Abstract
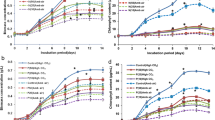
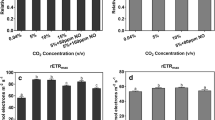
The consequences of the addition of CO2 (1%) in cultures of S. platensis are examined in terms of biomass yield, cell composition and external medium composition. CO2 enrichment was tested under nitrogen saturating and nitrogen limiting conditions. Increasing CO2 levels did not cause any change in maximum growth rate while it decreased maximum biomass yield. Protein and pigments were decreased and carbohydrate increased by high CO2, but the capability to store carbohydrates was saturated. C:N ratio remained unchanged while organic carbon released to the external medium was enhanced, suggesting that organic carbon release in S. platensis is an efficient mechanism for the maintenance of the metabolic integrity, balancing the cell C:N ratio in response to environmental CO2 changes. CO2 affected the pigment content: Phycocyanin, chlorophyll and carotenoids were reduced in around 50%, but the photosynthetic parameters were slightly changed. We propose that in S. platensis CO2 could act promoting degradation of pigments synthetised in excess in normal CO2 conditions, that are not necessary for light harvesting. Nitrogen assimilation was significantly not affected by CO2, and it is proposed that the inability to stimulate N assimilation by CO2 enrichment determined the lack of response in maximum growth rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MM, Smith J (1969) Nitrogen chlorosis in blue-green algae. Arch. Mikrobiol. 69: 114-120.
Beer S, Eshel A (1985) Determining phycoerythrin and phycocyanin concentrations in aquaeous crude extracts of red algae. Aust. J. mar. freshwat. Res. 36: 785-792.
Bowes G (1993) Facing the inevitable: Plants and increasing atmospheric CO2. Annual Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 44: 309-332.
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of micrograms quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248-254.
BÜchel C, Wilhelm C (1993) In vivo analysis of slow chlorophyll fluorescence induction kinetics in algae: Progress, problems and perspectives. Photochem. Photobiol. 58: 137-148.
Chen W, Wangersky PJ (1996) Production of dissolved organic carbon in phytoplankton cultures as measured by high-temperature catalytic oxidation and ultraviolet photo-oxidation methods. J. Plankton Res. 18: 1201-1211.
Cornet JF (1992) Etude cinétique et energétique d'un photobioréacteur. PhD Thesis. University of Paris-Sud.
Edwards G, Walker DA (1983) C3, C4. Cellular and Environment Regulation of Photosynthesis. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford: 734 pp.
Falkowski PG (1994) The role of phytoplankton photosynthesis in global biogeochemical cycles. Photosynth. Res. 34: 235-258.
Fogg GE (1983) The ecological significance of extracellular products of phytoplankton. Bot. mar. 26: 3-14.
Fogg GE, Nalewajko G, Watt WD (1965) Extracellular products of phytoplankton photosynthesis. Proc. Royal Soc. Lond. B 162: 517-534.
Fonseca F, Browsher CG, Stulen I (1997) Impact of elevated atmospheric CO2 on nitrate reductase transcription and activity in leaves and roots of Plantago major. Physiol. Plantarium 100: 940-948.
Fox RD (1996) SpirulinaProduction and Potential. Edisud, Aix-en-Provence.
Fujiwara S, Fukuzawa H, Tachiki A, Miyashi S (1990) Structure and differential expression of two genes encoding carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardii: Regulation by environmental CO2 concentration. Proc. natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 9779-9783.
García-Sanchez MJ, Fernández JA, Niell FX (1994) Effect of inorganic carbon supply on the photosynthetic physiology of Gracilaria tenuistipitata. Planta 194: 55-61.
Giordano M, Davis S, Bowes G (1994) Organic carbon release by Dunaliella salina(Chlorophyta) under different growth conditions of CO2, nitrogen and salinity. J. Phycol. 30: 249-257.
Jaworski GHM, Talling JF, Heaney SI (1981) The influence of carbon dioxide depletion on growth and sinking rate of two planktonic diatoms in culture. Br. phycol. J. 16: 395-410.
Kochert G (1978) Carbohydrate determination by phenol sulphuric acid method. In: Hellebust JA, Craigie JS (eds), Handbook of Physiological Methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 95-97.
Koprivnjak JF, Blanchette JG, Bourbonniere RA, Clair TA, Heyes A, Lum KR, McCrea R, Moore TR (1995) The underestimation of concentrations of dissolved organic carbon in freshwaters. Wat. Res. 29: 91-94.
Krapp A, Stitt M (1994) Influence of high carbohydrate content on the activity of plastidic and cytosolic isoenzyme pairs in photosynthetic tissues. Plant Cell Env. 17: 861-866.
Larsson M, Larsson CM, Guerrero MG (1985) Photosynthetic nitrogen metabolism in high and low CO2-adapted Scenedesmus. J. exp. Bot. 36: 1373-1395.
