Abstract
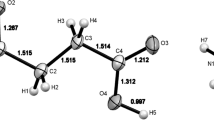
The crystal structure of calcium succinate monohydrate, Ca(C4H4O4)·H2O, has been determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction. The crystals are monoclinic witha=11.952(2),b=9.691(2),c=11.606(2)Å, β=108.81(1)°, space group C2/c,Z=8,V=1272.49 Å3,d m =1.80, andd c =1.818 Mg m−3. The structure was refined by full-matrix least-squares techniques toR=0.027,R w =0.040, for 829 reflections with1≥3δ(I). Ca is coordinated to seven oxygen atoms, and the coordination polyhedron is best described as a pentagonal bipyramid. One carboxylate group in the succinate ion is bonded to three different Ca ions, forming a four-membered chelate ring with one Ca ion is bonded to three different Ca ions, forming a four-membered chelate ring with one Ca ion and unidentate bridge bonds to two other Ca ions. The other carboxylate group is bonded to two Ca ions through unidentate bonds. The structure is highly polymeric. The general structural features are nearly identical to those of calcium adipate monohydrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, W.E.Nature 1962,196, 1048.
Mathew, M.; Brown, W.E.; Schroeder, L.W.; Dickens, B.J. Crystallogr. Spectrosc. Res. 1988,18, 235.
Monma, H.Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1984,57, 599.
Markovic, M.; Fowler, B.O.; Brown, W.E.Chem. Mater. 1993,5, 1401.
Mathew, M.; Brown, W.E.Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1987,60, 1141.
Mathew, M.; Takagi, S.; Ammon, H.L.J. Crystallogr. Spectrosc. Res. 1993,23, 617.
Germain, G.; Main, P.; Woolfson, M.M.Acta Crystallogr. 1971, A27, 368.
Zachariasen, W.H.Acta Crystallogr. 1967,23, 558.
International Tables for X-ray Crystallography. Vol. IV; Ibers, J.A.; Hamilton, W.C. (eds.), The Kynoch Press: Birmingham, England, 1974; pp. 155–175.
Johnson, C.K.ORTEPII. Report ORNL-5138; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, Tennessee; 1976.
Karipides, A.; Reed, A.T.Acta Crystallogr. 1980, B36, 1377.
Einspahr, H.; Bugg, C.E.Acta Crystallogr. 1981, B37, 1044.
Karipides, A.; Ault, J.; Reed, A.T.Inorg. Chem. 1977,16, 1381.
Brown, W.E.; Eidelman, N.; Tomazic, B.Adv. Dent. Res. 1987,1, 306.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Certain commercial materials and equipment are identified in this paper to specify the experimental procedure. In no instance does such identification imply recommendation or endorsement by the National Institute of Standards and Technology or the ADA Health Foundation or that the material or equipment identified is necessarily the best available for the purpose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathew, M., Takagi, S., Fowler, B.O. et al. The crystal structure of calcium succinate monohydrate. J Chem Crystallogr 24, 437–440 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01666091
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01666091