Abstract
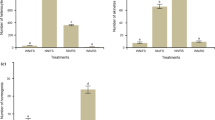
Seven species ofAzolla (A. caroliniana, A. microphylla, A. nilotica, A. filiculoides, A. mexicana, A. rubra, A. pinnata the last from both Malaysia and India) grown in pots of flooded soil were subjected to three different treatments with respect to P: none, single application, split application. The experiments were carried out under greenhouse conditions. Heterocyst frequency inAnabaena azollae and acetylene reducing activity (ARA) were studied in successiveAzolla leaves. Both variables increased from the first leaf (shoot apex) to the last one (before branch) in all species in the presence or absence of P. However, heterocyst frequency, ARA andAzolla biomass were all less in the treatment lacking P. Heterocyst frequency inA. azollae, ARA and biomass ofAzolla were higher when P was applied in split doses than in the other treatments.Azolla plants exhibited more ARA than the isolated leaves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haselkorn, R., 1978. Heterocyst. Ann. Rev. Pl. Physiol. 22: 319–344.
Hill, D. J., 1975. The pattern of development ofAnabaena in theAzolla-Anabaena symbiosis. Planta 122: 178–184.
Hill, D. J., 1977. The role ofAnabaena in theAzolla-Anabaena symbiosis. New Phytol. 78: 611–616.
Kaplan, D. & G. A.Peters, 1981. TheAzolla-Anabaena relationship. X.15N2 fixation and transport in main stem axes. New Phytol. 89: 337–346.
Moore, A. W., 1969.Azolla: biology and agronomic significance. Bot. Rev. 35: 17–35.
Patra, R. N. & P. K. Singh, 1984. Symbiotic algal heterocyst frequency in three species ofAzolla. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. B50: 128–131.
Peters, G. A. & H. E. Calvert, 1983. TheAzolla-Anabaena symbiosis. In Goff, L. (ed.) Algal Symbiosis: A continuum of Interaction Strategies. Cambridge Univ. Press, N.Y.: 109–145.
Peters, G. A., H. E. Calvert, D. Kaplan, O. Ito & R. E. Toia Jr., 1982. TheAzolla-Anabaena symbiosis: morphology, physiology and use. Israel J. Bot. 31: 305–323.
Rains, D. W. & S. N. Talley, 1979. Use ofAzolla in North America. In Nitrogen and Rice, International Rice Res. Inst., Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines: 419–433.
Scholhorn, R. & R. H. Burris, 1967. Acetylene as competitive inhibitor of N2-fixation. Proc. Natn. Acad. Sci. USA, 58: 213–216.
Singh, P. K., 1979a. Use ofAzolla in rice production in India. In Nitrogen and Rice. International Rice Res. Inst., Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines: 407–418.
Singh, P.K., 1979b. Symbiotic algal N2-fixation and crop productivity. In Mallik, C.P. (ed.) Annual Rev. Plant Sciences, Kalayani Publishers, New Delhi, India: 37–65.
Singh, P. K., R. N. Patra & S. K. Nayak, 1984. Sporocarp germination, cytology and mineral nutrition ofAzolla. In Silver, W. S. & Schroder, E. C. (eds.) Practical Application ofAzolla for Rice Production. Martinus Nijoff/W. Junk Publishers, The Netherlands: 55–77.
Singh, P. K. & A. L.Singh, 1985. Comparative studies onAzolla and blue-green algal biofertilization to rice crop. In A. C. Shukla & S. N. Pandey (eds.) Advances in Applied Phycological. International Society for Plant and Environment, Kanpur, India: 334–349.
Subudhi, B. P. R. & P. K. Singh, 1978. Hetorocyst spacing in the symbiotic blue-green algaAnabaena azollae. Curr. Sci. 470: 510–511.
Subudhi, B. P. R. & P. K.Singh, 1978. Effect of phosphorus, nitrogen on growth, chlorophyll, amino nitrogen soluble sugar contents and algal heterocysts of water fernAzolla pinnata. Biol. Plant. 21: 401–406.
Tung, H. F. & I. Watanabe, 1983. Differential response ofAzolla-Anabaena association to high temperature and minus phosphorus treatments. New Phytol. 93: 423–431.
Watanabe, I., 1982.Azolla-Anabaena symbiosis its physiology and use in tropical agriculture. In Dommergues, Y. R. & Diem, H. G. (eds.) Microbiology of Tropical Soils and Plant Productivity, W. Junk Publishers, London: 169–185.
Watanabe, I., M. S. Berja & D. C. Rosariodel, 1980. Growth ofAzolla in paddy fields as affected by phosphorus fertilizers. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 26: 301–307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R.P., Singh, P.K. Symbiotic algal nitrogenase activity and heterocyst frequency in sevenAzolla species after phosphorus fertilization. Hydrobiologia 169, 313–318 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007554
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007554