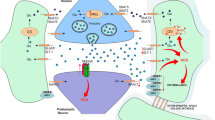
Abstract
We have studied the levels of neuroactive amino acids in synaptosomes (P2 fraction) isolated from brain tissue of ten patients with medically intractable epilepsy who were undergoing temporal lobectomy. First, lateral temporal tissue (nonfocal) was removed followed by medial temporal tissue (focal). A synaptosomal fraction (P2) was immediately prepared from each tissue and analyzed for free amino acid concentrations. Statistically significant reductions were seen in glutamine and GABA concentrations in focal tissue compared to nonfocal tissue. The ratio of excitatory amino acids (aspartate and glutamate) to inhibitory amino acids (taurine and GABA) was significantly higher in focal tissue compared to nonfocal. The glutamine/glutamate ratio was significantly reduced. These data support the hypothesis that alterations in the balance between excitatory and inhibitory amino acids may be involved in the expression of epilepsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Van Gelder, N.M., Sherwin, A.L., and Rasmussen, T. 1972. Amino acid content of epileptogenic human brain: focal versus surrounding regions. Brain Res. 40:385–393.
Van Gelder, N.M. and Courtois, A.1972. Close correlation between changing content of specific amino acids in epileptogeniccortex of cats, and severity of epilepsy. Brain Res. 43:477–484.
Hansen, S., Perry, T.L., Wada, J.A., and Sokol, M.1973.Brain amino acids in baboons with light-induced epilepsy. Brain Res. 50:480–483.
Perry, T.L. and Hansen, S.1976.Taurine content of epileptogenic foci in human brain.Pages 275–281,in Huxtable, R. and Barbeau, A.(eds.),Taurine,Raven Press, New York.
Perry, T.L., Hansen, S., Kennedy, J., Wada, J., and Thompson, G.B.1975. Amino acids in human epileptic foci. Arch.Neurol. 32:752–754.
Avoli, M.1991. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the human epileptogenic neocortex. Epilepsy Res. 10:33–40.
Bonhaus, D.W., Lippincott, S.E., and Huxtable, R.J.1984. Subcellular distribution of neuroactive amino acids in brains of genetically epileptic rats. Epilepsia 25:564–568.
Craig, C.R. and Hartman, E.R.1973. Concentration of amino acids in the brain of cobalt epileptic rat. Epilepsia 14:409–414.
Fumero, S. and Mondino, A.1976. Longitudinal changes of brain amino acid content occurring before, during and after epileptic activity. Brain Res. 24:1–9.
Hamberger, A., Haglid, K., Nystrom, B., and Silfvenius, H. 1993. Co-variation of free amino acids in human epileptogeniccortex. Neurochem. Res. 18:519–525.
Hiramatsu, M., Edamatsu, R., Suzuki, S., Shimada, M., and Mori, A.1990. Regional excitatory and inhibitory aminoacid levels in epileptic El mouse brain. Neurochem.Res. 15:821–825.
Huxtable, R.J., Bonhaus, D., and Lehmann, A.1986. Excitatory and inhibitory amino acids in the genetically seizure-susceptible rat. Pages 369–385,in Nistico, G., Morselli, P., Lloyd, K.G., Fariello, R.G., and Engel, J.(eds.), Neurotransmitters in Epilepsy, Raven Press, New York.
Huxtable, R.J., Laird, H., Bonhaus, D., and Thies, A.C.1982. Correlations between amino acid concentrations in brains of seizure-susceptible and seizure-resistant rats. Neurochem. Int. 4:73–78.
Huxtable, R.J. and Laird, H.E.1978. Are amino acid patterns necessarily abnormal in epileptic brains? Studies on the genetically seizure-susceptible rat. Neurosci.Lett. 10:341–345.
King, L.J., Carl, J.L., and Lao, L.1974. Brain amino acids during convulsions. J.Neurochem. 22:307–309.
Koyama, I. and Jasper, H.1977. Amino acid content of chronic undercut cortex of the cat in relation to electrical after discharge: comparison with cobalt epileptogenic lesions. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 55:523–536.
Lehmann, A., Sandberg, M., and Huxtable, R.J.1986. In vivo release of neuroactive amines and amino acids from the hippo-campus of seizure-resistant and seizure-susceptible rats. Neurochem.Int. 8:513–520.
Oja, S.S. and Kontro, P.1983. Free amino acids in epilepsy: possible role of taurine. Acta Neurol. Scand. 67 (Suppl.93):5–20.
Perry, T.L. and Hansen, S.1981.Amino acid abnormalities in epileptogenic foci. Neurology 31:872–876.
Sherwin, A., Robitaille, Y., Quesney, F., Olivier, A., Villemure, J., Leblanc, R., Feindel, W., Andermann, E., Gotman, J., Andermann, F., Ethier, R., and Kish, S.1988. Excitatory amino acids are elevated in human epileptic cerebral cortex. Neurology 38:920–923.
Tapia, R., Pasantes, H., Perez De La Mora, M., Ortega, B., and Massieu, G.1967.Free amino acids and glutamate decarboxylase activity in brain of mice during drug induced convulsions. Biochem.Pharmacol. 16:1211–1227.
