Abstract
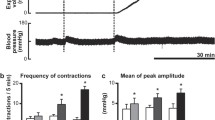
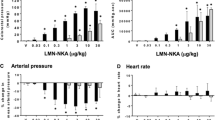
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) represents one ofthe most common gastrointestinal-related diagnoses.Although the precise etiologic basis of IBS is notknown, a common presenting symptom is abdominal pain or discomfort that is thought to develop, atleast in part, from a heightened awareness of visceralnociceptive input. Agents capable of reducing thisheightened visceral nociception would, therefore, have utility in the treatment of IBS. In this studywe evaluated the effects of intravenous andintracerebroventricular administration of a5-HT3 receptor antagonist, alosetron, onblood pressure changes associated with rectal distension in anesthetized andawake dogs. This vasoactive reflex serves as a model forvisceral nociception. For intracerebroventricularstudies, the cerebroventricular guides were placed over the lateral ventricle. In anesthetized studies,blood pressure was measured by femoral arterycannulation. In awake studies, blood pressure wasmonitored by noninvasive measurement. A rectal balloonwas placed in the rectum of each dog and maintainedthroughout the experiments. Each dose of alosetron wasgiven to the dogs as an intravenous orintracerebroventricular bolus, and every 30 min therectal balloon was inflated and blood pressure responsesobserved. In both anesthetized and awake dogs alosetronproduced a significant inhibition of the vasoactivereflex. In particular, alosetron showed high potency when administered intracerebroventricularly.Alosetron, administered either centrally orperipherally, appears to modulate the visceralnociceptive effect of rectal distension indogs.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Everhart JE, Renault PF: Irritable bowel syndrome in offi ce-base d practice in the United States. Gastroenterology 100:998–1005, 1991
Sandler RS: Epidemiology of irritable bowel syndrome in the United States. Gastroenterology 99:409–415, 1990
Mayer EA, Gebhart GF: Basic and clinical aspe cts of visceral hyperalge sia. Gastroenterology 107:271–293, 1994
Bueno L, Fioramonti J, Delvaux M, Frexinos J: Mediators and pharmacology of visceral sensitivity: From basic to clinical inve stigations. Gastroenterology 112:1714–1743, 1997
Camilleri M, Choi M-G: Irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 11:3–15, 1997
Ritchie J: Pain from distention of the pelvic colon by inflating a balloon in the irritable colon syndrome. Gut 14:125–132, 1973
Whitehead WE, Holtkotter B, Enck P, Hoelzi R, Holmes KD, Anthony J, Shabsin HS, Schuster MM: Tolerance for re ctosigmoid distention in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 98:1187–1192, 1990
Ness TJ, Gebhart GF: Colorectal distention as a noxious visce ral stimulus: Physiologic and pharmacologic characte rization of pseudaffective reflexes in the rat. Brain Res 450:153–169, 1988
Moss HE, Sanger GJ: The e ffects of granisetron, ICS 205-930 and ondanse tron on the visce ral pain reflex induced by duodenal distention. Br J Pharmacol 100:497–501, 1990
Scott CM, Grundy D, Boissonade F, Bountra C: Alosetron inhibits the colorectal distention-evoked depressor response and spinal c-fos expre ssion in the anesthetized rat. Gastroenterology 112:A822, 1997
Farthing MJG: 5-Hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine-3 receptor antagonists. Scand J Gastroenterol 26( suppl 188):92–100, 1991
Bardhan K, Bodemar G, Geldef H, Schultz E, Snell C, Darekar B: A double-blind placebo-controlled study to evaluate the effi cacy of alosetron in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 110:A630, 1996
Prior A, Read NW: Reduction of rectal sensitivity and postprandial motility by granisetron, a 5-HT3 rece ptor antagonist, in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 7:175–180, 1993
Goldberg PA, Kamm MA, Setti-Carraro P, van der Sijp JRM, Roth C: Modifi cation of visce ral sensitivity and pain in irritable bowel syndrome by 5-HT3 antagonism (ondanse tron). Digestion 57:748–483, 1996
Kilpatrick GK, Jones BJ, Tyers MB: Identification and distribution of 5-HT3 re ceptors in rat brain using radioligand binding. Nature 330:746–748, 1982
Kilpatrick GJ, Jones BJ, Tyers MB: Binding of the 5-HT3 ligand, (3H)GR65630, to rat are a postrema, vagus nerve and the brain of seve ral species. Eur J Pharmacol 159:157–164, 1989
Geoghegan JG, Lawson DC, Cheng CA, Pappas TN: Intrace-rebroventricular neuropeptide Y increase s gastric acid se cre-tion by decreasing tonic adrenergic inhibition of acid in dogs. Brain Res 635:118–124, 1994
Derkach V, Suprenant A, North RA: 5-HT3 re ceptors are membrane ion channe ls. Nature 339:706–709, 1989
Delvaux M, Louvel D, Mamet JP, Campos-Oriola R, Foster E, Frezinos J: Effect of alosetron on colonic sensitivity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 110:A665, 1996
Talley NJ, Phillips SF, Haddad A, Miller LJ, Twomey C, Zeinsmeister AR, MacCarty RL, Ciociola A: GR 38032F (ondanse tron), a sele ctive 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, slows colonic transit in healthy man. Dig Dis Sci 35:477–480, 1990
Foster JM, Houghton LA, Whorwell PJ: Alosetron slows colonic transit in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 112:A732, 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miura, M., Lawson, D.C., Clary, E.M. et al. Central Modulation of Rectal Distension-Induced Blood Pressure Changes by Alosetron, A 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist. Dig Dis Sci 44, 20–24 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026633629141
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026633629141