Abstract
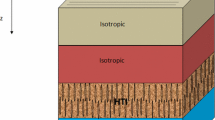
We show that the multiple scattering by small fractures of seismic waves with wavelengths long compared to the fracture size and fracture spacing is indistinguishable from multiple-scattering effects produced by ‘regular’ porosity, except for an orientation factor due to fracture alignment. The fractures reduce theP-wave andS-wave velocities and produce an effective attenuation of the coherent component of the seismic waves. The attenuation corresponds to 1000/Q of about unity for a Gaussian spectrum of fractures, and it varies with frequencyf asf 3. For a Kolmogorov spectrum of fractures of spectral index ν the attenuation is an order of magnitude or so larger and varies with frequency asf 3-v The precise degree of attenuation depends upon the matrix properties, the fracture porosity, the degree of fracture anisotropy, the type of fluid filling the fractures, and the incidence angle of the wave.
For fracture porosities less than about 15% theP-wave andS-wave velocities are decreased by the order of 5–10% with a lesser dependence on the type of fluid filling the fractures (gas, oil, or brine) and with a dependence on both the degree of anisotropy and the incident angle made by the wave. The tendency of fractures to occur perpendicularly to bedding suggests that the best way to measure seismically fractured rock behavior in situ is by using the travel-time delay and reflection amplitude. As both the offset and the azimuth of receivers vary from a shot, the travel-time delay and reflection amplitude should both show an elliptical pattern of behavior—the travel-time delay in response to the varying seismic speed, and the reflection amplitude in response to angular variations in the multiple scattering. Observations of attenuation at several frequencies should permit (a) determination of the spectrum of fractures (Gaussian versus Kolmogorovian) and (b) determination of the contribution of viscous damping to the effective attenuation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aki, K. (1981),Scattering and attenuation of high-frequency body waves (1–25 Hz) in the lithosphere, Phys. Earth Planet. Int.26, 241–243.
Aki, K. (1982),Scattering and attenuation, Bull. Seis. Soc. Am.78, B6, S319–330.
Aki, K. andRichards, P. G. (1980),Quantitative Seismology, Theory and Methods. Vol. 1 and 2. Freeman, San Francisco.
Banik, N. C., Lerche, I., andShuey, R. S. (1985),Stratigraphic filtering: Pt. I. Derivation of the O'Doherty-Anstey formula, Geophys. 50, 2768–2774.
Crampin, S. (1977).A review of the effects of anisotropic layering on the propagation of seismic waves. Geophys. J. Roy. Astr. Soc.49, 9–27.
Crampin, S. (1978).Seismic-wave propagation through a cracked solid: Polarization as a possible dilatancy diagnostic. Geophys. J. Roy. Astro. Soc.53, 467–496.
Crampin, S., McGonigle, R., andBamford, D. (1980),Estimating crack parameters from observations of P-wave velocity anisotropy. Geophys.45, 345–360.
Dainty, A. M. (1981),A scattering model to explain seismic Q observations in the lithosphere between 1 and 30 Hz. Geophys. Res. Lett.8, 1126–1128.
Dainty, A. M. (1984),High frequency acoustic backscattering and seismic attenuation. J. Geophys. Res.89, 3172–3176.
Eshelby, J. D. (1957),The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems. Proc. Roy. Soc. A,241, 376–396.
Flatté, S. M. (1979),Sound Transmission through a Fluctuating Ocean. Cambridge Univ. Press.
Frisch, U. (1968), ‘Wave propagation in random media’, inProbabilistic Methods in Applied Mathematics (A. T. Bharucha-Reid, ed.), Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.
Hudson, J. A. (1980),Overall properties of a cracked solid. Math. Camb. Phil. Soc.88, 371–384.
Hudson, J. A. (1982),Use of stochastic models in seismology. Geophys. J. Roy. Astr. Soc.69, 649–657.
Hudson, J. A. andHeritage, J. R. (1981).The use of the Born approximation in seismic scattering problems Geophys. J. Roy. Astr. Soc.66, 221–240.
Karal, F. C. andKeller, J. B. (1964),Elastic, electrodynamic and other waves in a random medium. J. Math. Phys.5, 537–547.
Kelley, K. R., Ward, R. W., Treitel, S., andAlford, R. M. (1976),Synthetic seismograms, a finite difference approach. Geophysics41, 2–27.
Kikuchi, M. (1981a),Dispersion and attenuation of elastic waves due to multiple scattering from inclusions. Phys. Earth Planet. Int.25, 159–162.
