Abstract
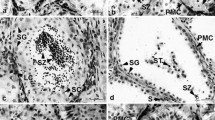
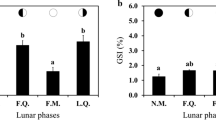
Immature and maturing male New Zealand freshwater eels, the shortfinned Anguilla australis and the longfinned A. dieffenbachii, were caught from the wild to obtain data on the natural reproductive physiology of these fish. Plasma samples were analysed for steroid hormones by radioimmunoassay and values related to the developmental stage of the testes. Our histological observations on testes largely confirmed those reported previously. Thus, the gonad of non-migrating eels often appeared undifferentiated or poorly developed, containing only type A or early type B spermatogonia. In contrast, the testes of migrating shortfins were in early spermatogenesis as evidenced by the presence of late type B spermatogonia. Similarly, early spermatogenic stages were common in migratory longfins, but eels in midspermatogenesis (all germ cell stages present) were also encountered. Unlike a previous study, patches of testicular regression were commonly seen in migrants of both species. Levels of several androgens, androstenedione (AD), testosterone and 11-ketotestosterone (KT), were elevated in migrants compared to non-migrants. AD was higher in early to midspermatogenic A. dieffenbachii (0.63 ng ml−1) than in A. australis (0.25 ng ml−1) in the spermatogonial proliferation stage, while the inverse was observed for KT (27.78 ng ml−1 and 50.52 ng ml−1, respectively). Levels of 17,20β-dihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one were nearly undetectable (less than 0.12 ng ml−1) in all animals. Plasma 17-hydroxyprogesterone concentrations in fyke-caught eels were elevated to a greater extent in non-migrants (up to 1.92 ng ml−1) than in migrants (around 0.5 ng ml−1), and correlated well with levels of cortisol in all groups. Histological results are compared to previous studies and the presence of regression in the testes is discussed. In addition, the role of steroid hormones, in particular AD and KT, in reproduction and stress is considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Billard, R. and Ginsburg, A. 1973. La spermiogenèse et le spermatozoïde d'Anguilla anguilla L. Étude ultrastructurale. Ann. Biol. anim. Biochim. Biophys. 13: 523–534.
Bondy, P.K. 1985. Disorders of the adrenal cortex. In Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, Seventh Edition pp. 816–890. Edited by J.D. Wilson and D.W. Foster. W.B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia.
Callard, G.V., Petro, Z. and Ryan, K.J. 1978. Conversion of androgen to estrogen and other steroids in the vertebrate brain. Am. Zool. 18: 511–523.
Colombo, G., Grandi, G. and Rossi, R. 1984. Gonad differentiation and body growth in Anguilla anguilla L. J. Fish Biol. 24: 215–228.
Dollerup, J. and Graver, Chr. M. 1985. Repeated induction of testicular maturation and spermiation, alternating with periods of feeding and growth in silver eels, Anguilla anguilla (L.). Dana 4: 19–39.
Dufour, S., Lopez, E., Le Menn, F., Le Belle, N., Baloche, S. and Fontaine, Y.-A. 1988. Stimulation of gonadotropin release and of ovarian development, by the administration of a gonadoliberin agonist and of dopamine antagonists, in female silver eel pretreated with estradiol. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 70: 20–30.
Fitzpatrick, M.S., Pereira, C.B. and Schreck, C.B. 1993. In vitro steroid secretion during early development of mono-sex rainbow trout: sex differences, onset of puberty control, and effects of dietary steroid treatment. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 91: 199–215.
Fontaine, M. 1936. Sur la maturation complète des organes génitaux de l'anguille mâle et l'émission spontanée de ses produits sexuels. C.R. Acad. Sci. 202: 1312–1314.
Foucher, J.-L. and Le Gac, F. 1989. Evidence for an androgen binding protein in the testis of a teleost fish (Salmo gairdneri R.): a potential marker of Sertoli cell function. J. Steroid Biochem. 32: 545–552.
Ikuta, K., Kitamura, S., Amano, M., Munakata, A. and Aida, K. 1996. The effects of sex steroids on migratory behavior of salmonid fish. In Proc. 3rd Congr. Asia and Oceania Society for Comparative Endocrinology. pp. 197–198. Edited by J.M.P. Joss. Macquarie University, Sydney.
Jellyman, D.J. and Todd, P.R. 1982. New Zealand freshwater eels. Their biology and Fishery. Fisheries Research Division Information leaflet No. 11, Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries, Wellington, New Zealand.
Jellyman, D.J. 1992a. Lake Ellesmere — an important fishery with an uncertain future. Freshwater Catch 48: 3–5.
Jellyman, D.J. 1992b. A review of the eel fishery within New Zealand. Freshwater Catch 49: 14–15.
Jellyman, D.J. 1994. The fishery for freshwater eels (Anguilla spp.) in New Zealand. New Zealand Fisheries Assessment Research Document 94/14. MAF Fisheries, N.Z. Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries, Wellington, New Zealand. 16 p.
Kagawa, H., Young, G. and Nagahama, Y. 1982. Estradiol-17β production in isolated amago salmon (Oncorhynchus rhodurus) ovarian follicles and its stimulation by gonadotropins. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 47: 361–365.
Khan, I.A., Lopez, E. and Leloup-Hâtey, J. 1987. Induction of spermatogenesis and spermiation by a single injection of human chorionic gonadotropin in intact and hypophysectomized immature European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 68: 91–103.
