Abstract
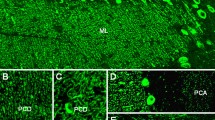
Monoclonal antibody At5 was primarily developed against chordin, a notochord-specific antigen of Acipenseridae (sturgeon fishes). In higher vertebrates the antibody reacted mainly with neural tissue antigens. In this study we have shown that the specificity of monoclonal antibody At5 is similar to that of antibodies of HNK-1 family which react with two glycolipids and with several high molecular weight glycoconjugates of neural tissue. We have demonstrated by protein sequencing and immunoblotting that one of At5 target antigens of human brain is dMAG, a derivative of myelin-associated glycoprotein. In the preparations of At5 antigens proteoglycans phosphacan and neurocan were identified by immunoblotting with specific monoclonal antibodies 6B4 and 1G2, respectively. The distribution of At5 and 6B4 immunoreactivity was studied on sections of mixed oligoastrocytoma. Oligodendroglioma area of this tumor was intensely stained with both antibodies, whereas astrocytoma area did not exhibit any At5 or 6B4 immunoreactivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Jungalwala, F. B. 1994. Expression and biological functions of sulfoglucoronyl glycolipids (SGGLs) in the nervous system-a review. Neurochem. Res. 19:945–957.
Schachner, M. and Martini, R. 1995. Glycans and modulation of neural-recognition molecular function. Trends. Neurosci. 18:183–191.
Kruse, J., Mailhammer, R., Wernecke, H., Faissner, A., Sommer, I., Goridis, C., and Schachner, M. 1984. Neural cell adhesion molecules and myelin-associated glycoprotein share a common carbohydrate moiety recognized by monoclonal antibodies L2 and HNK-1. Nature 311:153–155.
Kruse, J., Keilhauer, G., Faissner, A., Timpl, R., and Schachner, M. 1985. The J1 glycoprotein: a novel nervous system cell adhesion molecule of the L2/HNK-1 family. Nature 316:146–148.
Grumet, M., Hoffman, S., Crossin, K. L., and Edelman, G. M. 1985. Cytotactin, an extracellular matrix protein of neural and non-neural tissues that mediates glia-neuron interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:8075–8079.
McGarry, R. C., Helfand, S. L., Quarles, R. H., and Roger, J. C. 1983. Recognition of myelin-associated glycoprotein by the monoclonal antibody HNK-1. Nature 306:376–378.
Bollensen, E., Steck, A. J., and Schachner, M. 1988. Reactivity with the peripheral myelin glycoprotein P0 in sera from patients with IgM monoclonal gammopathy and polyneuropathy. Neurology 38:1266–1270.
Mikol, D. D., Gulcher, J. R., and Stefansson, K. 1990. The oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein belongs to a distinct family of proteins and contains the HNK-1 carbohydrate. J. Cell Biol. 110:471–479.
Burger, D., Steck, A. J., Bernard, C. C. A., Kerlero de Rosbo, N. 1993. Human myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein: a new member of the L2/HNK-1 family. J. Neurochem. 61:1822–1827.
Pesheva, P., Horwitz, A. F., and Schachner, M. 1987. Integrin, the cell surface receptor for fibronectin and laminin, expresses the L2/HNK-1 and L3 carbohydrate structures shared by adhesion molecules. Neurosci. Lett. 83:303–306.
Oohira, A., Katoh-Semba, R., Watanabe, E., and Matsui, F. 1994. Brain development and multiple molecular species of proteoglycan. Neurosci. Res. 20:195–207.
Domowicz, M., Li, H., Hennig, A., Henry, J., Vertel, B. M., and Schwartz, N. B. 1995. The Biochemically and immunologically distinct CSPG of notochord is a product of aggrecan gene. Develop. Biol. 171:655–664.
Abo, T., and Blach, C. M. 1981. A differentiation antigen of human HK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J. Immunol. 127:1024–1029.
Vincent, M., Duband, J.-L., and Thiery, J.-P. 1983. A cell surface determinant expressed early on migrating avian neural crest cells. Dev. Brain Res. 9:235–238.
Marton, L. S., and Stefansson, K. 1984. Developmental alterations in molecular weights of proteins in the human central nervous system that react with antibodies against myelin-associated glycoprotein. J. Cell Biol. 99:1642–1646.
Bon, S., Meflah, K., Musset, F., Grassi, J., and Massoulie, J. 1987. An immunoglobulin M monoclonal antibody, recognizing a subset of acetylcholinesterase molecules from electric organs of Electrophorus and Torpedo, belongs to the HNK-1 anti-carbohydrate family. J. Neurochem., 49:1720–1731.
