Summary
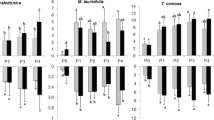
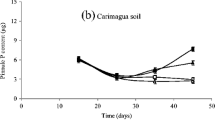
Non-mycorrhizal plants grown 5 weeks in a low-phosphate soil with different amounts of soluble P were transplanted to soil also with different levels of phosphate and inoculated with VA mycorrhiza. The intensity of mycorrhizal infection as affected by the interaction of differents levels of phosphate in soil and in the host was examined after a further 8 weeks. In the soil with no added phosphate mycorrhizal infection was not affected by the initial P content of the plants. When 0.8 or 1.5 g K2PO4 was given per kg soil both the external and the internal P negatively influenced the infection. In some conditions a P content that was supraoptimal for infection was not for plant growth. The critical P concentration in plants depends on the age of the host. An interaction between P and N as a factor contributing to phosphate ‘toxicity’ is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew, C. S. and Robins, M. F., The effect of phosphorus on the growth and chemical composition of some tropical pasture legumes. I. Growth and critical percentages of phosphorus. Aust. J. Agric. Res.20, 665–685 (1969).
Azcón, R., Barea, J. M. and Hayman, D. S., Utilziation of rock phosphate in alkaline soils by plants inoculated with mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Soil Biol. Biochem.8, 135–138 (1976).
Barea, J. M., Azcón, R. and Hayman, D. S., Possible synergistic interactions between Endogone and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in low-phosphate soils.In Endomycorrhizas (Ed. by F. E. Sanders, B. Mosse and P. B. Tinker), 409–417 (1975).
Bhatti, A. S. and Loneragan, J. F., The effect of early superphosphate toxicity on the subsequent growth of wheat. Aust. J. Agric. Res.21, 881–892 (1970).
Daft, J. M. and Nicolson, T. H., Effect of Endogone mycorrhiza on plant growth, III. Influence of inoculum concentration on growth and infection in tomato. New Phytol.68, 953–961 (1969).
Hayman, D. S., Barea, J. M. and Azcón, R., Vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza in southern Spain: its distribution in crops growing in soils of differing fertility. Phytopathol. Mediterr.15, 1–6 (1976).
Hewitt, E. J., Sand and water culture methods used in the study of plant nutrition. Tech. Commun.22. Farnhan Royal, Bucks: Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau. (1952).
Khan, A. G., The effect of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal associations on growth of cereals. I. Effects on maize growth. New Phytol.71, 613–619 (1972).
Loneragan, J. F., Carroll, M. D. and Snowball, K., Phosphorus toxicity in cereal crops. J. Aust. Inst. Agric. Sci.32, 221–223 (1966).
Mosse, B., Advances in the study of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol.11, 171–196 (1973).
Mosse, B., Plant growth responses to vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza. IV. In soil given additional phosphate. New. Phytol.72, 127–136 (1973).
Mosse, B. and Bowen, G. D., A key to the recognition of some Endogone spore types. Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc.51, 469–483 (1968).
Phillips, J. M. and Hayman, D. S., Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infectión. Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc.55, 158–161 (1970).
Sanders, F. E., The effect of foliar-applied phosphate on the mycorrhizal infections of onion roots.In Endomycorrhizas (Ed. by F. E. Sanders, B. Mosse and P. B. Tinker), 261–276 (1975).
Sanders, F. E. and Tinker, P. B., Phosphate flow into mycorrhzial roots. Pestic. Sci.4, 385–395 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azcón, R., Marin, A.D. & Barea, J.M. Comparative role of phosphate in soil or inside the host on the formation and effects of endomycorrhiza. Plant Soil 49, 561–567 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02183281
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02183281