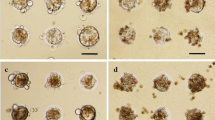
To improve long-term expression of drug biotransformation activities in hepatocytes, we have examined the suitability of several epithelial-like cell lines (MDCK, MS and L-132) for supporting functional co-cultures with rat hepatocytes. Cells were selected on the basis of their compatibility with hepatocytes, formation of stable monolayers in the absence of serum and lack of drug biotransformation activities. The expression of individual elements of the biotransformation system was evaluated in these co-cultures. Co-cultured hepatocytes remained viable and showed a characteristic polygonal shape for more than a week. Depending on the cell line used, levels of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase and 7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase activities of co-cultured hepatocytes oscillated between 24–47% of their initial value after 4 days in culture. The highest levels of monooxygenase activity were found in hepatocytes co-cultured with MS cells (41–47%). In contrast, these activities decreased to 6% when hepatocytes were maintained in pure culture for the same period. The activities of the conjugating enzymes UDP-glucuronyltransferase and glutathione S-transferase were maintained at nearly the initial levels during the complete period of study, both in pure and mixed-cultures, regardless of the cell line used. MS cells adapted themselves much better to serum-free culture conditions, and the co-culture with rat hepatocyte was technically easier. After one week, total cytochrome P450 and reduced glutathione in rat hepatocytes/MS co-cultures were 31% and 127% respectively of the day O values, whereas they were undetectable in pure culture. A clear induction of monooxygenase activities by methylcholanthrene, phenobarbital and ethanol could be observed by the 5th day in MS cells/hepatocyte co-cultures. The fact that the results of our work show the suitability of MS cells, an epithelial-derived cell line, for improving the expression of biotransformation enzymes of cultured hepatocytes opens new possibilities of simplifying co-cultures for their use in drug-metabolism studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHH:
-
aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase
- CDNB:
-
1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- ECOD:
-
7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
- Et-OH:
-
ethanol
- GSH:
-
reduced glutathione
- GSH-t:
-
glutathione S-transferase
- MC:
-
3-methylcholanthrene
- PB:
-
phenobarbital
- UDP-Gt:
-
UDP-glucuronyltransferase
References
BEGUE, J., GUGUEN-GUILLOUZO, C., PASDELOUP, N. and GUILLOUZO, A. (1984). Prolonged maintenance of active cytochrome P-450 in adult rat hepatocyte co-cultured with another liver cell type. Hepatology 4:839–842.
BISSELL, D.M., ARENSON, D.M., MAHER, J.J. and ROLL, F.G. (1987). Support of cultured hepatocytes by a laminin-rich gel. Evidence for a functionally significant subendothelial matrix in normal rat liver. J. Clin. Invest. 79:801–812.
BISSELL, D.M. and GUZELIAN, P.S. (1979) Ascorbic acid deficiency and cytochrome P-450 in adult rat hepatocytes in primary monolayer culture. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 192:569–576.
CLEMENT, B., GUGEN-GUILLOUZO, C., CAMPION, J.P., GLAISE, D., BOUREL, M. and GUILLOUZO, A. (1984). Long-term co-cultures of adult human hepatocytes with rat liver epithelial cells: modulation of elbumin secretion and accumulation of extracellular material. Hepatology 4:373–380.
DECAD, G.M., HSIEH, D.P.H., BYARD, J.L. (1977). Maintenance of cytochrome P-450 and metabolism of aflatoxin B1 in primary hepatocyte cultures. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 78:279–287.
DICKINS, M., PETERSON, R.E. (1980). Effects of a hormone-supplemented medium on cytochrome P-450 content and monooxygenase activities of rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Biochem. Pharmacol. 29:1231–1238.
DONATO, M.T., CASTELL, J.V. and GOMEZ-LECHON, M.J. (1990). Prolonged expression of biotransformation activities of rat hepatocytes co-cultured with established cell lines. Toxic. In Vitro 4:461–466.
GOMEZ-LECHON, M.J. and CASTELL, J.V. (1983). The role of fetal calf serum during the first stages of hepatocyte culture. In: Hormonally defined media. A tool in cell biology (A. Fisher and R.J. Wieseer, eds.), pp. 340–343. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
GOMEZ-LECHON, M.J., LOPEZ, P. and CASTELL, J.V. (1984). Biochemical functionality recovery of hepatocytes after deep-freezing storage. In Vitro 20:826–832.
GOULET, F., NORMAND, C. and MORIN O. (1988). Cellular interactions promote tissue-specific function, biomatrix deposition and junctional communication of primary cultured hepatocytes. Hepatology 8:1010–1018.
GREENLEE, W.F. and POLAND, A. (1978). Mainitenance and reversibility of active albumin secretion by adult rat of hepatic enzyme activity in C547 BL/6J and DBA/2J mice by phenobarbital, 3-methylcholanthrene and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorobenzo-p-dioxin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 205:569–605.
GUGUEN-GUILLOUZO, C., CLEMENT, B., BAFFET, G., BEAUMONT, C., MORELCHANY, E., GLAISE, D. and GUILLOUZO, A. (1983). Maintenance and reversibility of active albumin secretion by adult rat hepatocytes co-cultured with another liver epithelial cell type. Exptl. Cell. Res. 143:47–54.
GUZELIAN, P.S. and BISSELL, D.M. (1976) Effect of cobalt on synthesis of heme and cytochrome P-450 in the liver liver. Studies of adult rat hepatocytes in primary monolayer and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 251:4421–4427.