Quarles, R. H., Colman, D. R., Salzer, J. L., and Trapp, B. 1992. Myelin-associated glycoprotein: structure-function relationships and involvement in neurological diseases. Pages 413–448, in: Martensen R. M. (ed.), Myelin: Biology and Chemistry, CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Chou, D. K. H., Ilyas, A. A., Evans, J. E., and Jungalwala, F. B. 1985. Structure of a glycolipid reacting with monoclonal IgM in neuropathy and with HNK-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 128:383–388.
Chou, D. K. H., Ilyas, A. A., Evans, J. E., Costello, C., Quarles, R. H., and Jungalwala, F. B. 1986. characterization of sulfated glucuronyl glycolipids in the nervous system reacting with HNK-1 antibody and some IgM paraproteins in neuropathy. J. Biol. Chem. 261:11717–11725.
Ariga, T., Kohriyama, T., Freddo, L., Latov, N., Saito, M., Kon, K., Ando, S., Suzuki, M., Hemlin, M., Rinehart, K. L., Kusunoki, S., and Yu, R. K. 1987. Characterization of sulfated glucuronic acid containing glycolipids reacting with IgM-M proteins in patients with neuropathy. J. Biol. Chem. 262:848–853.
Nakano, T., Ito, Y., and Ogawa, T. 1993. Synthesis of sulfated glucuronylglycosphingolipids: carbohydrate epitopes of neural cell adhesion molecules. Carbohyd. Res. 243:43–69.
Ilyas, A. A., Dakakas, M. C., Brady, R. O., and Quarles, R. H. 1986. Sulfated glucuronyl glycolipids reacting with anti-myelinassociated glycoprotein monoclonal antibodies including IgM paraproteins in neuropathy: species distribution and partial characterization of epitopes. Brain Res. 385:1–9.
Ilyas, A. A., Chou, D. K., Jungalwala, F. B., Costello, C., and Quarles, R. H. 1990. Variability in the structural requirements for binding of human monoclonal anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein immunoglobulin M antibodies and HNK-1 to sphingoglycolipid antigens. J. Neurochem. 55:594–601.
Preobrazhensky, A. A., Rodionova, A. I., Trakht, I. N., and Rukosuev, V. S. 1987. Monoclonal antibodies against chordin. Use in structural and immunohistochemical studies. FEBS Lett. 224:23–28.
Preobrazhensky, A. A., and Glinka, A. V. 1985. Quantitation of chordin in developing Huso huso embryos and larvae by radioimmunoassay. FEBS Lett. 191:82–86.
Preobrazhensky, A. A., Rodionova, A. I., and Kasumova, S. Yu. 1988. Identification of proteolysis-resistant fragments carrying P-type antigenic determinants in chordin and immunologically related human brain antigen. Biokhimiya 53:1849–1857. (In Russian with English summary; English translation: Biokhimiya, Moscow 53:1593–1598.)
Preobrazhensky, A. A., Rodionova, A. I., and Barabanov, V. M. 1989. P-epitope is characteristic for the neural tissue of vertebrates. Molec. Reprod. Devel. 1:182–192.
Barabanov, V. M., and Preobrazhensky, A. A. 1989. Immunohistochemical study of tissue specificity of chordin epitope P5 and its appearance in true sturgeons ontogenesis. Ontogenez 20:263–272. (In Russian with English summary).
Preobrazhensky, A. A., Rodionova, A. I., Yaroshevich, E. Yu., and Feshenko, S. P. 1990. Human neurochordins: identification of several P-epitope-bearing polypeptides and a study of their ontogenetic expression. FEBS Lett. 277:19–22.
Preobrazhensky, A. A., Khalansky, A. S., and Kozlova, M. V. 1991. Neurochordins of higher vertebrates: similarities in P-epitope-bearing polypeptide composition and a study of P-epitope expression in cultured neural tissue cells. Neurosci. Lett. 133:284–286.
Preobrazhensky, A. A. 1993. Electrophoresis of neurochordins, a family of high molecular weight neural tissue glycoproteins, on horizontal submerged agarose gels in the presence of dodecyl sulfate. Analyt. Biochem. 209:315–317.
Preobrazhensky, A. A., Voronina, A. S., Kaliberda, E. N., and Vovk, T. S. 1995. Ontogenetic expression of neurochordin D, a specific glycoprotein of human brain. Biokhimiya 60:1841–1846. (In Russian with English summary; English translation: Biochemistry, Moscow 60:1405–1409).
Laemmli, U. K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685.
Stone, K. L., LoPresti, M. B., Crawford, J. M., DeAngelis, R., and Williams, K. R. 1988. Enzymatic digestion of proteins and HPLC peptide isolation. Pages 31–47, in Matsudaira P. T. (ed.), A practical Guide to Protein and Peptide Purification for Microsequencing. Academic Press, San Diego.
