Abstract
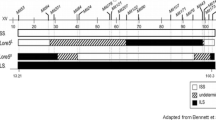
Influenza-infected C57BL/6J mice spend increased amounts of time in slow-wave sleep (SWS) during the dark phase of the circadian cycle compared to healthy mice. In contrast, infected BALB/cByJ mice show a normal or reduced time in SWS, particularly during the light phase. To identify genetic loci with linkage to these traits, we measured sleep in 13 CXB recombinant inbred (RI) strains derived from a cross between C57BL/6ByJ and BALB/cByJ mice. The probability density distribution of sleep patterns of influenza-infected CXB RI mice showed modes that correspond roughly with the parental modes during the dark phase of the circadian cycle and are intermediate or C57BL/6-like during the light phase. These patterns are consistent with the presence of a low number of major effect quantitative trait loci (QTLs). Chromosomal regions with provisional association to strain variation in influenza-induced SWS patterns were identified. In particular, a 10- to 12-cM interval on Chr 6 between D6Mit74 and D6Mit188 contains a QTL (LRS = 16.6 at 1 cM proximal to D6Mit316; genomewide p<.05) that influences the SWS response to influenza infection during the light phase. We have provisionally named this QTL Srilp1 (sleep response to influenza, light phase 1). Candidate genes for mediation of this phenotype include Ghrhr (growth hormone releasing hormone receptor), Crhr2 (corticotropin releasing hormone receptor 2), and Cd8a (an epitope on cytotoxic T lymphocytes). Several other intervals achieved suggestive probability scores that are sufficient to warrant further analysis either with additional RI strains or with F2 panels. The analysis also suggests that dark phase and light phase responses are regulated by different genetic factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Allan, W., Zsuzsanna, T., Cleary, A., and Doherty, P. C. (1990). Cellular events in the lymph node and lung of mice with influenza. J. Immunol. 144:3980–3986.
Ashman, R. B., Fulurija, A., and Papadimitriou, J. M. (1996). Strain-dependent difference in host response to Candida albicans infection in mice are related to organ susceptibility and infectious load. Infect. Immun. 64:1866–1869.
Autenrieth, I. B., Beer, M., Bohn, E., Kaufmann, S. H. E., and Heesemann, J. (1994). Immune responses to Yersinia enterocolitica in susceptible BALB/c and resistant C57BL/6 mice: An essential role for gamma interferon. Infect. Immun. 62:2590–2599.
Belknap, J. K., Crabbe, J. C., Plomin, R., McClearn, G. E., Sampson, K. E., O'Toole, L. A., and Gora-Maslak, G. (1992). Single-locus control of saccharin intake in BXD/Ty recombinant inbred (RI) mice: Some methodological implications for RI strain analysis. Behav. Genet. 22:81–100.
Boyse, E. A., Miyazawa, M., Aoki, T., and Old, L. J. (1968). Ly-A and Ly-B: Two systems of lymphocyte isoantigens in the mouse. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 170:175–193.
Churchill, G. A., and Doerge, R. W. (1994). Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971.
De Maeyer, E., and De Maeyer-Guignard, J. (1969). Gene with quantitative effect on circulating interferon induced by newcastle disease virus. J. Virol. 3:506–512.
Doherty, P. C., Topham, D. J., Tripp, R. A., Cardin, R. D., Brooks, J. W., and Stevenson, P. G. (1997). Effector CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell mechanisms in the control of respiratory virus infections. Immunol. Rev. 159:105–117.
Eleftheriou, B. E. and Bailey, D. W. (1972). Genetic analysis of plasma corticosterone levels in two inbred strains of mice. J. Endocrinol. 55:415–420.
Elliot, R. W., and Moore, K. J. (1998). Mouse chromosome 6. Mammal. Genome 8:S114–S135.
Fung-Leung, W. P., Schilham, M. W., Rahemtulla, A., Kundig, T. M., Vollenweider, M., Potter, J., van Ewijk, W., and Mak, T. W. (1991). CD8 is needed for development of cytotoxic T cells but not helper T cells. Cell 65:443–449.
Haley, C. S., and Knott, S. A. (1992). A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 69:315–324.
Hegmann, J. P., and Possidente, B. (1981). Estimating genetic correlations from inbred strains. Behav. Genet. 11:103–114.
Iizawa, Y., Wagner, R. D., and Czuprynski, C. J. (1993). Analysis of cytokine mRNA expression in Listeria-resistant C57BL/6 and Listeria-susceptible A/J mice during Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect. Immun. 61:3739–3744.
