
R. E. Rocklin, R. P. McDermott, L. Chess, S. F. Schlossman and J. R. David,Studies on mediator production by highly purified human T and B lymphocytes, J. exp. Med.140, 1303 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, S. Studies on mechanisms of immobilization of mononuclear cells in the delayed hypersensitivity (DH) reaction. Agents and Actions 6, 16–27 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972181
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972181