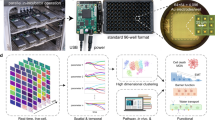
Abstract
A major bottleneck to the early stages of drug discovery is the absence of integration of high throughput screening (HTS) with smarter assays that screen “hits” from HTS to identify leads (High content screening, HCS). We propose a solution using novel fluorescent engineered protein biosensors integrated into a miniaturized live-cell-based screening platform (CellChip™ System) that markedly shortens the early drug discovery process. Microarrays of selectively localized living cells, containing engineered fluorescent biosensors, serve to integrate HTS and HCS onto a single platform. HTS “hits” are identified using one biosensor while reading the whole chip array of cells. The high-biological content information is then obtained from probing target activity at inter-cellular, sub-cellular and molecular levels in the “hit” wells. HCS assays yield temporal-spatial dynamic maps of the drug-target interaction within each living cell. We predict that a new platform incorporating HTS and HCS assays that are automated, miniaturized, and information-rich will dramatically improve the decision making process in the pharmaceutical industry and optimize lead compounds during the early part of the drug discovery process. There is an opportunity to establish a new paradigm for drug discovery based on integration of fluorescence technology, micropatterning of living cells, automated optical detection and data analysis, and a new generation of knowledge building bioinformatics approaches. The technology will have an expansive impact spanning the fields of drug discovery, biomedical research, environmental monitoring, life sciences, and clinical diagnostics. The integrated CellChip™ Platform with miniaturized tissue-specific microarrayed cells capable of providing inter-cellular and sub-cellular spatio-temporal information in response to drug-cell, toxin-cell, or pathogen-cell interactions will serve to enhance the decision making process in drug discovery, toxicology, and clinical diagnostics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Bachelet et al., Res. Immunol. 149, 727-732 (1998).
P. A. Baeuerle, Science 242, 540-546 (1988).
A. Beg, Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 3301-3310 (1993).
B. Conway et al., Journal of Biomolecular Screening 4(2), 75-86 (1999).
G. Ding, The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273(44), 28897-28905 (1998).
K. Giuliano et al., Journal of Biomolecular Screening 2, 249-259 (1997).
K. Giuliano et al., Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 24, 405-434 (1995).
K. Giuliano and D.L. Taylor, TIBTECH 16, 135-140 (1998).
High-Throughput Screening: Strategies and Suppliers (Report issued by HighTech Business Decisions, PO Box 6743, Moraga, CA 94570, 1998).
R. Kapur et al., CellChip™ System for Fluorescent Reporting of Toxins (GOMAC Proceedings, Monterey, CA, 1999).
R. Kapur, Drug Discovery & Development 61-62 (1999).
N. Ketis and M. J. Karnovsky, Heat-shock response as a possible model for (patho)physiological stress in endothelial cells (Endothelial Cell Biology in Health and Disease, Plenum Press, 1988).
S. Marshall, R&D Magazine 41(2), (1999).
R. Service, Science 282, 400-401 (1998).
U. Siebenlist, in Inducible Gene Expression, ed. P. Baeuerle, 93-142 (1995).
C. Wu, “The Incredible Shrinking Lab”, Science News, (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapur, R., Giuliano, K.A., Campana, M. et al. Streamlining the Drug Discovery Process by Integrating Miniaturization, High Throughput Screening, High Content Screening, and Automation on the CellChip™ System. Biomedical Microdevices 2, 99–109 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009993519771
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009993519771