Abstract
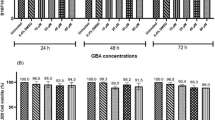
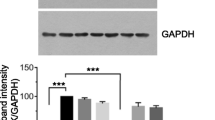
Quercetin has been known to have anti-tumor and anti-oxidation activities. In the present study, we have investigated its in vitro anti-metastatic activity. Quercetin inhibited the invasion and mobility of murine melanoma B16-BL6 cells in a dose-dependent manner but did not affect their adhesion to either laminin, fibronectin, or type VI collagen. Moreover, quercetin significantly inhibited the proliferation of B16-BL6 cells only in the case of time incubation longer than 48 h. Quercetin dose-dependently decreased the cell rates in S and G2–M phases of cell cycle. The effect of quercetin to cause a remarkable apoptosis of B16-BL6 cells was also demonstrated by flow cytometric assay as well as DNA fragmentation with a typical 180-bp ladder band in agarose electrophoresis and a quantitative analysis. Furthermore, quercetin markedly inhibited the expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 but hardly influenced Bcl-XL. These results suggest that the inhibition of quercetin on invasiveness and migration of B16-BL6 cells are closely associated with the arrest of cell cycle as well as the induction of apoptosis by decreasing the Bcl-2 expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker AH, George SJ, Zaltsman AB et al. Inhibition of invasion and induction of apoptotic cell death of cancer cell lines by overexpression of TIMP-3. Br J Cancer 1999; 79: 1347–55.
Cho SY, Klemke RL. Extracellular-regulated kinase activation and CAS/Crk coupling regulate cell migration and suppress apoptosis during invasion of extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol 2000; 149: 223–36.
Takasu M, Tada Y, Wang JO et al. Resistance to apoptosis induced microenvironmental stresses is correlated with metastatic potential in Lewis lung carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 1999; 17: 409–16.
Korobko EV, Saschenko LP, Prockorchouk EB et al. Resistance to tumor necrosis factor induced apoptosis in vitro correlates with high metastatic capacity of cells in vivo. Immunol Lett 1999; 67: 71–6.
Bohle AS, Kalthoff H. Molecule mechanisms of tumor metastasis and angiogenesis. Lungenbecks Arch Surg 1999; 384: 133–40.
Jaattela M. Escaping cell death: Survival proteins in cancer. Exp Cell Res 1999; 248: 30–43.
Fernandez Y, Espana L, Manas S et al. Bcl-xL promotes metastasis of breast cancer cells by induction of cytokines resistance. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: 350–9.
Biroccio A, Candiloro A, Mottolese M et al. Bcl-2 overexpression and hypoxia synergistically act to modulate vascular endothelial growth factor expression and in vivo angiogenesis in a breast carcinoma line. FASEB J. 2000; 14: 652–60.
Nagao M, Nakajima Y, Hisanaga M et al. The alteration of Fas receptor and ligand system in hepatocellular carcinomas: How do hepatoma cells escape from the host immune surveillance in vivo? Hepatology 1999; 30: 413–21.
Harn HJ, Shen KL, Yueh KC et al. Apoptosis occurs more frequently in intraductal carcinoma than infiltrating duct carcinoma of human breast cancer and correlated with altered p53 expression: detected by terminal-deoxynucleotidyl-transferase-mediated dUTP-FITC nick end labeling (TUNEL). Histopathology 1997; 31: 534–9.
Cheng JD, Werness BA, Babb JS et al. Paradoxical correlations of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitions p21waf1/cipl and p27kip1 in metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 1057–62.
Megha T, Lazzi S, Ferrari F et al. Expression of G2-M checkpoint regulators cyclin B1 and P34CDC2 in breast cancer: A correlation with cellular kinetics. Anticancer Res 1999; 19: 163–9.
Keam JS, Kong G, Yang SC et al. Cyclin D1 overexpression is an indicator of poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 1996; 81: 127–32.
Kato M, Liu W, Yi H et al. The herbal medicine Sho-saiko-to inhibits growth and metastasis of malignant melanoma primarily developed in ret-transgenic mice. J Invest Dermatol 1998; 111: 640–4.
Yan C, Han R. Suppression of adhesion-induced protein tyrosine phosphorylation decreases invasive and metastatic potentials of B16-BL6 melanoma cells by protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein. Invasion Metastasis 1997; 17: 189–98.
Hollman PO, Katam MB. Bioavailability and health effects of dietary flavonols in man. Arch Toxicol 1998; 20 (Suppl): 237–48.
Kawaii S, Tomono Y, Katase E et al. Antiproliferative activity of flavonoids on several cancer cell lines. Biosci Biotech Biochem 1999; 63: 896–9.
Paganga g, Miller N, Rice Evans CA. The polyphenolic content of fruit and vegetables and their antioxidant activities. What does a serving constitute? Free Radical Res 1999; 10: 153–62.
