Abstract
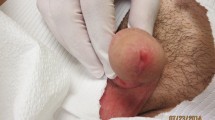
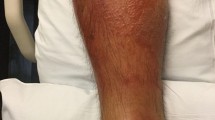
A 15 year-old girl and her 50-year-old mother from Jabalpur, India, were found to have phaeohyphomycotic skin lesions due toPhialophora richardsiae. Among the antimycotics testedin vitro, clotrimazole was found to be most active. Topical application of clotrimazole cream cured the lesions completely.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajello L, Georg LK, Steigbigel RT & Wang CJK (1974) A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species ofPhialophora. Mycologia 66: 490–498
Corrado ML, Kramer M, Cummings M & Eng RH (1982) Susceptibility of dematiaceous fungi to Amphotericin B, miconazole, ketoconazole, flucytosine and rifampin alone and in combination. Sabouraudia 20: 109–113
Corrado ML, Weitzman I, Stanek A, Goetz R & Agyare E (1980) Subcutaneous infection withPhialophora richardsiae and its susceptibility to 5-fluorocytosine, amphotericin B and miconazole. Sabouraudia 18: 97–104
Dixon DM, Polak A & Walshe TJ (1988) Phaeohyphomycosis. In: JM Torres-Rodríguez (Ed) Proc. X Int. Congress ISHAM, (pp 84–92). JR Prous Science, Barcelona.
Dixon DM & Polak A (1987)In vitro andin vivo drug studies with three agents of Central Nervous System Phaeohyphomycosis. Chemotherapy 33: 129–140
Guého E, Bonnefoy A, Luboinski J, Petit JC & Hoog GSde (1989) Subcutaneous granuloma caused byPhialophora richardsiae: case report and review of the literature. Mycoses 32: 219–223
Hoog GSde (1983) On the potentially pathogenic dematiaceous hyphomycetes. In: DH Howard (Ed): Fungi Pathogenic for Humans and Animals, Part A (Biol.) (pp 149–216). Marcel Dekker, New York
Kobayashi GS & Medoff G (1977) Measurement of activity of antifungal drug. In: DH Howard & M Dekker (Eds) Fungi Pathogenic for Humans and Animals (Part B) (pp 357–372)
Listemann H (1976) Die kulturelle Untersuchung eines Tränensteines mit Isolierung des PilzenPhialophora richardsiae. E. Rodenwaldt Archiv 2: 45–52
Mehta FS, Bhonsle RB, Murti PR, Daftary DK, Gupta PC & Pindborg JJ (1989) Central papillary atrophy of the tongue among bidi smokers in India: a 10-year study of 182 lesions. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 18: 475–480
Moskowitz LB, Cleary JJ, McGinnis MR & Thomson CB (1983)Phialophora richardsiae in a lesion appearing as a giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath. Arch. Path. Lab. Med. 107: 374–376
Polak FM, Siverio C & Bresky RH (1976) Corneal chromomycosis: Double infection with Phialophora verrucosa (Medlar) andCladosporium cladosporioides (Fresenius). Ann. Ophthalmol. 8: 139–144.
Schwartz IS & Emmons CW (1968) Subcutaneous cystic granuloma caused by a fungus of wood pulpPhialophora richardsiae. Amer. J. Clin. Pathol. 49: 500–505
Singh SM & Barde AK (1986) Opportunistic infections of skin and nails by non-dermatophytic fungi. Mykosen 29: 272–277
Weitzman I, Gordon MA, Henderson RW & Lapa EW (1984)Phialophora parasitica an emerging pathogen. Sabouraudia 22: 331–339
Yangco BG, Testrake D & Okafor J (1984)Phialophora richardsiae isolated from infected human bone: morphological, physiological and antifungal susceptibility studies. Mycopathologia 86: 103–111
Zeifer A & Connor DH (1980) Phaeomycotic cyst: A clinicopathologic study of twenty-five patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 29: 901–911
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.M., Agrawal, A., Naidu, J. et al. Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused byPhialophora richardsiae and the effect of topical clotrimazole in its treatment. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 61, 51–55 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572122
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572122