Summary
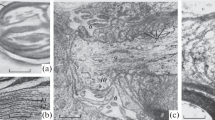
Nodes of Ranvier from normal and ‘dystrophic’ mice have been examined with quantitative freeze-fracture electron microscopy. Regions of nodal, paranodal and interparanodal axolemma of normal fibres are clearly distinguishable on the basis of particle size distributions in electron micrographs of freeze-fractured replicas. Protoplasmic fracture faces of normal nodes of Ranvier, contain approximately 40% 100 Å particles and about 25% elongated particles 150 by 250 Å. Paranodal and interparanodal membranes contain a more uniform distribution of smaller diameter particles. ‘Dystrophic’ mice of the 129/ReJ-Dy strain have a genetic defect of Schwann cell development and myelinogenesis. Axons of the sciatic and deep peroneal nerves in dystrophic mice, which appear to be normally myelinated, possess approximately the same distributions of particles as axons in normal mice. However, in affected regions of the ventral and dorsal roots, Schwann cell wrappings may be missing, creating heminodes of Ranvier where the myelination terminates or begins again. At such heminodes, there is a circular band of axonal membrane which bears particles of sizes and packing densities similar to that found at normal nodes. High voltage electron microscopic examination of 0.25–1 μm thick sections from these hemi-nodal regions reveals the presence of a filamentous layer beneath the particle-rich membrane. In addition, completely amyelinated regions of root axons contain particle patches having size-density distributions similar to that of both normal and hemi-nodal membranes. Thus, the nodal membrane displays a characteristic particle-size distribution profile. The occurrence of this particle profile does not appear to be dependent upon the presence or absence of Schwann cells. These observations suggest that the functions subserved by the numerous particles at the node of Ranvier are not dependent upon myelination for their local differentiation within the axonal membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew, W. S., Levinson, S. R., Brabson, J. S. andRaftery, M. A. (1978) Purification of the tetrodotoxin-binding component associated with the voltage-sensitive sodium channel fromElectrophorus electrieus electroplax membranes.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (U.S.A.)75, 2606–10.
Biscoe, T. J., Caddy, K., Pallot, D., Pherson, M. andStirling, C. A. (1974) The neurological lesion in the dystrophic mouse.Brain Research 76, 534–6.
Bradley, W. G. andJenkinson, M. (1973) Abnormalities of peripheral nerves in murine muscular dystrophy.Journal of the Neurological Sciences 18, 227–47.
Bray, G. M. andAguayo, A. J. (1975) Quantitative ultrastructural studies of the axon Schwann cell abnormality in spinal nerve roots from dystrophic mice.Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 54, 517–30.
Bray, G. M., Perkins, S., Peterson, A. L. andAguayo, A. J. (1977) Schwann cell multiplication deficit in nerve roots of new-born dystrophic mice: A radioautographic and ultrastructural study.Journal of the Neurological Sciences 32, 203–12.
Cragg, B. G. andThomas, P. K. (1957) The relationships between conduction velocity and the diameter and internodal length of peripheral nerve fibres.Journal of Physiology 136, 606–14.
Deguchi, N., Jongensen, P. L. andMaunsbach, A. B. (1977) Ultrastructure of the sodium pump.Journal of Cell Biology 75, 619–34.
Ellisman, M. H. (1976) The distribution of membrane molecular specializations characteristic of the node of Ranvier is not dependent upon myelination.Neurosciences Abstracts 2, 410.
Ellisman, M. H. (1977) High voltage electron microscopy of cortical specializations associated with membranes at nodes of Ranvier.Journal of Cell Biology 75, 108a.
Ellisman, M. H., Brooke, M. H., Kaiser, K. K. andRash, J. E. (1977) Appearance in slow muscle sarcolemma of specializations characteristic of fast muscle after reinnervation by a fast muscle nerve.Experimental Neurology 58, 59–67.
Ellisman, M. H., Rash, J. E., Staehelin, L. A. andPorter, K. R. (1976) Studies of excitable membranes. II. A comparison of specializations at neuromuscular junctions and non-junctional sarcolemmas of mammalian fast and slow twitch muscle fibres.Journal of Cell Biology 68, 752–74.
Friede, R. L. andSamorajski, T. (1967) Relation between the number of myelin lamellae and axon circumference in fibers of vagus and sciatic nerves of mice.Journal of Comparative Neurology 130, 223–31.
