Abstract
In order to enhance general reactivity of immune system in the tumor-bearing host, we employed extract ofCordyceps sinensis (CSE) as a biological response modifier.Cordyceps sinensis is an interesting material produced by a kind of mushroom parasitic to larval moths and was used to hasten recovery from exhaustion in ancient China.
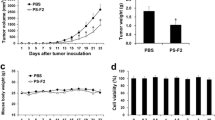
In this experiment, C57BL/6 mice implanted subcutaneously with syngeneic EL-4 lymphoma cells were employed as the host. Oral administration of the extract leads to a reduction of tumor size and prolongation of the host survival time. As judged by plaque-forming cells against T-dependent (sheep erythrocytes) and T-independent (bacterial lipopolysaccharide) antigens, CSE showed to augment the antibody responses. As for the activities of peritoneal macrophages, chemotaxis was dramatically depressed within a few days after EL-4 transplantation up to the end of life, but treatment with CSE at −14, −7, −4, +4, +7 and +10 days after the tumor transplantation augmented the activity about four times stronger than that of control. Phagocytic activity of macrophages was also decreased in tumor-bearing mice treated with cyclophosphamide (100 mg/kg) 3 and 5 days after tumor transplantation. But administration of CSE restored the activity to more than the normal level. The overall efficacy of CSE was tested with protective activity against systemic infection bySalmonella enteritides. The tumor-bearing mice receiving this medicine lived significantly longer than any other groups without CSE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takei F, Levy JG, Kilburn DG.In Vitro induction of cytotoxicity against syngenic mastocytoma and its suppression by spleen and thymus cells from tumor-bearing mice. J Immun 1976; 116: 288–93.
Kurashige S, Yoshida T, Kodama K, Mitsuhashi S. Immunopotentiating activity of whole cells and mini-cells ofSalmonella typhimurium. Microbiol Immunol 1981; 25: 467–77.
Symoens J, Rosenthal M. Levamisole in the modulation of the immune response: The current experimental and clinical state. J Recticuloendothel Soc 1976; 21: 175.
Van Belle H. Alkaline phosphatase. I. Kinetics and inhibition by levamisole of purified isoenzymes from humans. Clin Chem 1976; 22: 972.
Odashima S, Nakayabu Y, Honjo N, Abe H, Arichi S. Induction of phenotypic reverse transformation by ginsenosides in cultured Morris hepatoma cells. Eur J Cancer 1979; 15: 885–92.
Miyata H, Himeno K, Nomoto K. Mechanisms of the potentiation of specific antitumor immunity by intratumor injection ofCorynebacterium parvum. Cancer Res 1983; 43: 4670–5.
Tanaka K, Konishi F, Himeno K, Taniguchi K, Nomoto K. Augmentation of antitumor resistance by a strain of unicellular green-algae,Chlorella vulgaris. Cancer Immunol Immunother 1984; 17: 90–4.
Tsuru S, Nomoto K, Kitani H, Watanabe M, Zinnaka Y. Depression of macrophage functions and T cell-mediated immunity in tumor-bearing mice and its prevention by PSK. Cancer Immunol Immunother 1984; 18: 160–3.
Kumagai K, Itoh K, Hinuma S, Tada M. Pretreatment of plastic petridishes with fetal calf serum. A simple method for macrophage isolation. J Immunol Methods 1979; 29: 17–25.
Boyden S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med 1962; 115: 453–66.
Jerne NK, Nordin AA. Plaque forming in agar by single antibody producing cells. Science 1963; 140: 405–10.
Odashima S, Ohta T, Kohno H, Matsuda T, Kitagawa I. Control of phenotypic expression of cultured B16 melanoma cells by plant glycosides. Cancer Res 1985; 45: 2781–4.
Kurashige S, Mitsuhashi S. Macrophage activities in sarcoma 180-bearing mice and EL-4-bearing mice. Gann 1982; 73: 85–90.
Yamamoto M, Kumagai A, Yamamura Y. Structure and actions of saikosaponins isolated from Bupleurum falcaltum L. 1. Anti-inflammatory action of Saikosaponins. Arzneim Forsch 1975; 25: 1021–3.
Yamaguchi Y, Kohno H, Tawara M, Odashima S, Abe H. Effect of saikosaponin derivatives upon the immune response against T-dependent and -independent antigens in mice. Int J Immunopharmacol 1985; 7: 827–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, N., Yoshida, J., Ren, L.J. et al. Augmentation of various immune reactivities of tumor-bearing hosts with an extract ofCordyceps sinensis . Biotherapy 2, 199–205 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173520
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173520