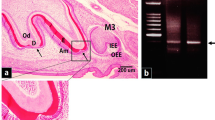
Abstract
Enamel-producing cells (ameloblasts) pass through several phenotypic and functional stages during enamel formation. In the transition between secretory and maturation stages, about one quarter of the ameloblasts suddenly undergo apoptosis. We have studied this phenomenon using the continuously erupting rat incisor model. A special feature of this model is that all stages of ameloblast differentiation are presented within a single longitudinal section of the developing tooth. This permits investigation of the temporal sequence of gene and growth factor receptor expression during ameloblast differentiation and apoptosis. We describe the light and electron microscopic morphology of ameloblast apoptosis and the pattern of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression by ameloblasts in the continuously erupting rat incisor model. In the developing rat incisor, ameloblast apoptosis is associated with downregulated expression of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that ameloblasts are “hard wired” for apoptosis and that insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression is required to block the default apoptotic pathway. Possible mechanisms of insulin-like growth factor-1 inhibition of ameloblast apoptosis are presented. The rat incisor model may be useful in studies of physiological apoptosis as it presents apoptosis in a predictable pattern in adult tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warshawsky H, Smith CE. Morphological classification of rat incisor ameloblasts. Anat Rec 1976; 179: 423-446.
Robinson C, Kirkham J, Shore, RC. Extracellular matrix of enamel and the ameloblast. Epith Cell Biol 1992; 1: 90-97.
Joseph BK, Savage NW, Young WG, Waters MJ. Prenatal expression of growth hormone receptor/binding protein and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) in the enamel organ. Role for growth hormone and IGF-1 in cellular differentiation during early tooth formation? Anat Embryol 1994; 75: 313-320.
Hardcastle Z, Mo R, Hui CC. Sharpe PT. The Shh signalling pathway in tooth development: defects in Gli2 and Gli3 mutants. Development 1998; 125: 2803-2811.
Warshawsky H, Moore CE. A technique for fixation and decalcification of rat incisors for electron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 1967; 15: 543.
Smith CE, Warshawsky H. Quantitative analysis of cell turnover in the enamel organ of the rat incisor. Anat Rec 1977; 187: 63-98.
Shibata S, Suzuki S, Tengan T, Yamashita Y. A histochemical study of apoptosis in the reduced ameloblasts of erupting mouse molars. Arch Oral Biol 1995; 40: 677-680.
Bronckers ALJJ, Lyaruu DM, Goei W, et al. Nuclear DNA fragmentation during postnatal tooth development of mouse and hamster and during dentine repair in the rat. Eur J Oral Sci 1996; 104: 102-111.
Vaahtokari A, Aberg T, Thesleff I. Apoptosis in the developing tooth: association with an embryonic signaling center and suppression by EGF and FGF-4. Development 1996; 122: 121-129.
Jernvall J, Aberg T, Kettunen P, Keranen S, Thesleff I. The life history of an embryonic signaling center: BMP-4 induces p21 and is associated with apoptosis in the mouse tooth enamel knot. Development 1998; 125: 161-169.
Lesot H, Vonesch JL, Peterka M, Tureckova J, Peterkova R, Ruch JV. Mouse molar morphogenesis revisited by three-dimensional reconstruction. II. Spatial distribution of mitoses and apoptosis in cap to bell staged first and second upper molar teeth. Int J Dev Biol 1996; 40: 1017-1031.
Smid JR, Monsour PA, Rousseau EM. Young WG. Cytochemical localization of dipeptidyl peptidase II activity in rat incisor tooth ameloblasts. Anat Rec 1992; 233: 493-503.
Joseph BK, Savage NW, Young WG, Waters MJ. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in the cell biology of the ameloblast: an immunohistochemical study. Epi Cell Biol 1994; 3: 47-53.
Joseph BK, Gobé GC, Savage NW, Young WG. Expression and localisation of sulphated glycoprotein-2mRNA in the rat incisor tooth ameloblasts: relationships with apoptosis. Int J Exp Path 1994; 75: 313-320.
Joseph BK, Savage NW, Harbrow DJ, Young WG. Nonexpression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor is associated with apoptosis: an ultrastructural study on rat ameloblasts. Apoptosis 1997; 2: 471-477.
Joseph BK, Harbrow DJ, Savage NW, Young WG. Apoptosis in rat incisor ameloblasts: an ultrastructural study Abstract IADR Brisbane. J Dent Res Sept 27–29, 1998; 78: 950.
