Abstract
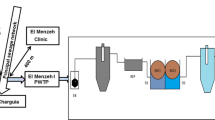
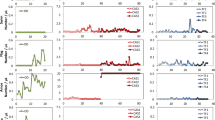
The microfauna of adhered biofilms treating a simulated petrochemical plant wastewater was investigated in relation to the organic loading and the toxicity. Experiments in a six-compartment laboratory rotating biological reactor were performed at organic loadings of 0.99, 1.38 and 1.97g/l.day. The concentration of organic compounds in the artificial wastewater (phenol, acetophenone and styrene), toxicity of the wastewater, number of representative types of microfauna, their biomass and species diversity were monitored along the reactor. During this study 25 species were identified and attributed to seven classes of the three types Sarcomastigophora, Ciliophora and Nemathelminthes. Eight species from 18 ciliates have been reported in the literature as being commonly found inhabitants of aerobic wastewater treatment plants. An inverse relationship between the number of microfauna representatives and the organic loading was found. The presence of the most common species was related to the reactor operating conditions. A correlation between the toxicity of the wastewater measured by the Paramecium express-test and the distribution and abundance of microfauna was established. This express-test made it possible to predict the biological quality of the biofilm of activated sludge. Therefore, it is recommended as one of the control parameters to monitor systems of biological wastewater treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aescht, E. & Foissner, W. 1992 Biology of high-rate activated sludge plant of pharmaceutical company. Archives of Hydrobiology 90, 207-251.
Balushkina, E.B. & Vinberg, G.G. 1978 The relation between the mass and the length of the body of the plankton animals. In Experimental and field investigation of biological basis of the lake productivity. pp. 58-72. Leningrad: Zoology Institute Publisher.
Banina, N.N., Kutikova, L.A. & Cololichin, C.Y. 1984 Systematical part. In Fauna of aerotencs, ed. Kutikova, L.A. pp. 136-249. Leningrad: Nauka.
Curds, C.R. & Cockburn, A. 1970 Protozoa in biological sewagetreatment processes. II. Protozoa as indicators in activatedsludge process. Water Research 4, 237-249.
Esteban, G., Tellez, C. & Bautista, L.M. 1991 Dynamics of ciliated protozoa communities in activated sludge processes. Water Research 8, 967-972.
Kahl, A. 1930-1935 Urtiere oder Protozoa. I. Wimpertiere oder Ciliata (Infusorien). Ein Bearbeitung der freileben und ectocommensalen Infusorien der Erde, unter Ausschluss den marinen Tintinnidae. In Die Tierwelt Deutschlands, ed F. Dahl. pp. 1-886. Parts 18(1930), 21(1931), 25(1932), 30(1935). Jena, Germany: Verlag von Gustav Fisher.
Kinner, N.E., Curds, C.R. & Meeker, L.D. 1988 Protozoa and metazoa as indicators of effluent quality in rotating biological contactors. Water Science and Technology 20, 199-204.
Luna-Pabello, V.M., Aladro-Lubel, A. & Duran-de-Bazua, C. 1992 Temperature effects on ciliates diversity and abundance in a rotation biological reactor. Bioresource Technology 39, 55-60.
Luna-Pabello, V.M., Mayen, R., Olvera-Viascan, V., Saavedra, J., & Duran de Bazua, C. 1990 Ciliated protozoa as indicators of a wastewater Treatment system performance. Biological Wastes 32, 81-90.
Madoni, P. 1986 Protozoa in waste treatment systems. Perspect. Microbiology and Ecology: Proceedings 4th International Symposium, Lubljana, 24-29 August, 1996. Lubljana pp. 86-90.
Madoni, P. 1994 A sludge biotic index (SBI) for the evaluation of the biological performance of activated sludge plants based on microfauna analysis. Water Research 28, 67-75.
Magejkayte, C.I. 1977 Ciliates. In Definition of freshwater invertebrates of the European part of USSR, eds Kutikova, L.A., & Starobogatov, L.I. pp. 46-97. Leningrad: Gydromet.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selivanovskaya, S., Petrov, A., Egorova, K. et al. Protozoan and metazoan communities treating a simulated petrochemical industry wastewater in a rotating disc biological reactor. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 13, 511–517 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018505107030
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018505107030