Loehle C (1995) Anomalous response of plants to CO2 enrichment. Oikos 73: 181-187.
Markager S, Sand-Jensen K (1994) The physiology and ecology of light-growth relationship in macroalgae. In: Found FE, Chapman DJ (eds), Progress in Phycological Research. Biopress Ltd, Bristol: 209-298.
Mercado JM, Niell FX, Figueroa FL (1997) Regulation of the mechanism for HCO -3 use by the inorganic carbon level in Porphyra leucostictaThus. in Le Jolis (Rhodophyta). Planta 201: 319-325.
Ormerod JG (1983) The carbon cycle in aquatic ecosystems. In: Slater JH, Whittenbury R, Wimpenny JWT (eds), Microbes in their Natural Environments. Soc. Gen. Microb. Symp. 34. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 463-482.
Qiang H, Guterman H, Richmond A (1996) Physiological characteristics of Spirulina plantensis(cyanobacteria) cultured at ultrahigh cell densities. J. Phycol. 32: 1066-1073.
Ramanathan V (1988) The greenhouse theory of climate change: a test by an inadvertent global experiment. Science 240: 293-299.
Raven JA (1984) Energetics and Transport in Aquatic Plants. AR Liss, Inc., New York.
Raven JA (1991) Physiology of inorganic C acquisition and implications for resource use efficiency by marine phytoplankton: relation to increased CO2 and temperature. Plant Cell Env. 14: 774-794.
Snell FD, Snell CT (1949) Colorimetric Methods of Analysis. Van Nostrand, Princeton, New Jersey.
Torzillo G, Vonshak A (1994) Effect of light and temperature on the photosynthetic activity of the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. Biom. Bioen. 6: 399-403.
Turpin DH (1991) Effects of inorganic N availability on algal photosynthesis and carbon metabolism. J. Phycol. 27: 14-20.
Vanlerberge G, Schuller KA, Smith RG, Feil R, Plaxton WC, Turpin DH (1990) Relationship between NH +4 assimilation and in vivophosphoenol pyruvate carboxylase activity: regulation of anaplerotic carbon flow in the green alga Selenastrum minutum. Plant Physiol. 94: 284-290.
Vergara JJ, Niell FX (1993) Effects of nitrate availability and irradiance on internal nitrogen constituents in Corallina elongata(Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 29: 285-293.
Vonshak A (1992) Microalgal biotechnology: is it an economic success? In: DaSilva EJ, Ratledge C, Sasson A (eds), Biotechnology. Economic and Social Aspects, Issues for Developing Countries. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Vonshak A, Chanawongse L, Bunnag B, Tanticharoen M (1996a) Light acclimation and photoinhibition in three Spirulina plantensis(cyanobacteria) isolates. J. appl. Phycol. 8: 35-40.
Vonshak A, Kancharaksa N, Bunnag B, Tanticharoen M (1996b) Role of light and photosynthesis on the acclimation process of the cyanobacterium spirulina platensisto salinity stress. J. appl. Phycol. 8: 119-124.
Vonshak A (1997) Spirulina platensis(Arthrospira): Cell-Biology and Biotechnology. Taylor & Francis, London.
Webber AN, Nie GY and Long SP (1994) Acclimation of photosynthetic protein to rising atmospheric CO2. Photos. Res. 39: 413-425.
Wellburn AT (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J. Pl. Physiol. 144: 307-313.
Winder TL, Anderson JC and Spaldin MH (1992) Translational regulation of the large and small subunits of ribulose biphophate carboxylase/ oxygenase during induction of the CO2-concentrating mechanism in Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Plant. Physiol. 98: 1409-1414.
Wood AM, Rai H, Garnier J, Kairesalo T, Gresens S, Orive E, Ravail B (1992) Practical approaches to algal excretion. Mar. Microb. Food Webs 6: 21-38.
Wood ED, Armstrong FAJ and Richards FA (1967) Determination of nitrate in sea water by cadmium-copper reduction to nitrite. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 47: 23-31.
Wyman M, Gregory RPF and Carr NG (1985) Novel role of phycoerythrin in the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcusstrain DC 2. Science 165: 908-909.
Yunes J (1995) Effects of light and CO2 on nitrite liberation by the heterocystous cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis. J. Plant. Physiol. 147: 313-320.
Zarrouk C (1966) Contribution à l'étude d'une cyanophycée. Influence de divers facteurs physiques et chimiques sur la croissance et la photosynthèse de Spirulina maxima(Setch. et Gardner) Geitler. PhD Thesis, University of Paris, France, 74 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gordillo, F.J., Jiménez, C., Figueroa, F.L. et al. Effects of increased atmospheric CO2 and N supply on photosynthesis, growth and cell composition of the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis (Arthrospira). Journal of Applied Phycology 10, 461–469 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008090402847
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008090402847