Abstract
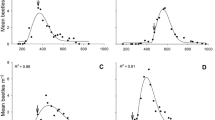
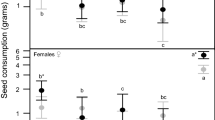
At many beaver (Castor canadensis) sites at Allegany State Park in New York State, red maple (Acer rubrum) is the only or one of the few tree species left standing at the ponds' edges. The relative palatability of red maple (RM) was studied in three ways. (1) At seven beaver sites, the available and utilized trees were recorded and an electivity index (E) computed. Of 15 tree species, RM ranked second or fourth lowest. (2) In experiment I, RM, sugar maple (A. saccharum, SM), and quaking aspen (Populus tremuloides) logs were presented cafeteria style at 10 colonies. RM was the least preferred. (3) Bark of RM was extracted with solvents. Aspen logs were painted (experiment II) or soaked (experiment III) with this RM extract and presented to beaver cafeteria-style, along with aspen and RM controls. This treatment rendered aspen logs less palatable, indicating that a chemical factor had been transferred.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, W.J., andDibble, E. 1988. The effects of beaver in riverbank forest succession.Can. J. Bot. 66:40–44.
Basey, J.M., Jenkins, S.H., andBusher, P.E. 1988. Optimal central-place foraging by beavers: Tree-size selection in relation to defensive chemicals of quaking aspen.Oecologia 76:278–282.
Basey, M.J., Jenkins, S.H., andMiller, G.C. 1990. Food selection by beavers in relation to inducible defenses ofPopulus tremuloides.Oikos 59:57–62.
Bate-Smith, E.C. 1977. Astringent tannins ofAcer spp..Phytochemistry 16:1421–1426.
Belovsky, G.E. 1984. Summer diet optimization by beaver.Am. Midl. Nat. 111:209–222.
Doucet, C.M., Walton, R.A., andFryxell, J.M. 1994. Perceptual cues used by beavers foraging on woody plants.Anim. Behav. 47:1482–1484.
Edwards, W.R.N. 1978. Effect of salicin content on palatability ofPopulus foliage to opossum (Trichosurus vulpecula).N.Z.J. Sci. 21:103–106.
Engelhart, A., andMüller-Schwarze, D. 1994. Responses of beaver (Castor canadensis Kuhl) to predator odors.
Fryxell, J.M., andDoucet, C.M. 1993. Diet choice and the functional response of beavers.Ecology 74:1297–1306.
Henry, D.B., andBookhout, T.A. 1970. Utilization of woody plants by beavers in northeastern Ohio.Ohio J. Sci. 70:123–127.
Jacobs, J. 1974. Quantitative measurement of food selection: A modification of the forage ratio and Ivlev's electivity index.Oecologia 14:413–417.
Jenkins, S.H. 1975. Food selection by beaver: A multidimensional contingency table analysis.Oecologia 21:157–173.
Jenkins, S.H. 1978. Food selection by beaver: Sampling behavior.Brevora (Harvard Mus. Comp. Zool.) 447:1–6.
Jenkins, S.H. 1979. Seasonal and year-to-year differences in food selection by beavers.Oecologia 44:112–116.
Jenkins, S.H. 1980. A size-distance relation in food selection by beavers.Ecology 61:740–746.
Jenkins, S.H. 1981. Problems, progress and prospects in studies of food selection by beavers. Proceedings International Furbearer Symposium, pp. 559–579.
Johnston, C.A., andNaiman, R.J. 1990. Browse selection by beaver: Effects on riparian forest composition.Can. J. For. Res. 20:1036–1043.
Shadle, A.R., andAustin, T.S. 1939. Fifteen months of beaver work at Allegany State Park, NY.J. Mammal. 20:299–303.
Shadle, A.R., Nauth, A.M., Gese, E.C., andAustin, T.S. 1943. Comparison of tree cuttings of six beaver colonies in Allegany State Park, New York.J. Mammal. 24:32–39.
Sullivan, T.P., Nordstrom, L.O., andSullivan, D.S. 1985. The use of predator odors as repellents to reduce feeding damage by herbivores. II. Black-tailed deer (Odocoileus hemionus columbianus).J. Chem. Ecol. 11:921–935.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller-Schwarze, D., Schulte, B.A., Sun, L. et al. Red maple (Acer rubrum) inhibits feeding by beaver (Castor canadensis). J Chem Ecol 20, 2021–2034 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02066240
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02066240