Kikuchi, M. (1981b),Dispersion and attenuation of elastic waves due to multiple scattering from cracks. Phys. Earth Planet. Int.27, 100–105.
Kuster, G. T. andToksoz, M. N. (1974a),Velocity and attenuation of seismic waves in two-phase media: Pt. I. Theoretical formulations. Geophys.39, 587–606.
Kuster, G. T. andToksoz, M. N. (1974b),Velocity and attenuation of seismic waves in two-phase media: Pt. II. Experimental results. Geophys.39, 607–618.
Lerche, I. (1979).Scintillations in astrophysics: I. An analytic solution of the second order moment equation. Astrophys. J.234, 262–274.
Levander, A. R. andHill, N. R. (1985),P-SV resonance in irregular low-velocity surface layers. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am.75, 847–864.
Mavko, G. M., andNur, A. (1979),Wave attenuation in partially saturated rocks. Geophys.44, 161–178.
McLaughlin, K. L. (1983),Coherency of seismic waveforms. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. Calif. Berkeley.
Menke, W. (1983a),On the effect of P-S coupling on the apparent attenuation of elastic waves in randomly layered media. Geophys. Res. Lett.10, 1145–1147.
Menke, W. (1983b).A formula for the apparent attenuation of acoustic waves in randomly layered media. Geophys. J. Roy. Astr. Soc.75, 541–544.
Menke, W. (1984),Asymptotic formulas for the apparent Q of weakly scattering three-dimensional media. Bull. Seis. Soc. Am.74, 1079–1081.
Menke, W. (1986), private communication.
Morse, P. M., andFeshbach, H. (1953),Methods of Theoretical Physics, Vol. 1 and 2. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Nagatani, T. (1980),Effective permittivity in random anisotropic media. J. Appl. Phys.51, 4944–4949.
Nordberg, H. E. (1981), Paper NSE/8: ‘Seismic hydrocarbon indicators in the North Sea)’ inNorwegian Symposium on Exploration. Bergen, Norway.
O'Connell, R. J. andBudiansky, B. (1977),Viscoelastic properties of fluid-saturated cracked solids. J. Geophys. Res.82, 5719–5735.
Resnick, J. R., Lerche, I. andShuey, R. T. (1986),Reflection, Transmission and the Generalized Primary Wave. Geopys. J. Roy. Astr. Soc.87, 349–377.
Richards, P. G. andMenke, W. (1983),The apparent attenuation of a scattering medium. Bull. Seis. Soc. Am.73, 1005–1021.
Sato, H. (1982a),Attenuation of S waves in the lithosphere due to scattering by its random velocity structure. J. Geophys. Res.87, 7779–7786.
Sato, H. (1982b),Amplitude attenuation of impulsive waves in random media on the travel time corrected wave formalism. J. Acoust. Soc. Am.71, 559–564.
Schoenberger, M. andLevin, F. K. (1974),Apparent attenuation due to intrabed multiples. Geophys.39, 1221–1241.
Schoenberger, M. andLevin, F. K. (1978),Apparent attenuation due to intrabed multiples: II Geophys.43, 730–737.
Schoenberger, M. andLevin, F. K. (1979),The effect of subsurface sampling on one-dimensional synthetic seismograms. Geophys.44, 1813–1829.
Shuey, R. T. (1982), personal communication.
Tartarskii, V. I. (1971),The effect of the turbulent atmosphere on wave propagation. Israel Progr. Sci. Translation, Jerusalem.
Toksoz, M. N., Cheng, C. H. andTimur, A. (1976),Velocities of seismic waves in porous rocks. Geophys.41, 621–645.
Uscinski, B. J. (1977),The Elements of Wave Propagation in a Random Medium, McGraw-Hill.
Walsh, J. B. (1968),Attenuation in partially melted material. J. Geophys. Res.73, 2209–2216.
Walsh, J. B. (1969),New Analysis of attenuation in partially melted rocks. J. Geophys. Res.74, 4333–4337
Wu, R-S. (1982a),Attenuation of short period seismic waves due to scattering. Geophys. Res. Lett.9, 9–12.
Wu, R.-S. (1982b),Mean field attenuation and amplitude attenuation due to wave scattering. Wave Motion4, 305–316.
Wu, T. T. (1966),The effect of inclusion shape on the elastic moduli of a two-phase material. Intern. J. Solids Structures2, 1–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lerche, I., Petroy, D. Multiple scattering of seismic waves in fractured media: Velocity and effective attenuation of the coherent components ofP waves andS waves. PAGEOPH 124, 975–1019 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879928
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879928