Summary
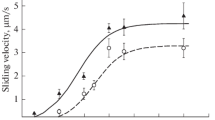
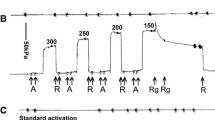
The relationship between calcium concentration ([Ca2+]) and force in smooth muscle can be studied by permeabilizing the sarcolemma and bathing the preparation in a mock intracellular solution. Normally [Ca2+] is set in these solutions using the Ca2+ chelator EGTA in the concentration range of 4–10 mm. This study shows that lowering total EGTA concentration ([EGTA]t) below 10 mm depresses Ca2+-activated force generated in 0.1 μm Ca2+. The observed threshold for the effect of EGTAt is 0.2 mm, and the effect is maximal at approximately 10 mm. BAPTA, another Ca2+ chelator, also produces this effect. Tension production in smooth muscle is controlled by acto-myosin interaction. This in turn is mediated by the relative activities of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and phosphatase (MLCP). Inhibiting MLCP with Microcystin LR (10 μm), an increase [EGTAt] from 0.2 mm to 10 mm still enhanced force. This suggests that EGTA promotes phosphorylation of myosin by the activation of MLCK and not by inhibition of MLCP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ARIGGS, A. H. (1963) Characterisation of contraction in glycerinated uterine smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 204, 739–42.
ARUSCHI, G., ARUSCHI, M. E., REGOLISTI, G. & AORGHETTI, A. (1988) Myoplasmic Ca2+-force relationship studies with fura-2 during stimulation of rat aortic smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 254, H840-H854.
CRICHTON, C. A. & SMITH, G. L. (1990) GTP and noradrenaline-induced force in isolated toxin-permeabilized rat anococcygeus and guinea pig portal vien. J. Physiol. 437, 543–61.
DiSALVO, J., GIFFOR, D., AIALOJAN, C. & RUEGG, J. C. (1983) An aortic spontaneously active phosphatase dephosphorylates myosin and inhibits acto-myosin interaction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 111, 906–11.
ENDO, M. (1977) Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol. Revs. 57, 71–108.
FABIATO, A. & FABIATO, F. (1979) Calculator programs for computing the composition of solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments on skinned muscle cells. J. de Physiologie 75, 463–505.
GARDNER, J. P., STOUT, M. A. & HARRIS, S. R. (1989) Calmodulin loss in vascular smooth muscle following Triton X-100 or saponin skinning. Pflügers Archiv 414, 484–91.
GORDON, A. R. (1978) Contraction of detergent-treated smooth muscle. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 3527–30.
HAI, C. M. & MURPHY, R. A. (1989) Ca2+, crossbridge phosphorylation and contraction. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 51, 285–98.
HAIECH, J., VALLET, B., AQUORON, R. & DEMAILLE, J. G. (1980) Ligand binding to macromolecules: determination of binding parameters by combined use of ligand buffers and flow dialysis; application to calcium-binding proteins. Anal. Biochem. 105, 18–23.
HIMPENS, B. & CASTEELS, R. (1990) Different effect of depolarization and muscarinic stimulation on the Ca2+/force relationship during the contraction-relaxation cycle in the guinea pig ileum. Pflügers Archiv 416, 28–35.
HIMPENS, B., KITAZAWA, T. & SOMLYO, A. P. (1990) Agonist-dependent modulation of Ca2+ sensitivity in rabbit pulmonary artery smooth muscle. Pflügers Archiv 417, 21–8.
HONKANEN, R. E., Zwiller, J., MOORE, R. E., DAILY, S. L., KHATRA, B. S., DUKELOW, M. & AOYNTON, A. L. (1990) Characterisation of Microcystin-LR, a potent inhibitor of type 1 and type 2A protein phosphatases. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 19401–4.
KHALIL, M. A. & VanAREEMAN, C. (1990) Intracellular free calcium concentration/force relationship in rabbit inferior vena cava activated by norepinephrine and high K+, Pflügers Archiv 416, 727–34.
KITAZAWA, T., KOBAYASHI, S., HORIUTI, K., SOMLYO, A. V. & SOMLYO, A. P. (1989) Receptor-coupled, permeabilized smooth muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 5339–42.
KOSSMAN, T., FURST, D. & SMALL, J. V. (1987) Structural and biochemical analysis of skinned smooth muscle preparations. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 8, 135–44.
MACKINTOSH, C., AEATTIE, K. A., KLUMPP, S., COHEN, P. & CODD, G. A. (1990) Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phophatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 264, 187–92.
MOISESCU, D. G. & THIELECZEK, R. (1978) Calcium and strontium concentration changes within skinned muscle preparations following a change in the external bathing solution. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 275, 241–62.
NGAI, P. K. & WALSH, M. P. (1985) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 127, 533–9.
NISHIMURA, J., KOBLER, M. & VanAREEMEN, C. (1988) Norepinephrine and GTP-Y-S increase myofilament calcium sensitivity in α-toxin permeabilized arterial smooth muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 157, 677–83.
RODRRIGUEZ-CABELLO, J. C., AGAPITO, I., GARCCIA-HERRERO & RECIO, J.M. (1989) Effects of EGTA and calmodulin, neutrol thiol proteinases and protein kinase C inhibitors on loss of chicken pineal serotonin N-acetyltransferase activity. J. Comp. Physiol. B. 159, 583–8.
SAIDA, K. & NONOMURA, Y. (1978) Characteristics of calcium and magnesium induced tension development in chemically skinned smooth muscle fibres. J. Gen. Physiol. 72, 1–14.
SILLEN, L. G. & MARTELL, A. E. (1979) Stability Constants, Special Publication No. 17, The Chemical Society (London).
SMITH, G. L. & MILLER, D. J. (1984) Potentiometric measurements of stoichiometric and apparent affinity constants of EGTA for protons and divalent ions including calcium. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 893, 287–99.
SMITH, G. L., CRICHTON, C. A. & STEELE, D. S. (1992) The effect of EGTA on Ca-activated force in α-toxin permeabilized rat anococcygeus muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond). 446, 243.
SOBIESK, A. (1977) Calcium-linked phosphorylation of light chain vertebrate smooth muscle myosin. Europ. J. Biochem. 73, 477–83.
WINDER, S. J. & WALSH, M. P. (1990) Smooth muscle calponin: inhibition of actomyosin MgATPase and regulation by phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 10148–55.
YAGI, S., AECKER, P. L. & FAY, F. S. (1988) Relationship between force and Ca2+ concentration in smooth muscle as revealed by measurements on single cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 4109–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, G.L., Crichton, C.A. Ca-EGTA affects the relationship between [Ca2+] and tension in α-toxin permeabilized rat anococcygeus smooth muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 14, 76–84 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00132182
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00132182