HABIG, W.H. and JAKOBY, W.B. (1981). Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-transferases. In: Methods in Enzymology (P.S. Colowick and N.O. Kaplan, eds.) vol. 77, pp. 398–405. Academic Press, New York.
HISSIN, P.J. and HILF, R. (1976). A fluorimetric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal. Biochem. 274:214–226.
HOLME, J.A. (1985). Xenobiotic metabolism and toxicity in primary monolayer cultures of hepatocytes. NIPH Annals 8:49–63.
HOLME, J.A., SODERLUND, E. and DYDING, E. (1983). Drug metabolism activities of isolated rat hepatocytes in monolayer culture. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 52:348–356.
JONGEN, W.M.F., SIJTSMA, S.R., ZWIJSEN, R.M.L. and TEMMINK, J.H.M. (1987). A co-cultivation system consisting of primary chick embryo heepatocytes and V79 Chinese hamster cells as a model for metabolic cooperation studies. Carcinogenesis 8:767–772.
KURI-HARCUCH, W. and MENDOZA-FIGUEROA, T. (1989). Cultivation of adult rat hepatocytes on 3T3 cells: expression of various liver differentiated functions. Differentiation 41:148–157.
LANGENBACH, R., MALICK, L., TOMPA, A., KUSZYNSKI, C., FREED, H., and HUBERMAN, E. (1979). Maintenance of adult rat hepatocytes on C3H/1OT1/2 cells. Cancer Res. 39:3509–3514.
LILIENBLUM, W., WALI, A.K. and BOCK, K.W. (1982). Differential induction of rat liver microsomal UDP-glucuronyltransferase activities by various inducing agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 31:907–913.
LOWRY, O.H., ROSENBROUGH, N.J., FARR, A.L. and RANDALL, R.J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
MAIER, P. (1988). Development of in vitro toxicity tests with cultures of freshly isolated rat hepatocytes. Experientia 44:807–817.
MICHALOPOULOS, G., SATTLER, G.L. and PITOT, H.C. (1976). Maintenance of microsomal cytochrome b5 and P-450 in primary cultures of parenchymal liver cells on collagen membranes. Life Sci. 18:1139–1144.
MICHALOPOULOS, G., RUSELL, F. and BILES, C. (1979). Primary cultures of hepatocytes on human fibroblasts. In Vitro 15:796–806.
MORIN, O. and NORMAND, C. (1986). Lont-term maintenance of hepatocyte functional activity in co-culture: Requirements for sinusoidal endothelial cells and dexamethasone. J. Cell. Physiol. 129:103–110.
NEBERT, D.W. and GELBOIN, H.V. (1968). Substrate-inducible microsomal aryl hydroxylase in mammalian cell culture. J. Biol. Chem. 243:6242–6249.
OMURA, T. and SATO, R. (1964). The carbon monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes. J. Biol. Chem. 239:2370–2378.
PAINE, A.J. and HOCKIN, L. (1980). Nutrient imbalance causes the loss of cytochrome P-450 in liver cell culture: Formulation of culture media which maintain cytochrome P-450 at in vivo concentrations. Biochem. Pharmacol. 29:3215- 3218.
PAINE, A.J., VILLA, P. and HOCKIN, L. (1980). Evidence that ligand formation is a mechanism underlying the maintenance of cytochrome P-450 in rat liver cell culture. Potent maintenance by metyrapone. Biochem. J. 188:937–939.
RAINE, A.J., WILLIAMS, L.J. and LEGG, R.F. (1979). Apparent maintenance of cytochrome P-450 by nicotinamide in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Life Sciences 24:2185–2192.
REID, L.M., NARITA, M., FUJITA, M., MURRAY, Z., LIVERPOOL C. and ROSENBERG, L. (1986). Matrix and hormonal regulation in liver cultures. In: Research in isolated and Culture Hepatocytes (A. Guillouzo and C. Guguen-Guillouzo, eds.), pp. 225–258. John Libbey Eurotext Ltd./INSERM, London.
SAWADA, N., TOMOMURA, A., SATTLER, C.A., SATTLER, G.L., KLEINMAN, H.K. and PITOT, H.C. (1987). Effects of extracellular matrix components on the growth and differentiation of cultured rat hepatocytes. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 23:267–273.
SCHUETZ, E.G., LI, D., OMIECINSKI, C.J., MULLER-EBERHARD, U., KLEINMAN, H.K., ELSWICK, B. and GUZELIAN, P.S. (1988). Regulation of gene expression in adult rat hepatocytes cultured on a basement membrane matrix. J. Cell. Physiol. 134:309–323.
SUOLINNA, E.M. (1982). Isolation and culture of liver cells and their use in the biochemical research of xenobiotics. Med. Biol. 60:237–254.
TURNER, N.A., WILSON, N.M., JEFCOATE, C.R. and PITOT, H.C. (1988). The expression and metabolic activity of cytochrome P-450 isozymes in control and phenobarbital-induced primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 263:204–215.
VANDENBERGHE, Y., RATANASAVANH, D., GLAISE, D. and GUILLOUZO, A. (1988). Influence of medium composition and culture conditions on glutathione S-transferase activity in adult rat hepatocytes during culture. In Vitro Cell. Develop. Biol. 24:281–288.
WARREN, M., FRY, J.R. and BALLS, M. (1985). The effect ofgglucose, insulin and dexamethasone upon 7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase activity of adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Xenobiotica 15:775–779.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donato, M.T., Castell, J.V. & Gómez-Lechón, M.J. Co-cultures of hepatocytes with epithelial-like cell lines: Expression of drug-biotransformation activities by hepatocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol 7, 1–14 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121326
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121326