Abstract
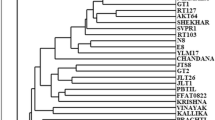
Forty-four taro (Colocasia esculenta), two tanier (Xanthosoma species) and one Colocasia gigantea accessions were evaluated for genetic diversity using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) primers. Seventy-three of 112 primers amplified PCR DNA products used to fingerprint the accessions. Thirty-two primers were considered highly informative because they amplified more than 5 bands or amplified one or more polymorphic bands that distinguished between accessions. RAPDs showed high genetic diversity in taro accessions from Indonesia, were capable in distinguishing between Hawaiian accessions, and could separate triploid from diploid accessions. UPGMA cluster analysis of genetic similarity estimates (Jaccard's coefficient), separated the accessions into 3 main groups with C. esculenta divided into 5 subgroups. These primers will be useful for future genetic analysis and provide taro breeders with a genetic basis for selection of parents for crop improvement. Polymorphic markers identified in the DNA fingerprinting study will be useful to screen a segregating population which is being generated in our laboratory aimed at developing a taro genetic linkage map.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernatzky, Z.R. & S.D. Tanksley, 1986. Genetics of actin related sequences in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 72: 314–321.
Chang, T.K., 1958. Dispersal of taro in Asia. Ann Assoc Am Geo 48: 255–256.
Coates, D.J., D.E. Yen & P.M. Gaffey, 1988. Chromosome variation in taro, Colocasia esculenta: implications for the origin in the Pacific. Cytologia 53: 551–560.
Dudley, J.W., 1994. Comparison of genetic distance estimators using molecular marker data. Proc ASHS/CSSA Symp on Analysis of Molec Marker Data: 3–7.
Guman, Z. & Z. Dongxiao, 1990. The relationship between geographic distribution and ploidy level of taro, Colocasia esculenta. Euphytica 47: 25–27.
Handy, E.S.C. & E.G. Handy, 1972. Native planters in Hawaii: their life, lore, and environment. Bernice P. Bishop Museum Bull 233, Bishop Museum Press, Honolulu.
Keil, M. & A.R. Griffin, 1994. Use of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers in the discrimination and verification of genotypes in Eucalyptus. Theor Appl Genet 89: 442–450.
Krauss, B.H., 1993. Plant in Hawaiian culture. Univ Hawaii Press, Honolulu.
Kuruvilla, K.M. & A. Singh, 1981. Karyotypic and electrophoretic studies on taro and its origin. Euphytica 30: 405–413.
Lashermes, P., P. Trouslot, F. Anthony, M.C. Combes & A. Charrier, 1996. Genetic diversity for RAPD markers between cultivated and wild accession of Coffea arabica. Euphytica 87: 59–64.
Lavi, U., P. Cregan, T. Schaap & J. Hillel, 1994. Application of DNA markers for identification and breeding of perennial fruit crops. Plant Breed Rev 12: 195–226.
Lebot, V. & K.M. Aradhya, 1991. Isozyme variation in taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott) from Asia and Oceania. Euphytica 56: 55–66.
Maga, J.A., 1992. Taro - composition and food uses. Food Rev Int 8: 443–473.
Martin, G.B., J.G.K. Williams & S.D. Tanksley, 1991. Rapid identification of markers linked to a Pseudomonas resistance gene in tomato by using random primers and near-isogenic accessions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 2336–2340.
Matthews, P., Y. Matsushita, T. Sato & M. Hirai, 1992. Ribosomal and mitochondrial variation in Japanese taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott). Jpn J Breed 42: 825–833.
Michelmore, R.W., I. Paran & R.V. Kesseli, 1991. Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 9828–9832.
Murray, M.G. & W.F. Thompson, 1980. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acid Res 8: 4321–4325.
Perron, M., A.G. Gordon & J. Bousquet, 1995. Species-specific RADP fingerprints for the closely related Picea mariana and P. rubens. Theor Appl Genet 91: 142–149.
Pillay, M. & S.T. Kenny, 1996. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers in hop, Humulus lupulus: level of genetic variability and segregation in F1 progeny. Theor Appl Genet 92: 334–339.
Plucknett, D.L., 1976. Edible aroids. In: N. Simmonds (Ed.), Evolution of Crop Plants, pp. 10–12. Longman Group, Ltd. London.
Plucknett, D.L., 1983. Taxonomy of the genus Colocasia. In: J.K. Wang (Ed.), A Review of Colocasia esculenta and its Potentials, pp. 14–19. Univ Hawaii Press, Honolulu.
Plucknett, D.L., R.S. de la Peña & F. Obero, 1970. Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott): a review. Field Crop Abstr 23: 419–426.
Reiter, R.S., J.G.K. Williams, K.A. Feldman, J.A. Rafalski, S.A. Tingey & P.A. Scolnik, 1992. Global and local genome mapping in Arabidopsis thaliana by using recombinant inbred accessions and random amplified polymorphic DNAs. Proc Natl Sci USA 89: 1477–1481
Strauss, M.S., G.C. Stephens, C.J. Gonzales & J. Arditti, 1980. Genetic variability in taro, Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott (Araceae). Ann Bot 45: 429–437.
Stuber, C.W., 1992. Biochemical and molecular markers in plant breeding. Plant Breed Rev 9: 37–61.
Tanimoto, T. & T. Matsumoto, 1986. Variations of morphological characters and isozyme patterns in Japanese accessions of Colocasia esculenta Schott and C. gigantea Hook. Jpn J Breed 36: 100–111.
Whitney, L.D., F.A.I. Bowers & M. Takahashi, 1939. Taro varieties in Hawaii. Bull No. 84 Hawaii Agric Exp Stn, Univ Hawaii, Honolulu.
Williams, J.G.K., A.R. Kubelik, K.J. Livak, J.A. Fafalski & S.V. Tingey (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl Acid Res 18: 6531–6535.
Yen, D.E. & J.M. Wheeler, 1968. Introduction of taro into the Pacific: the indications of the chromosome numbers. Ethnology 7: 259–267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Irwin, S., Kaufusi, P., Banks, K. et al. Molecular characterization of taro (Colocasia esculenta) using RAPD markers. Euphytica 99, 183–189 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018309417762
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018309417762