Gasser, H. S. (1955) Properties of dorsal root unmedullated fibers on two sides of the ganglion.Journal of General Physiology 38, 709–28.
Huxley, A. F. andStämpfli, R. (1949) Evidence for saltatory conduction in peripheral myelinated nerve fibres.Journal of Physiology 108, 315–39.
Kristol, C., Akert, K., Sandri, C., Wyss, U. R., Bennett, M. V. L. andMoor, H. (1977) The Ranvier nodes in the neurogenic electric organ of the knifefishStenarchus: A freeze-etching study on the distribution of membrane-associated particles.Brain Research 125, 197–212.
Kristol, C., Sandri, C. andAkert, K. (1978) Intramembranous particles at the nodes of Ranvier of the cat spinal cord: A morphometric study.Brain Research 142, 391–400.
Kubo, M., Onot, S. andTasaki, I. (1954)The Microphysiology of Nerve (edited byKaro, G.), pp. 68–76. Tokyo: Mauruzen.
Levinson, S. R. andEllory, J. C. (1973) Molecular size of the tetrodotoxin binding site estimated by irradiation inactivation.Nature New Biology 245, 122–3.
Livingston, R. B., Pfenninger, K., Moor, H. andAkert, K. (1973) Specialized paranodal and interparanodal glial-axonal junctions in the peripheral and central nervous system: A freeze-etching study.Brain Research 58, 1–24.
Madrid, R. E., Jaros, E., Cullen, M. J. andBradley, W. G. (1975) Genetically determined defect of Schwann cell basement membrane in dystrophic mouse.Nature 257, 319–21.
Nonner, W., Rojas, E. andStämpfli, R. (1975) Gating currents in the node of Ranvier: Voltage and time dependence.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society (London)B270, 483–92.
Peters, A. (1966) The node of Ranvier in the central nervous system.Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology 51, 229–39.
Quick, D. C. andWaxman, S. G. (1977) Specific staining of the axon membrane at nodes of Ranvier with ferric ion and ferrocyanide.Journal of the Neurological Sciences 31, 1–11.
Rasminsky, M. (1977) Cross-talk between single fibres in spinal roots of dystrophic mice.Neurology 27, 394.
Ritchie, J. M. andRogart, R. B. (1977) Density of sodium channels in mammalian myelinated nerve fibres and nature of the axonal membrane under the myelin sheath.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (U.S.A.) 74, 211–5.
Rosenbluth, J. (1976) Intramembranous particle distribution at the node of Ranvier and adjacent axolemma in myelinated axons of the frog brain.Journal of Neurocytology 5, 731–45.
Schnapp, B., Peracchia, C. andMugnaini, E. (1973) Freeze-fracture of Ranvier nodes.Journal of Cell Biology 59, 360a.
Schnapp, B., Peracchia, C. andMugnaini, E. (1976) The paranodal axo-glial junction in the central nervous system studied with thin sections and freeze-fracture.Neuroscience 1, 181–90.
Stämpfli, R. (1954) Saltatory conduction in nerve.Physiological Reviews 34, 101–12.
Stirling, C. A. (1974) Abnormalities in Schwann cell sheaths in spinal nerve roots of dystrophic mice.Journal of Anatomy 119, 169–80.
Tasaki, I. (1959) Conduction of the nerve impulse. InHandbook of Physiology, Section 1, Vol. 1, (edited byField, J., Magoun, H. W. andHall, V. E.), pp. 75–121. Washington, D.C.: American Physiological Society.
Thomas, P. K. (1955) Growth changes in the myelin sheath of peripheral nerve fibres.Proceedings of the Royal Society (London) B143, 380–91.
Webster, H. deF. (1971) The geometry of peripheral myelin sheaths during their formation and growth in rat sciatic nerves.Journal of Cell Biology 48, 348–67.
Webster, H. deF., Martin, J. R. andO'connell, M. F. (1973) The relationships between interphase Schwann cells and axons before myelination: A quantitative electron microscopic study.Developmental Biology 32, 401–16.
Wood, J. G., Jean, D. H., Whitaker, J. N., McLaughlin, B. J. andAlbers, R. W. (1977) Immunocytochemical localization of the sodium, potassium activated ATPase in knifefish brain.Journal of Neurocytology 6, 571–81.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellisman, M.H. Molecular specializations of the axon membrane at nodes of Ranvier are not dependent upon myelination. J Neurocytol 8, 719–735 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01206672
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01206672