Summary
129 blood donors found to be HBsAg-positive on routine testing were studied for evidence of hepatic disease. Twelve had already lost the antigen from the serum when histologically examined. None of these has had clinical or histological evidence of inflammatory liver disease. Two of the 129 patients showed mild icteric hepatitis, cleared the antigen during the follow up and became anti-HBs positive. The remaining 115 patients who appeared clinically healthy and who had no history of previous icteric liver disease remained HBsAg positive during a mean follow up period of 17.3±3.0 months. Forty patients from these had a normal liver histology and 37 mild to distinct steatosis but no signs of inflammatory liver disease. 11 patients a mild nonspecific mesenchymal activity but no focal necrosis, 16 patients had mild infiltration in portal tracts and a few necrotic parenchymal cells with mesenchymal reaction, 6 patients had chronic persistent hepatitis, 4 chronic aggressive hepatitis, and 1 definite posthepatitic cirrhosis.
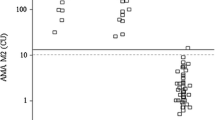
A number of biochemical and immunological variables of these patients were compared to those of a group of 88 HBsAg-negative blood donors. Significant higher SGOT values were found only in the groups of patients with steatosis, necrosis of parenchymal cells, and chronic aggressive hepatitis. SGPT values were significantly higher only in the two latter groups. The mean value for the gamma GT was significantly higher only in the group with steatosis, compared to the HBsAg carrier group with normal liver histology. A significant difference could not be established when compared to HBsAg-negative controls. Significantly higher, but still within normal range, were bilirubin values in all groups except for the 4 patients with chronic aggressive hepatitis. The relative frequencies of HBsAg subtypes were evenly distributed among the different groups. 7 carriers also had anti-HBs detectable in their serum. Autoimmune phenomena were rarely found.
With the direct fluorescent antibody technique intracytoplasmic HBsAg was found in 77% of the liver biopsy specimens with an even distribution of the frequencies among the groups. Intranuclear HBcAg however could only be found in patients who either had or developed a chronic inflammatory liver disease when rebiopsied during the follow up.
The results definitely establish that there are completely healthy HBsAg carriers with normal liver histology who do not differ from normal controls in their liver function and frequencies of positive autoimmune phenomena. They frequently have intracycloplasmic HBsAg but never HBcAg or IgG in the nuclei of their hepatocytes.
Zusammenfassung
Wir haben 129 Blutspender, bei denen bei Routineuntersuchungen HBsAg im Serum festgestellt wurde, zur diagnostischen Klärung einer möglichen Lebererkrankung untersucht. Zwölf hatten, als sie zur klinischen und leberbioptischen Untersuchung aufgenommen wurden, schon kein HBsAg mehr im Serum. Keiner von diesen hatte klinisch oder histologisch Anhalt für eine entzündliche Lebererkrankung. Zwei der 129 Patienten hatten eine milde, ikterische Hepatitis, verloren das Antigen während des Verlaufes und wurden anti-HBs-positiv. Die übrigen 115 Patienten, die klinisch gesund erschienen und keine frühere ikterische Leberkrankheit hatten, blieben HBsAg-positiv während des bisherigen Verlaufes von im Mittel 17,3±3,0 Beobachtungsmonaten. 40 dieser Patienten hatten histologisch eine normale Leber und 37 geringe bis deutliche Verfettungen des Parenchyms ohne Entzündungszeichen. 11 Patienten hatten eine leichte unspezifische Mesenchymaktivierung ohne fokale Nekrosen, 16 Patienten hatten neben Einzelzellnekrosen mit mesenchymaler Reaktion milde portale Infiltrationen, 6 hatten eine chronisch persistierende Hepatitis, 4 eine chronisch aggressive Hepatitis und 1 Patient eine posthepatitische Cirrhose.