Van Gelder, N.M., Edmonds, H.L.,Jr., Hegreberg, G.A., Chatburn, C.C., Clemmons, R.M., and Sylvester, D.M.1980. Amino acid changes in a genetic strain of epileptic beagle dogs. J.Neurochem.35:1087–1091.
Emson, P.C.1978.Biochemical and metabolic changes inepilepsy. Pages 319–338,in Barbeau, A. and Huxtable, R.J. (eds.), Taurine and Neurological Disorders, Raven Press, New York.
Huxtable, R.J.1981. Insights on function: metabolism and pharmacology of taurine in the brain. Pages 53–97,in Lombardini, J.B. and Kenny, A.(eds.), The Role of Peptides and Amino Acids as Neurotransmitters, Alan R.Liss,Inc., New York.
Lieu, P.L., Labiner, D.M., Weinand, M.E., and Huxtable, R.J. 1995. Neuroactive amino acids in synaptosomes from focal and nonfocal temporal lobe tissue of patients with intractable complex partial seizures. Pages 435–443,in Huxtable, R.J. and Michalk, D.V.(eds.),Taurine in Health and Disease, PlenumPress, New York.
Gray, E.G. and Whittaker, V.P.1962. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J. Anat. 96:79–88.
Lowry, O.J., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J. 1951. Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Van Gelder, N.M.1978. Glutamic acid in nervous tissue and changes of the taurine content: the action of taurine. Pages 387–402,in Barbeau, A. and Huxtable, R.J.(eds.),Taurine and Neurological Disorders, Raven Press, New York.
Van Gelder, N.M.1981. The role of taurine and glutamic acid in the epileptic process: a genetic predisposition. Rev. Pure Appl. Pharmacol. Sci. 2:293–316.
Van Gelder, N.M.1981. Glutamic acid in nervous tissue and changes of the taurine content: its implication in the treatment of epilepsy. Pages 115–125,in De Feudis, F.V. and Mandel, P. (eds.), Amino Acid Neurotransmitters, Raven Press, New York.
Berl, S. and Clarke, D.D.1978. Metabolic compartmentationof the glutatnate-glutamine system: glial contribution.Pages 691–708,in Fonnum, F.,(ed.), Amino Acids as Chemical Transmitters, enum Press, New York.
Hertz, L., Kvamme, E., McGeer, E.G., and Schousboe, A. 1984.Glutamine, Glutamate, and GABA in the Central Nervous System, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
Tapia, R. and Gonzalez, R.M.1978.Glutamine and glutamate as precursors of the releasable pool of GABA in brain cortexslices. Neurosci. Lett. 10:165–169.
Almarghini, K., Remy, A., and Tappaz, M.1991.Immuno-cytochemistry of the taurine biosynthesis enzyme, cysteinesulfinate decarboxylase, in the cerebellum: evidence for aglial localization. Neuroscience 43:111–119.
Tappaz, M., Almarghini, K., and Do, K.1994. Cysteine sulfinate decarboxylase in brain: identification, characterization and immunocytochemical localization in astrocytes.Pages 257–268,in Huxtable, R.J. and Michalk, D.V.(eds.), Taurine in Health and Disease, Plenum Press, New York.
Van Gelder, N.M.1983. Metabolic interactions between neurons and astroglia: glutamine synthetase, carbonic anhydrase and water balance. Pages 5–29,in Anonymous, Basic Mechanisms of Neuronal Hyperexcitability, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
Dodd, P.R., Bradford, H.F., Abdul-Ghani, A.S., Cox, D.W.G.,and Continho-Netto, J.1980. Release of amino acids from chronic epileptic and sub-epileptic foci in vivo. Brain Res. 193:505–517.
Koyama, I.1972. Amino acids in the cobalt induced epileptogenic and nonepileptogenic cat's cortex. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 50:740–752.
Huxtable, R.J., Laird, H., Lippincott, S.E., and Walson, P. 1983. Epilepsy and the concentrations of plasma amino acids in humans. Neurochem. Int. 5:125–135.
Van Gelder, N.M., Janjua, N.A., Metrakos, K.,Mac Gibbon, B., and Metrakos, J.D.1980. Plasma amino acids in 3/s spike wave epilepsy. Neurochem. Res. 5:659–671.
Janjua, N.A., Itano, T., Kugoh, T., Hosokawa, K., Nakano, M., Matsui, H., and Hatase, O.1992. Familial increase in plasma glutamic acid in epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 11:37–44.
Carl, G.F., Thompson, L.A., Williams, J.T., Wallace, V.C., and Gallagher, B.B.1992. Comparison of glutamine sythetases from brains of genetically epilepsy prone and genetically epilepsy resistant rats. Neurochem.Res. 17:1015–1019.
Perry, T.L., Berry, K., Hansen, S., Diamond, S., and Mok, C. 1971. Regional distribution of amino acids in human brain obtained at autopsy. J.Neurochem. 18:513–519.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labiner, D.M., Yan, C.C., Weinand, M.E. et al. Disturbances of Amino Acids from Temporal Lobe Synaptosomes in Human Complex Partial Epilepsy. Neurochem Res 24, 1379–1383 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022528522373
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022528522373