Summary
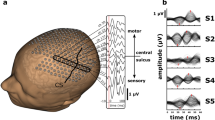
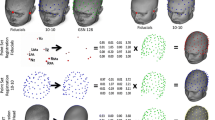
A functional-anatomical brain scanner that has a temporal resolution of less than a hundred milliseconds is needed to measure the neural substrate of higher cognitive functions in healthy people and neurological and psychiatric patients. Electrophysiological techniques have the requisite temporal resolution but their potential spatial resolution has not been realized. Here we briefly review progress in increasing the spatial detail of scalp-recorded EEGs and in registering this functional information with anatomical models of a person's brain. We describe methods and systems for 124-channel EEGs and magnetic resonance image (MRI) modeling, and present first results of the integration of equivalent-dipole EEG models of somatosensory stimulation with 3-D MRI brain models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Algazi, V.R., Reutter, B.W., van Warmerdam, W.L.G and Liu, C.C. Three-dimensional image analysis and display by space-scale matching of cross sections. J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1989: 6, 890–899.
Brickett, P. and Gevins, A.S. Retinotopic source localization of 15-Hz pattern-reversal evoked potentials, in preapration.
Doyle, J.C. and Gevins, A.S. Technical Note: Spatial filters for event-related brain potentials. EEG clin. Neurophysiol., submitted.
Geddes, L.A. and Baker, L.E. The specific resistance of biological material - a compendium of data for the biomedical engineer and physiologist. Med. Biol. Engr., 1967: 5, 271–293.
Gevins, A.S. Application of pattern recognition to brain electrical potentials. IEEE Trans. Pattern Ana. Mach. Intell., 1980: PAM-12, 383–404.
Gevins, A.S. Analysis of the electromagnetic signals of the human brain: Milestones, obstacles and goals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Enginr., 1984: BME12(31), 833–850.
Gevins, A.S. Statistical pattern recognition. In A. Gevins and A. Remond (Eds.), Methods of Analysis of Brain Electrical and Magnetic Signals: Handbook of Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology (Vol. 1), Amsterdam, Elsevier, 1987.
Gevins, A.S. Recent advances in neurocognitive pattern analysis. In: E. Basar (Ed.), Dynamics of Sensory and Cognitive Processing of the Brain. Heidelberg, Springer-Verlag, 1988: 88–102.
Gevins, A.S. Signs of model making by the human brain. In: E. Basar and T. Bullock (Eds.), Dynamics of Sensory and Cognitive Processing by the Brain. Springer-Verlag, 1989a: 408–419.
Gevins, A.S. Dynamic Functional Topography, Brain Topography, 1989b: 2(1), 37–56.
Gevins, A.S. and Bressler, S.L. Functional topography of the human brain. In: G. Pfurtscheller (Ed.), Functional Brain Imaging. Hans Huber Publishers, Bern, 1988: 99–116.
Gevins, A.S. and Morgan, N.H. Applications of neural-network (NN) signal processing in brain research. IEEE ASSP Trans., 1988: 7, 1152–1161.
Gevins, A.S. and Remond, A. (Eds.) Methods of Analysis of Brain Electrical and Magnetic Signals. Handbook of Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, Vol.1. Amsterdam, Elsevier, 1987.
Gevins, A.S. and Yeager, C.L. EEG spectral analysis in real time. DECUS Proc. Computers in Medicine, 3 1972: 4, 71–74.
Gevins, A.S. Yeager, C.L., Diamond, S.L., Spire, J.P., Zeitlin, G.M. and Gevins, A.H. Automated analysis of the electrical activity of the human brain (EEG): A progress report. IEEE Proc., 1975: 63(10), 1382–1399.
Gevins, A.S. Doyle, J.C., Cutillo, B.A., Schaffer, R.F., Tannehill, R.L., Ghannam, J.H., Gilcrease, V.A. and Yeager, C.L. Electrical potentials in human brain during cognition: New method reveals dynamic patterns of correlation. Science, 213, 1981: 918–922.
Gevins, A.S., Cutillo, B.A., Bressler, S.L., Morgan, N.H., White, R.M., Greer, D.S., Illes, J. Event-related covariances during a bimanual visuomotor task, Part I: Methods and analysis of stimulus-and response-locked data. EEG clin. Neurophysiol., 1989: 74(1), 58–75.
Hjorth, B. An on-line transformation of EEG scalp potentials into orthogonal source derivations Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1975: 39, 526–530.
Hjorth, B. Source derivation simplifies topographical EEG interpretation. Amer. J. EEG Technol., 1980: 20, 121–132.
Hosek, A.R. An experimental and theoretical analysis of effects of volume conduction in a nonhomogeneous medium on scalp and cortical potentials generated in the brain. Doctoral dissertation, Marquette Univ. Biomed. Engr., 1970.
Jasper, H. H. The ten-twenty electrode system of the international federation. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1958: 10, 371–375.
Landau, L.D, Lifshitz, E.M. and Pitaevskii, Electrodynamics of Continuous Media. New York: Pergammon, 1984.
Le, J., Brickett, P. Surkis, A. and Gevins, A.S. Finite element modeling of Maxwell's equations in a realistic human head, in preparation.
Lopes da Silva, F., Storm van Leeuwen W., Remond, A. (Eds.), Handbook of Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, Vol. 2: Clinical Applications of Computer Analysis of EEG and other Neurophysiological Signals. Amsterdam, Elsevier, 1986.
Luders, H., Dinner, D.S., Lesser, R.P. and Morris, H.H. Evoked potentials in cortical localization. J. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1986: 3, 75–84.
Nunez, P. Electric Fields of the Brain. New York: Oxford, 1981. Reutter, B.W., Brickett, P., Gevins, A.S. Algorithms for analysis of Magnetic Resonance Images, in preparation.
Thickbroom, G., Mastaglia, F., Carroll, W. and Davies, H. Source derivation: application to topographic mapping of visual evoked potentials. J. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1984: 59, 279–285.
Wood, C., Cohen, D., Cuffin, B.N., Yarita, M. and Allison, T. Electrical sources in human somatosensory cortex: Identification by combined magnetic and potential recordings. Science, 1985: 227, 1051–1053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Acknowledgments: This work was supported by grants from agencies of the Federal government of the United States of America, including The National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Strokes, The National Institute of Mental Health, The Air Force Office of Scientific Research and The National Science Foundation. We gratefully acknowledge this support, as well as the efforts of our colleagues at the EEG Systems Laboratory, Drs. S. Bressler, B. Cutillo, and J. Illes, for their contributions to the research presented here.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gevins, A., Brickett, P., Costales, B. et al. Beyond topographic mapping: Towards functional-anatomical imaging with 124-channel EEGs and 3-D MRIs. Brain Topogr 3, 53–64 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01128862
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01128862