Eine Anzahl biochemischer und immunologischer Werte dieser Patientengruppen wurden mit denen einer Gruppe von 88 HBsAg-negativen Blutspendern verglichen. Signifikant höhere SGOT-Werte wurden nur in der Gruppe der Patienten mit Verfettungen, der Gruppe mit Nekrosen und Reaktionen und der Gruppe mit chronisch aggressiver Hepatitis gefunden. Die SGPT-Werte waren nur in den beiden letzteren Gruppen signifikant höher. Der Mittelwert der gamma-GT war nur in der Patientengruppe mit Verfettungen signifikant höher als in der HBsAg-Trägergruppe mit normaler Histologie, nicht aber verglichen mit dem HBsAg-negativen Kontrollkollektiv. Signifikant erhöht waren auch die Bilirubinwerte in allen Gruppen außer der Gruppe mit chronisch aggressiver Hepatitis, jedoch blieben die Mittelwerte immer im Normbereich.
Die relativen Häufigkeiten der HBsAg-Subtypen verteilten sich gleichmäßig auf die verschiedenen Gruppen. Bei 7 Trägern fanden wir auch Anti-HBs im Serum. Autoimmunphänomene wurden nur selten beobachtet.
Mit der direkten fluorescierenden Antikörpertechnik wurde in 77% der Leberbiopsien intrazytoplasmatisches HBsAg mit einer gleichmäßigen Häufigkeitsverteilung in den Gruppen festgestellt. Intranucleäres HBcAg konnte aber nur bei Patienten gefunden werden, die entweder eine chronisch entzündliche Lebererkrankung hatten oder entwickelten, während sie im Verlauf zur Kontrolle biopsiert wurden.
Die Ergebnisse beweisen schlüssig, daß es vollkommen gesunde HBsAg-Träger mit normaler Leberhistologie gibt, die sich in bezug auf ihre Leberfunktion und Häufigkeit von positiven Autoimmunphänomenen nicht von normalen Kontrollpersonen unterscheiden. Diese Träger haben häufig intrazytoplasmatisches HBsAg aber nie HBcAg oder IgG in Kernen von Hepatocyten.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B Virus [11]
- HBsAg:
-
Hepatitis B-surface Antigen [11]
- HBcAg:
-
Hepatitis B-core Antigen [11]
- anti-HBs :
-
Antikörper gegen HBsAg [11]
- anti-HBc :
-
Antikörper gegen HBc [11]
- AGF:
-
Antigammaglobulinfaktor (Rheumafaktor)
- ANA:
-
Antinucleäre Antikörper
- AMA:
-
Antimitochondriale Antikörper
- SMA:
-
Smooth muscle antibody (Antikörper gegen glatte Muskulatur)
- GER:
-
Glattes endoplasmatisches Reticulum
- FAT:
-
Fluorescierende Antikörpertechnik
- CPH:
-
Chronisch persistierende Hepatitis
- CAH:
-
Chronisch aggressive Hepatitis
Literatur
Akeyama, T., Kamada, T., Koizumi, T., Abe, H.: The lokalization of the Australia-antigen in the liver by immunofluorescence. J. clin. Path.25, 1071 (1972)
Anderson, K.E., Sun, S.C., Berg, H.S., Chang, N.K.: Liver function and histology in asymptomatic Chinese military personnel with hepatitis B antigenemia. Am. J. Dig. Dis.19, 693 (1974)
Arnold, W., Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H., Hess, G., Knolle, J.: The diagnostic significance of intrahepatocellular hepatitis-B-surface-antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis-B-core-antigen (HBcAg) and IgG for the classification of inflammatory liver diseases. Studies on HBsAg-positive and -negative patients. Klin Wschr.53, 1069 (1975)
Arnold, W., Purcell, R.H., Hess, G., Knolle, J., Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H.: DNA-polymerase and anti-HBc titers in asymptomatic HBsAg carriers. Digestion im Druck
Biswas, R., Gerlich, W., Stamm, B., Thomssen R.: Untersuchungen über das gleichzeitige Vorkommen von HBsAntigen und anti-HBs. 2. Rundgespräch DFG-Schwerpunkt Virushepatitisforschung Göttingen 15. 12. 1975