Fujii H, Inobe M, Kimura F et al. Vaccination of tumor cells transfected with the B7-1 (CD80) gene induces the anti-metastatic effect and tumor immunity in mice. Int J Cancer 1996; 66: 219–24.
Tokuyama S, Moriya S, Taniguchi S et al. Suppression of pulmonary metastasis in murine B16melanoma cells by transfection of a sialidase cDNA. Int J Cancer 1997; 73: 410–5.
Tokuyama M, Kogawa K, Nishihori Y et al. Suppression of intracellular Cu-Zn SOD results in enhanced motility and metastasis of Meth A sarcoma cells. Int J Cancer 1997; 73: 187–92.
Sheng Y, Yoshimura M, Inoue S et al. Remodeling glycoconjuates on CD44 enhances cell adhesion to hyaluronate, tumor growth and metastasis in B16 melanoma cells expressing β-1,4-Nacetylglucosaminyltransferase III. Int J Cancer 1997; 73: 850–8.
Cendan JC, Souba WW, Copeland EM et al. Increased L-arginine transport in a nitric oxide-producing metastatic colon cancer cell line. Ann Surg Oncol 1996; 3: 502–8.
Difilippantonio MJ, Zhu J, Chen HT et al. DNA repair protein Ku80 suppresses chromosomal aberrations and malignant transformation. Nature 2000; 404: 510–4.
Fu MY, Yu ZX, Pelayo BA et al. Focal adhesion kinase-dependent apoptosis of melanoma induced by tyrosine and phenylalaninedeficiency. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 758–65.
Sellias KS, Cohen JJ. Gene induction by γ-irradiation leads to DNA fragmentation in lymphocytes. J Immunol 1987; 139: 3199–206.
Emlen W, Niebur J, Kadera R. Accelerated in vitro apoptosis of lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 1994; 152: 3685–92.
Montero L, Nagamine Y. Regulation by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase of adenylate-and uridylate-rich element-mediated urokinasetype plasminogen activator (uPA) messenger RNA stability and uPAdependent in vitro cell invasion. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 5286–93.
Kahari VM, Saarialho Kere U. Matrix metalloproteinase and their inhibitors in tumor growth and invasion. Ann Med 1999; 31: 34–45.
Iwasaki T, Shinkai K, Mukai M et al. Cell-cycle-dependent invasion in vitro by rat ascites hepatoma cells. Int J Cancer 1995; 63: 282–7.
Reed JA, Loganzo F, Shea CR et al. Loss of expression of the p16/cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2 tumor suppressor gene in melanocytic lesions correlates with invasive stage of tumor progression. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 2713–8.
Ono M, Handa K, Withers DA et al. Motility inhibition and apoptosis are induced by metastasis-suppressing gene product CD82 and its analogue CD9, with concurrent glycosylation. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 2335–9.
Reed JC. Dysregulation of apoptosis in cancer. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 2941–53.
Wu J, Shen ZZ, Lu JS et al. Prognostic role of p27kip1 and apoptosis in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer 1999; 79: 1572–8.
Hashimoto S, Koji T, Kohara N et al. Frequency of apoptosis relates inversely to invasiveness and metastatic activity in human colorectal cancer. Virchows Arch 1997; 131: 241–8.
Inbal B, Cohen O, Polak Charcon J et al. DAP kinase links the control of apoptosis to metastasis. Nature 1997; 390: 180–4.
Yang E, Zha JP, Jockel J et al. Bad, a heterodimeric partner for Bcl-XL and Bcl-2 displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell 1995; 80: 285–91.
Boise LH, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Postema CE et al. bcl-x, a bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell 1993; 74: 597–606.
Oltval ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 1993; 74: 609–19.
Sierra A, Castellsague X, Tortola S et al. Apoptosis loss and bcl-2 expression: Key determinants of lymph node metastasis in T1 breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1996; 2: 1887–94.
Sierra A, Lloveras B, Castellsague X et al. Bcl-2 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in human ductal breast carcinoma. Int J Cancer 1995; 60: 54–60.
Fujieda S, Inuzuka M, Tanaka N et al. Expression of p27 is associated with Bax expression and spontaneous apoptosis in oral and oropharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 1999; 84: 315–20.
Liu DF, Ferguson K, Cooper GS et al. p27 cell-cycle inhibitor inversely correlated with lymph node metastasis in right-sided colon cancer. J Clin Lab Anal 1999; 13: 291–5.
Kim DH, Lee HJ, Nam ES et al. Reduced expression of cell-cycle inhibitor p27kip1 is associated with progression and lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma. Histopathology 2000; 36: 245–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Xu, Q. & Saiki, I. Quercetin inhibits the invasion and mobility of murine melanoma B16-BL6 cells through inducing apoptosis via decreasing Bcl-2 expression. Clin Exp Metastasis 18, 415–421 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010960615370
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010960615370