Kadotani, H., Faraco, J., and Mignot, E. (1998). Genetic studies in the sleep disorder narcolepsy. Genome Res. 8:427–434.
Krueger, J. M., and Fang, J. (1999). Cytokines and sleep regulation. In Lydic, R., and Baghdoyan, H. (eds.), Handbook of Behavioral State Control: Molecular and Physiological Mechanisms, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 609–622.
Krueger, J. M., Fang, J., Hansen, M. K., Zhang, J., and Obál, F. (1998). Humoral regulation of sleep. News Physiol. Sci. 13:189–194.
Lander, E. S., and Botstein, D. (1989). Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:241–247.
Lander, E., and Kruglyak, L. (1995). Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nature Genet. 11:241–247.
Langdon, N., Lock, C., Welsh, K., Vergani, D., Dorow, R., Wachtel, H., Palenschat, D., and Parker, J. D. (1986). Immune factors in narcolepsy. Sleep 9:143–148.
Lynch, M., and Walsh, B. (1998). Mapping and characterizing QTLs: Inbred line crosses. In Genetics and Analysis of Quantitative Characters, Sinauer, San Francisco, pp. 91–131.
Marshall, D. J., Mu, J.-L., Cheah, Y.-C., Nesbitt, M. N., Frankel, W. N., and Paigen, B. (1992). The AXB and BXA set of recombinant inbred mouse strains. Mammal. Genome 3:669–680.
Mizuhara, H., Kuno, M., Seki, N., Yu, W.-G., Yamaoka, M., Yamashita, M., Ogawa, T., Kaneda, K., Fujii, T., Senoh, H., and Fujiwara, H. (1998). Strain difference in the induction of T-cell activation-associated interferon gamma-dependent hepatic injury in mice. Hepatology 27:513–519.
Mountjoy, K. G., Robbins, L. S., Mortrud, M. T., and Cone, R. D. (1992). The cloning of a family of genes that encode melanocortin receptors. Science 257:1248–1251.
Opp, M. R. (1995). Corticotropin-releasing hormone involvement in stressor-induced alterations in sleep and in the regulation of waking. Adv. Neuroimmunol. 5:127–143.
Opp, M. R., Obál, F., and Krueger, J. M. (1988). Effects of α-MSH on sleep, behavior, and brain temperature: Interactions with IL-1. Am. J. Physiol. 255:R914–R922.
Raj, N. B. K., Cheung, S. C., Rosztoczy, I., and Pitha, P. M. (1992). Mouse genotype affects inducible expression of cytokine genes. J. Immunol. 148:1934–1940.
Staeheli, P., Horisberger, M. A., and Haller, O. (1984). Mx-dependent resistance to influenza viruses is induced by mouse interferons α and β but not γ. Virology 132:456–461.
Staeheli, P., Pravcheva, D., Lundin, L.-G., Acklin, M., Ruddle, F., Lindenmann, J., and Haller, O. (1986). Interferon-regulated influenza virus resistance gene Mx is localized on mouse chromosome 16. J. Virol. 58:967–969.
Toth, L. A. (1996). Strain differences in the somnogenic effects of interferon inducers in mice. J. interferon Cytokine Res. 16:1065–1072.
Toth, L. A. (1999). Microbial modulation of arousal. In Lydic, R., and Baghdoyan, H. (eds.), Handbook of Behavioral State Control: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 641–657.
Toth, L. A., and Krueger, J. M. (1990). Infectious disease, cytokines and sleep. In Mancia, M., and Márina, G. (eds.), The Diencephalon and Sleep, Raven Press, New York, pp. 331–341.
Toth, L. A., Gardiner, T. W., and Krueger, J. M. (1992). Modulation of sleep by cortisone in normal and bacterially infected rabbits. Am. J. Physiol. 263:R1339–R1346.
Toth, L. A., Tolley, E. A., and Krueger, J. M. (1993). Sleep as a prognostic indicator during infectious disease in rabbits. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 203:179–192.
Toth, L. A., Rehg, J. E., and Webster, R. G. (1995). Strain differences in sleep and other pathophysiological sequelae of influenza virus infection in naive and immunized mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 58:89–99.
Zhang, J., Obal, F., Fang, J., Collins, B. J., and Krueger, J. M. (1996). Sleep is suppressed in transgenic mice with a deficiency in the somatotropic system. Neurosci. Lett. 220: 97–100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toth, L.A., Williams, R.W. A Quantitative Genetic Analysis of Slow-Wave Sleep in Influenza-Infected CXB Recombinant Inbred Mice. Behav Genet 29, 339–348 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021661901196
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021661901196