Leatherland, J.F., Copeland, P., Sumpter, J.P. and Sonstegard, R.A. 1982. Hormonal control of gonadal maturation and development of secondary sexual characteristics in coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch, from Lakes Ontario, Erie and Michigan. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 48: 196–204.
Leloup-Hâtey, J., Hardy, A. and Quérat, B. 1989. Responses of gonadosomatic indice and plasma levels of sex steroids to gonadotrophic stimulation in freshwater European eel at yellow and silver stages. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 74: 251 (abstract).
Lokman, P.M., Vermeulen, G.J., Lambert, J.G.D. and Young, G. 1998. Gonad histology and plasma steroid profiles in wild New Zealand freshwater eels (Anguilla dieffenbachii and A. australis) before and at the onset of the natural spawning migration. I. Females. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 19: 325–338.
Miura, T., Yamauchi, K., Nagahama, Y. and Takahashi, H. 1991a. Induction of spermatogenesis in male Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica, by a single injection of human chorionic gonadotropin. Zool. Sci. 8: 63–73.
Miura, T., Yamauchi, K., Takahashi, H. and Nagahama, Y. 1991b. Hormonal induction of all stages of spermatogenesis in vitro in the male Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 5774–5778.
Miura, T., Yamauchi, K., Takahashi, H. and Nagahama, Y. 1991c. Involvement of steroid hormones in gonadotropin-induced testicular maturation in male Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica). Biomed. Res. 4: 241–248.
Miura, T., Yamauchi, K., Takahashi, H. and Nagahama, Y. 1992. The role of hormones in the acquisition of sperm motility in salmonid fish. J. exp. Zool. 261: 359–363.
Nazian, S.J. and Mahesh, V.B. 1980. Delay in some aspects of the sexual maturation of the male rat induced by androstenedione. Biol. Reprod. 22: 451–458.
Prokhorchik, G.A., Petukhov, V.B. and Petrikov, A.M. 1987. Embryonic development of European eel, Anguilla anguilla, under experimental conditions. J. Ichthyol. 27: 37–43.
Prokhorchik, G.A., Petukhov, V.B., Emel'yanova, N.G. and Makeeva, A.P. 1989. Ultrastructure of ovulated oocytes of European eel, Anguilla anguilla. J. Ichthyol. 29: 14–20.
Schreck, C.B., Bradford, C.S., Fitzpatrick, M.S. and Patiño, R. 1989. Regulation of the interrenal of fish: non-classical control mechanisms. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 7: 259–265.
Slater, C.H., Schreck, C.B. and Swanson, P. 1994. Plasma profiles of the sex steroids and gonadotropins in maturing female spring chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 109A: 167–175.
Thorarensen, H., Young, G. and Davie, P.S. 1996. 11-Ketotestosterone stimulates growth of heart and red muscle in rainbow trout. Can. J. Zool. 74: 912–917
Todd, P. R. 1974. Studies on the reproductive biology of New Zealand freshwater eels. Ph.D. Thesis, Victoria University of Wellington, New Zealand.
Todd, P. R. 1976. Ultrastructure of the spermatozoa and spermiogenesis in New Zealand freshwater eels (Anguillidae). Cell Tiss. Res. 171: 221–232.
Todd, P.R. 1980. Timing and periodicity of migrating New Zealand freshwater eels (Anguilla spp.). New Zeal. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 15, 225–235.
Todd, P.R. 1981a. Morphometric changes, gonad histology, and fecundity estimates in migrating New Zealand freshwater eels (Anguilla spp.). New Zeal. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 15: 155–170.
Todd, P.R. 1981b. Hormone-induced maturation in male New Zealand freshwater eels (Anguilla spp.). New Zeal. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 15: 237–246.
Vermeulen, A. and Rubens, R. 1992. Adrenal virilism. In The Adrenal Gland. pp. 413–414. Edited by V.H.T. James. Raven Press, New York.
Yamamoto, K., Hiroi, O., Hirano, T. and Morioka, T. 1972. Artificial maturation of cultivated male Japanese eels by Synahorin injection. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 38: 1083–1090.
Yamauchi, K. 1990. Studies of gonadal steroids involved in final gonadial maturation in the Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica, a review. Int. Rev. Ges. Hydrobiol. 75: 859–860.
Yamauchi, K. 1993. Endocrinological aspects of gonadal development in the Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. In Fish Biology: From Genes to Organism. pp. 67–80. Edited by V.P.E. Phang, Y.M. Sing, T.M. Lim, C.H. Tan, A. Shima and T.J. Lam. National University of Singapore, Singapore.
Yamauchi, K. and Yamamoto, K. 1974. In vitro maturation of Japanese eel eggs and early development of the egg. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 40: 153–157.
Young, G., Crim, L.W., Kagawa, H., Kambegawa, A. and Nagahama, Y. 1983. Plasma 17α,20β-dihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one levels during sexual maturation of amago salmon (Oncorhynchus rhodurus): correlation with plasma gonadotropin and in vitro production by ovarian follicles. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 51: 96–105.
Young, G. 1986. Cortisol secretion in vitro by the interrenal of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) during smoltification: Relationship with plasma thyroxine and plasma cortisol. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 63: 191–200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lokman, P., Young, G. Gonad histology and plasma steroid profiles in wild New Zealand freshwater eels (Anguilla dieffenbachii and A. australis) before and at the onset of the natural spawning migration. II. Males. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 19, 339–347 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007767330225
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007767330225