Abstract
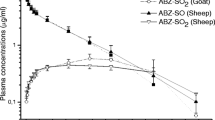
The pharmacokinetics of albendazole was studied in sheep following single oral and intraruminal administration at nematocidal dose rates. The disposition curves of its metabolites indicated increased uptake of the drug in sheep following intraruminal as compared to oral dosing (p<0.05). The increased bioavailability of benzimidazole anthelmintics given by the intraruminal route could be exploited for optimizing the use of anthelmintic for sustained parasite control in small ruminants.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Gyurik, R.J., Chow, A.W., Zaber, B., Brunner, E.L., Miller, J.A., Villani, A.J., Petka, L.A. and Parish, R.C., 1981. Metabolism of albendazole in cattle, sheep, rats and mice. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 9, 503–508
Hennessy, D.R., 1993. Pharmacokinetic disposition of benzimidazole drugs in the ruminant gastrointestinal tract. Parasitology Today, 9, 329–333
Hennessy, D.R., 1994. The disposition of antiparasitic drugs in relation to the development of resistance by parasites of livestock. Acta Tropica, 56, 125–141
Hennessy, D.R., Steel, J.W., Lacey, E., Eagleson, G.K. and Richard, R.K., 1989. The disposition of albendazole in sheep. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 8, 270–275
Hennessy, D.R., Ali, D.N. and Tremain, S.A., 1994. The partition and fate of oxfendazole in soluble and particulate digesta material in the gastrointestinal tract of sheep. International Journal for Parasitology, 24, 327–333
Hennessy, D.R., Lacey, E., Richard, R.K. and Steel, J.W., 1985. Potentiation of the anthelmintic activity of oxfendazole with parbendazole. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 12, 270–275
Prichard, R.K., Hennessy, D.R. and Steel, J.W., 1978. Prolonged administration: a new concept for increasing spectrum and effectiveness of anthelmintics.Veterinary Parasitology, 4, 309–315
Sangster, N.C., Rickard, J.M., Hennessy, D.R., Steel, J.W. and Collins, G.H., 1993. Disposition of oxfendazole in goats and efficacy compared with sheep. Research in Veterinary Science, 51, 258–263
Sanyal, P.K., 1994. Pharmacokinetic study of triclabendazole in sheep and goats using a high performance liquid chromatography method. Indian Journal of Pharmacology, 26, 200–203
Sanyal, P.K., 1997. Disposition kinetics of albendazole in buffalo and cattle. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 20, 240–242
Sanyal, P.K. and Ghodke, Y.S., 1996. The in£uence of species and subclinical parasitism on the kinetic disposition of fenbendazole in domestic small ruminants. Indian Veterinary Journal, 73, 392–395
Theodorides, V.J., Gyurik, R.J., Kingsbury, W.D. and Parish, R.C., 1976. Anthelmintic activity of albendazole against liver £ukes, tapeworms, lung and gastrointestinal round worms. Experientia, 32, 702–703
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swarnkar, C., Sanyal, P., Singh, D. et al. Comparative Disposition Kinetics of Albendazole in Sheep Following Oral and Intraruminal Administration. Vet Res Commun 22, 545–551 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006145820818
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006145820818