Norton, W. T. and Poduslo, S. E. 1973. Myelination in rat brain: method of myelin isolation. J. Neurochem. 21:749–757.
Sato, S., Quarles, R. H., and Brady, R. O. 1982. Susceptibility of myelin-associated glycoprotein and basic protein to neutral protease in highly purified myelin from human and rat brain. J. Neurochem. 39:97–105.
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T., and Gordon, J. 1979. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76:4350–4354.
Young, P. 1989. Enhancement of immunoblot staining using a mixed chromogenic substrate. J. Immunol. Methods 121:295–296.
Oehm, A., Behrmann, I., Falk, W., Pawlita, M., Maier, G., Klas, C., Min Li-Weber, Richards, S., Dhein, J., Trauth, B. C., Ponstingl, H., and Krammer, P. H. 1992. Purification and molecular cloning of the APO-1 cell surface antigen, a member of the tumor necrosis factor/nerve growth factor receptor superfamily. Sequence identity with the Fas antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 267:10709–10715.
Oohira, A., Matsui, F., Watanabe, E., Kushima, Y., and Maeda, N. 1994. Developmentally regulated expression of a brain specific species of chondroitin sulfate proteogglycan, neurocan, identified with a monoclonal antibody IG2 in the rat cerebrum. Neuroscience 60:145–157.
Preobrazhensky, A. A., Likhosherstov, L. M., Senchenkova, S. N., Rodionova, A. I., and Feshenko, S. P. 1989. Chordin structure: the properties of protein and carbohydrate components and their role in antigenicity. Biokhimiya 54:1235–1246. (In Russian with English summary; English translation: Biokhimiya, Moscow 54:1011–1020).
Van Noorden, S. 1986. Tissue preparation and immunostaining techniques for light microscopy. Pages 26–53, in Polak, J. M. and Van Noorden, S. (eds), Immunocytochemistry. Modern methods and applications. Wright, Bristol.
Maeda, N., Matsui, F., and Oohira, A. 1992. A chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan that is developmentally regulated in the cerebellar mossy fiber system. Dev. Biol. 151:564–574.
Sato, S., Fujita, N., Kurihara, T., Kuwano, R., Sakimura, K., Takahashi, Y., and Tadashi, M. 1989. cDNA cloning and amino acid sequence for human myelin-associated glycoprotein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 163:1473–1480.
Burger, D., Pidoux, L., and Steck, A. J. 1993. Identification of the glycosylated sequons of human myelin-associated glycoprotein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 197:457–464.
Barabanov, V. M. 1989. Expression of chordin epitope P5 in tissues of Pleurodeles waltlii michah. during development. Ontogenez 20:486–494. (In Russian with English summary).
Rauch, U., Ping Gao, Janetzko, A., Flaccus, A., Hilgenberg, L., Tekotte, H., Margolis, R. K., and Margolis, R. U. 1991. Isolation and characterization of developmentally regulated chondroitin sulfate and chondroitin/keratan sulfate proteoglycans of brain identified with monoclonal antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 266:14785–14801.
Rauch U., Karthikeyan L., Maurel P., Margolis R.U., and Margolis R.K. 1992. Cloning and primary structure of neurocan, a developmentally regulated, aggregating chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan of brain. J. Biol. Chem. 267:19536–19547.
Matsui F., Watanabe E., and Oohira A. 1994. Immunological identification of two proteoglycan fragments derived from neurocan, a brain-specific chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan. Neurochem. Int. 25:425–431.
Maeda N., Hamanaka H., Oohira A., and Noda M. 1995. Purification, characterization and developmental expression of a brain-specific chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, 6B4 proteoglycan/phosphacan. Neuroscience 67:23–35.
Maurel P., Rauch U., Flad M., Margolis R.K., Margolis R.U. 1994. Phosphacan, a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan of brain that interacts with neurons and neural cell-adhesion molecules, is an extracellular variant of a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:2512–2516.
Milev P., Friedlander D.R., Sakurai T., Karthikeyan L., Flad M., Margolis R.K., Grumet M., and Margolis R.U. 1994. Interactions of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan phosphacan, the extracellular domain of a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase, with neurons, glia, and neural cell adhesion molecules. J. Cell Biol. 127:1703–1715.
Maeda N., Hamanaka H., Shintani T., Nishiwaki T., and Noda M. 1994. Multiple receptor-like tyrosine phosphatases in the form of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan. FEBS Lett. 354:67–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Preobrazhensky, A.A., Oohira, A., Maier, G. et al. Identification of Monoclonal Antibody At5 as a New Member of HNK-1 Antibody Family: The Reactivity with Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein and with Two Brain-Specific Proteoglycans, Phosphacan and Neurocan. Neurochem Res 22, 133–140 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027355221525
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027355221525