Abstract
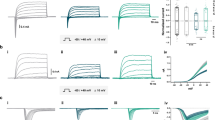
We have analyzed Ca2+ currents in two neuroblastoma-motor neuron hybrid cell lines that expressed normal or glutamine-expanded human androgen receptors (polyGln-expanded AR) either transiently or stably. The cell lines express a unique, low-threshold, transient type of Ca2+ current that is not affected by L-type Ca2+ channel blocker (PN 200-110), N-type Ca2+ channel blocker (ω-conotoxin GVIA) or P-type Ca2+ channel blocker (Agatoxin IVA) but is blocked by either Cd2+ or Ni2+. This pharmacological profile most closely resembles that of T-type Ca2+ channels [1-3]. Exposure to androgen had no effect on control cell lines or cells transfected with normal AR but significantly changed the steady-state activation in cells transfected with expanded AR. The observed negative shift in steady-state activation results in a large increase in the T-type Ca2+ channel window current. We suggest that Ca2+ overload due to abnormal voltage-dependence of transient Ca2+ channel activation may contribute to motor neuron toxicity in spinobulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA). This hypothesis is supported by the additional finding that, at concentrations that selectively block T-type Ca2+ channel currents, Ni2+ significantly reduced cell death in cell lines transfected with polyGln-expanded AR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bkaily G, Sculptoreanu A, Jacques D, Jasmin G: Increases of T-type Ca2+ current in heart cells of cardiomyopathic hamster. Mol Cell Biochem 176: 199-204, 1997
Ertel SI, Ertel EA: Low-voltage-activated T-type Ca2+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci 18: 37-42, 1997
Nooney JM, Lambert MC, Feltz A: Identifying neuronal non-L Ca2+ channels-more than stamp collecting? Trends Pharmacol Sci 18: 363-371, 1997
Johansson J, Forsgren L, Sandgren O, Brice A, Holmgren G, Holmberg M: Expanded CAG repeats in Swedish spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) patients: Effect of CAG repeat length on the clinical manifestation. Hum Mol Genet 7: 171-176, 1998
Ross CA: Intranuclear neuronal inclusions: A common pathogenic mechanism for glutamine-repeat neurodegenerative diseases? Neuron 19: 1147-1150, 1997
Brooks BP, Fischbeck KH: Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy: A trinucleotide-repeat expansion neurodegenerative disease. Trends Neurosci 10: 459-461, 1995
Brooks BP, Merry DE, Paulson HL, Lieberman AP, Kilson DL, Fischbeck KH: A cell culture model for androgen effects in motor neurons. J Neurochem 70: 1054-1060, 1998
Kennedy WR, Alter M, Sung JH: Progressive proximal spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy of late onset. A sex-linked recessive trait. Neurol 18: 671-680, 1968
Paulson HL, Fischbeck KN: Trinucleotides repeats in neurogenetic disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci 19: 79-100, 1996
La Spada AR, Wilson EM, Lubahn DB, Harding AB, Fischbeck KH: Androgen receptor gene mutations in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Nature 352: 77-79, 1991
Matsuyama Z, Kawakami H, Maruyama H, Izumi Y, Komure O, Udaka F, Kameyama M, Nishio T, Kuroda Y, Nishimura M, Nakamura S: Molecular features of the CAG repeats of spinocerebellar ataxia 6 (SCA6). Hum Mol Genet 6: 1283-1287, 1997
Andrew SW, Goldberg YP, Hayden, MR: Rethinking genotype and phenotype correlations in polyglutamine expansion disorders. Hum Mol Genet 6: 2005-2010, 1997
Trifiro MA, Kazemi-Esfarjani P, Pinsky L: X-linked muscular atrophy and the androgen receptor. Trends Endocrinol Metab 5: 416-421, 1994
Nordeen EJ, Nordeen KW, Sengelaub DR, Arnold AP: Androgens prevent normally occurring cell death in a sexually dimorphic spinal nucleus. Science 229: 671-682, 1985
Perez J, Kelley DB: Trophic effects of androgen: Receptor expression and the survival of laryngeal motor neurons after axotomy. J Neurosci 16: 6625-6631, 1996
Perez J, Kelley DB: Androgen mitigates axotomy-induced decreases in calbindin expression in motor neurons. J Neurosci 17: 7396-7403, 1997
Tanzer L, Jones KJ: Gonadal steroid regulation of hamster facial nerve regeneration: Effects of dihydrotestosterone and estradiol. Exp Neurol 146: 258-266, 1997
Yu WH: Administration of testosterone attenuates neuronal loss following axotomy in the brain-stem motor nuclei of female rats. J Neurosci 9: 3908-3922, 1989
Zhuchenko O, Bailey J, Bonnen P, Ashizawa T, Stockton DW, Amos C, Dobyns WB, Subramony SH, Zoghbi HY, Lee CC: Autosomal cerebellar ataxia (SCA6) associated with small polyglutamine expansions in the a1A-voltage-dependent calcium channel. Nature Genet 15: 62-69, 1997