Moe H, Jessen H. Phagocytosis and elimination of amelocyte debris by stratum intermedium cells in the transitional zone of the enamel organ of the rat incisor. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 1972; 131: 63-75.
Smith CE. Ameloblasts: Secretory and resorptive functions. J Dent Res 1979; 58B: 695-706.
Nishikawa S, Sasaki F. Phagocytotic processing of apoptotic bodies of transitional ameloblasts by MHC Class II-expressing macrophages in rat incisor. J Histochem Cytochem 1996; 44: 1459-1467.
Smid JR, Young WG, Monsour PA, Rousseau EM. Ultrastructural localization of cathepsin B in rat incisor ameloblasts. J Dent Res 1992; 71(Spec. Issue): 728 (Abs1703).
Salama AH, Zaki AE, Eisenmann DR. Fine structural changes and lysosomal phosphatase cytochemistry of ameloblasts associated with the transitional stage of enamel formation in the rat incisor. Am J Anat 1991; 190: 279-290.
Joseph BK, Savage NW, Young WG, Gupta GS, Breier BH, Waters MJ. Expression and regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I in the rat incisor. Growth Factors 1993; 8: 267-275.
Zhang CZ, Young WG, Waters MJ. Immunocytochemical localization of growth hormone receptor in rat maxillary teeth. Arch Oral Biol 1992; 37: 7-84.
Zhang CZ, Young WG, Li H, Garcia-Aragon J, Clayden AM, Waters MJ. Expression of growth hormone receptor by immunocytochemistry in rat molar root formation and alveolar bone remodelling. Calcif Tissue Int 1992; 50: 541-546.
Joseph BK, Savage NW, Daley TJ, Young WG. In situ hybridisation evidence for a paracrine/autocrine role for insulin-like growth factor-1 in tooth development. Growth Factors 1996; 13: 11-17.
D'Ambrosio C, Valentinis B, Prisco M, Reiss K, Rubini M, Baserga R. Protective effect of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor on apoptosis induced by okadaic acid. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 3264-3271.
Kulik G, Klippel A, Weber, MJ Antiapoptotic signalling by the insulin-like growth factor I receptor, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and Akt. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 1595-1606.
Valentinis B, Baserga R. The IGF-1 receptor protects tumor cells from apoptosis induced by high concentrations of serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 16: 362-368.
Prisco M, Hongo A, Rizzo MG, Sacchi A, Baserga, R. The insulin-like growth factor I receptor as a physiologically relevant target of p53 in apoptosis caused by interleukin-3 withdrawal. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 1084-1092.
Armstrong RC, Aja T, Xiang J, et al. Fas-induced activation of the cell death-related protease CPP32 is inhibited by Bcl-2 and by ICE family protease inhibitors. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 16850-16855.
Monney L, Otter I, Olivier R, et al. Bcl-2 overexpression blocks activation of the death protease CPP32/YAMA/apopain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 221: 340-345.
Toms SA, Hercbergs A, Liu J, et al. Antagonist effect of insulin-like growth factor I on protein kinase inhibitor-mediated apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells in association with Bcl-2 and bcl-xL. J Neurosurg 1998; 88: 884-889.
Minshall C, Arkins S, Straza J, et al. IL-4 and insulin-like growth factor-I inhibit the decline in Bcl-2 and promote the survival of IL-3-deprived myeloid progenitors. J Immunol 1997; 159: 1225-1232.
Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, et al. Regulation of neuronal survival by the serinethreonine protein kinase Akt. Science 1997; 275: 661-665.
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 1997; 91: 231-241.
del Peso L, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Page C, Herrera R, Nunez G. Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science 1997; 278: 687-689.
Evan G, Littlewood T. A matter of life and cell death. Science 1998; 281: 1317-1322.
Wang L, Ma W, Markovich R, Chen JW, Wang PH. Regulation of cardiomyocyte apoptotic signaling by insulin-like growth factor I. Circ Res 1998; 83: 516-522.
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homologue, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 1993; 74: 609-619.
Boldin MP, Goncharov TM, Goltsev YV, Wallach D. Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1-and TNF receptor-induced cell death. Cell 1996; 85: 803-815.
Enari M, Talanian RV, Wong WW, Nagata S. Sequential activation of ICE-like and CPP32-like proteases during Fas-mediated apoptosis. Nature 1996; 380: 723-726.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, B.K., Harbrow, D.J., Sugerman, P.B. et al. Ameloblast apoptosis and IGF-1 receptor expression in the continuously erupting rat incisor model. Apoptosis 4, 441–447 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009600409421
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009600409421