Abstract
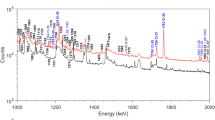
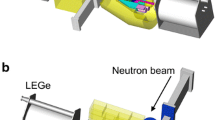
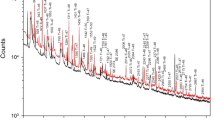
Prompt gamma-activation analysis (PGAA) is an important complementary technique to conventional instrumental activation analysis that can be successfully used in a number of cases when INAA is not applicable. Therefore, a PGAA facility has been constructed at the recently refurbished and upgraded Budapest Research Reactor. It occupies the end position of a new curved themal guide of 30 m length and 2.5×10 cm2 cross section which provides a clean beam of low energy neutrons. The sophisticated HPGe-BGO γ-ray spectrometer system can be operated in Compton-suppression and pair-spectrometer modes simultaneously. The octal splitting of the main BGO improves efficient pair mode operation when coincidences between pairs of opposite segments and the HPGe detector are required separately. Gamma-gamma coincidence measurements will also be possible when the new multiparameter data acquisition system is completed. One of the main tasks at the new facility will be the accumulation of new spectroscopic data for detector calibration and standardisation, as well as for the construction of a more accurate prompt γ-ray library for the chemical elements. Various applications are planned, such as the determination of hydrogen in fullerenes and of toxic trace elements in environmental samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prompt Gamma Neutron Activation Analysis,Z. B. Alfassi, C. Chung (Eds), CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1995.
R. Zeisler, 8th Int. Conf. on Modern Trends in Activation Analysis, Vienna, 1991, unpublished paper.
M. Lindstrom, C. Yonezawa, in:Ref. 1, p. 93.
M. Rossbach, Anal. Chem., 63 (1991) 2156.
M. Lindstrom, R. Zeisler, D. H. Vincent, R. R. Greenberg, C. A. Stone, D. L. Anderson, D. D. Clark, E. A. Mackey, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 167 (1993) 121.
C. Yonezawa, Analyt. Sci., 9 (1993) 185.
K. Kawabata, M. Suzuki, A. Tsuruno, N. Onishi, Physica, B180 (1992) 987.
K. Henkelmann, H.-J. Born, J. Radioanal. Chem., 16 (1973) 473.
C. Yonezawa, A. K. Haji Wood, M. Hoshi, Y. Ito, E. Tachikawa, Nucl. Instrum. Meth., A329 (1993) 207.
A. Lone, R. A. Leavitt, D. A. Harrison, Atomic Data Nucl. Data Tables, 26 (1981) 511.
K. Tuli, in:Ref. 1, p. 177.
G. Molnár, R. M. Lindstrom, in: Proc. Specialists' Meeting on Measurement, Calculation and Evaluation of Photon Production Data —ENEA Bologna, NEA/NSC/DOC(95)1, p. 351.
L. Paul, R. M. Lindstrom, Contribution to this Conference, Log. No. 50.
M. Lindstrom, R. M. Fleming, R. F. Paul, E. A. Mackey, in: Proc. Int.k 0 Users Workshop, Gent, Belgium,F. De Corte (Ed.), U. Gent, 1992, p. 121.
M. Rossbach, F. De Corte, in: Proc. Int.k 0 Users Workshop, Gent, Belgium,F. De Corte (Ed.), U. Gent, 1992, p. 125.
F. De Corte, A. Simonits, A. De Wispelaere, J. Hoste, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 113 (1987) 145.
G. Molnár, Zs. Révay, Á. Veres, A. Simontts, H. Rausch, in: Proc. 8th Int. Conf. on Modem Trends in Activation Analysis, Vienna, 1991, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 167 (1993) 133.
G. Molnár, T. Belgya, I. Diószegi, B. Fazekas, Zs. Révay, Á. Veres, L. Dabolczi, in: Proc. Int. Symp. Capture Gamma-Ray Spectroscopy and Related Topics,J. Kern (Ed.), World Scientific, Singapore, 1994, p. 938.
G. Molnár, T. Belgya, I. Diószegi, B. Fazekas, Zs. Révay, Á. Veres, L. Dabolczi, in Proc. Int. Workshop on Neutron Research, Budapest, Hungary, 24–26 March 1994, Acta Phys. Hung., 75 (1994) 349.
X-ray and Gamma-Ray Standards for Detector Calibration, IAEA-TECDOC-619, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1991.
M. J. Spits, J. Kopecky, Nucl. Phys., A264 (1976) 63.
Evaluated Nuclear Structure Data File, National Nuclear Data Center, BNL, Upton, NY, USA and IAEA Nuclear Data Section, Vienna, Austria.
Krusche, K. P. Lieb, H. Daniel, T. von Egidy, G. Barreau, H. G. Borner, R. Brissot, C. Hopmeyr, R. Rascher, Nucl. Phys., A386 (1982) 245.
B. Fazekas, G. Molnár, T. Belgya, L. Dabolczi, A. Simonits, Introducing Hypemet-PC for automatic analysis of complex gamma-ray spectra, Contribution to this Conference, Log. No. 148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molnár, G., Belgya, T., Dabolczi, L. et al. The new prompt gamma-activation analysis facility at Budapest. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 215, 111–115 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02109886
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02109886