Butler R, Leigh PN, McPhaul MJ, Gallo JM: Truncated forms of the androgen receptor are associated with polyglutamine expansion in Xlinked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet 7: 121-127, 1998
Abdullah AAR, Trifiro M.A, Panet-Raymond V, Alvarado C, de Tourreil S, Frankel D, Schipper HM, Pinsky L: Spinobulbar muscular atrophy: Polyglutamine-expanded androgen receptor is trypsin resistant in vitro and processed abnormally in transfected cells. Hum Mol Genet 7: 379-384, 1998
Wellington CL, Ellerby L M, Hackam AS, Margolis RL, Trifiro MA, Singaraja R, McCutcheon K, Salvesen GS, Propp SS, Bromm M, Rowland KJ, Zhang T, Rasper D, Roy S, Thornberry N, Pinsky L, Kakizuka A, Ross CA, Nicholson DW, Bredesen DE, Hayden MR: Caspase cleavage of gene products associated with triplet expansion disorders generates truncated fragments containing the polyglutamine tract. J Biol Chem 273: 9158-9167, 1998
Ellerby L, Hackman A, Propp S, Ellerby H, Rabizadeh S, Trifiro M, Pinsky L: Kennedy's disease: Caspase cleavage of the androgen receptor is a crucial event in cytotoxicity. J Neurochem 72: 185-195, 1998
Perutz MF: Glutamine repeats and inherited neurodegenerative diseases: molecular aspects. Curr Opin Struct Biol 6: 848-858, 1996
Ikeda H, Yamaguchi M, Sugai S, Aze Y, Narumiya S, Kakizuka A: Expanded polyglutamine in the Machado-Joseph disease protein induces cell death in vitro and in vivo. Nature Genet 13: 196-202, 1996
Kahlem P, Terré C, Green H, Djian P: Peptides containing glutamine repeats as substrates for transglutaminase-catalyzed cross-linking: Relevance to diseases of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 14580-14585, 1996
Merry DE, Kobayashi Y, Bailey CK, Taye AA, Fischbeck KH: Cleavage, aggregation and toxicity of the expanded androgen receptor in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet 7: 631-701, 1998
Paulson HL: Protein fate in neurodegenerative proteinpathies: Polyglutamine diseases join the (mis)fold. Am J Hum Genet 64: 339-345, 1999
Cashman N, Durham HD, Blusztajn JK, Oda K, Tabira T, Shaw IT, Dahrouge S, Antel JP: Neuroblastoma x spinal cord (NSC) hybrid cell lines resemble developing motor neurons. Dev Dynamics 194: 209-221, 1992
Salazar-Grueso EF, Kim S, Kim H: Embryonic mouse spinal cord motor neuron hybrid cells. Neuroreport 2: 505-508, 1991
Brooks BP, Paulson HL, Merry DE, Salazar-Grueso EF, Brinkmann AO, Wilson EM, Fischbeck KH: Characterization of an expanded glutamine repeat androgen receptor in a neuronal cell culture system. Neurobiol Dis 4: 313-323, 1997
Martin SJ, Matear PM, Vyakarnam A: HIV-1 infection of CD4 and T cells in vitro: Differential induction of apoptosis in these cells. J Immunol 152: 330-342, 1994
Sculptoreanu A, Figourov A, deGroat WC: Voltage-dependent potentiation of neuronal L-type Ca2+ channel currents due to statedependent phosphorylation. Am J Physiol 269: C725-C732, 1995
Bean BP, McDonough SI: Two for T. Neuron 20: 825-828, 1998
Bhattacharjee A, Whitehurst RM, Zhang M, Wang L, Li M: T-Type Calcium channels facilitate insulin secretion by enhancing general excitability in the insulin-secreting β-cell line, INS-1. Endocrinology 138: 3735-3740, 1997
McConkey DJ, Orrenius S: The role of calcium in the regulation of apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 20: 357-366, 1997
Unemiya M, Araki I, Kuno M: Electrophysiological properties of axotomized facial motoneurones that are destined to die in neonatal rats. J Physiol (Lond) 462: 661-678, 1993
George EB, Glass JD, Griffin JW: Axotomy-induced axonal degeneration is mediated by calcium influx through ion-specific channels. J Neurosci 15: 6445-6452, 1995
Lesort M, Attanavanich K, Zhang J, Johnson GVW: Distinct nuclear localization and activity of tissue transglutaminase. J Biol Chem 273: 11991-11994, 1998
Igarashi S, Koide R, Shimohata T, Yamada M, Hayashi Y, Takano H, Date H, Oyake M, Sato T, Sato A, Egawa S, Ikeuchi T, Tanaka H, Nakano R, Tanaka K, Hozumi I, Inuzuka T, Takahashi H, Tsuji S: Suppression of aggregate formation and apoptosis by transglutaminase inhibitors in cells expressing truncated DRPLA protein with an expanded polyglutamine stretch. Nature Genet 18: 111-117, 1998
Wang L. Bhattacharjee A. Zuo Z. Hu FQ. Honkanen RE. Berggren PO. Li M: A low voltage-activated Ca2+ current mediates cytokineinduced pancreatic beta-cell death. Endocrinology 140: 1200-1204, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sculptoreanu, A., Abramovici, H., Abdullah, A.A. et al. Increased T-type Ca2+ channel activity as a determinant of cellular toxicity in neuronal cell lines expressing polyglutamine-expanded human androgen receptors. Mol Cell Biochem 203, 23–31 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007010020228
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007010020228