Blumberg, B.S., Friedlaender, J.S., Woodside, A., Sutnick, A.J., London, W.J.: Hepatitis and Australia antigen: autosomal rescessive inheritance of susceptibility to infections in humans. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci, (USA)62, 1108 (1969)
Bolin, T.D., Davis, A.E., Liddelow, A.G.: Liver disease and cell-mediated immunity in hepatitis-associated antigen (HAA) carriers. Gut14, 365 (1973)
Cherubin, C.E.: Risk of post-transfusion hepatitis in recipients of blood containing S.H. antigen at Harlem hospital. LancetI, 627 (1971)
Chicot, D., Delaruelle, S.: Etude clinique, épidémiologique et biochimique d'une population de donneurs des sang porteurs de l'antigene de l'hépatite B. Rev. Franc. Transfus.17, 75 (1974)
Coller, J.A., Millman, J., Halbherr, T.C., Blumberg, B.S.: Radioimmunoprecipitation assay for Australia antigen, antibody and antigen-antibody complexes. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.138, 249 (1971)
Committee on Viral Hepatitis of the NRC/NAS: Nomenclature of antigens associated with viral hepatitis Type B. Intervirology2, 134 (1973/1974)
Dane, D.S., Cameron, C.H., Briggs, H.: Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen associated hepatitis. LancetI, 695 (1970)
De Groote, J., Desmet, V.J., Gedigk, P., Korb, G., Popper, H., Poulsen, H., Scheuer, P., Schmid, M., Thaler, H., Uehlinger, E., Wepler, W.: A classification of chronic hepatitis. LancetII, 628 (1968)
Dietrichson, O., Juhl, E., Christoffersen, P., Elling, P., Faber, U., Iversen, K., Nielsen, J.O., Petersen, P., Poulsen, H.: Acute viral hepatitis: factors possibly predicting chronic liver disease. Acta path. microbiol. Scand. Sect. A.83, 183 (1975)
Dudley, F.J., Fox, R.A., Sherlock, S.: Cellular immunity and hepatitis-associated Australia antigen liver disease. LancetI, 723 (1972)
Ehrke, K.: Die Bestimmung des HA-Antigens mit der Komplementbindungsreaktion in einem Autoanalyzer-System. Dissertation Mainz 1973
Eleftheriou, N., Thomas, H.C., Heathcote, J., Sherlock, S.: Incidence and clinical significance of e antigen and antibody in acute and chronic liver disease. LancetII, 1171 (1975)
El Sheikh, N., Woolf, J.L., Galbraith, R.M., Dymock, J.W., Eddleston, A.L.W.F., Williams, R.: The “e” antigen as a marker of chronic liver disease in hepatitis B antigen-positive patients and blood donors. 10. Meeting EASL Barcelona 11.–13. Sept. 1975
Fairnaru, M., Levij, I.S.: Asymptomatic hepatitis B antigen carriers: a clinicopathological study. Acta Hepato-Gastroenterol.21, 186 (1974)
Fay, O.H., Tanno, H., Roucoroni, M., Findor, J., Igartua, E.B., Domecq, R.: Das e-Antigen bei akuter und chronischer Hepatitis. Leber-Magen-Darm5, 140 (1975)
Feinman, S.V., Berris, B., Sinclair, J.C., Wrobel, D.M., Alter, H.J., Holland, P.V.: Relation of hepatitis-B-antgen subtypes in symptom-free carriers to geographical origin and liver abnormalities. LancetII, 867 (1973)
Feinman, S.V., Cooter, N., Sinclair, J.C., Wrobel, D.M., Berris, B.: Clinical and epidemiological significance of the HBsAg Australia antigen): carrier state. Gastroenterology68, 113 (1975)
Feinman, S.V., Berris, B., Sinclair, J.C., Wrobel, D.M., Murphy, B.L., Maynard, J.E.: e-Antigen and anti-e in HBsAg carriers. LancetII, 1173 (1975)
Freudenberg, J., Weiller, H., Knolle, J., Berger, J., Bitz, H., Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H.: HLA and immunoreactivity to HBsAg. Z. Immunitätsforsch.151, (1976) im Druck
Gerety, R.J., Hoofnagle, J.M., Markenson, J.A., Barker, L.F.: Exposure to hepatitis B Virus and development of the chronic HBAg carrier state in children. J. Pediat.84, 661 (1974)
Gocke, D.J.: A prospective study of posttransfusion hepatitis. The role of Australia antigen. J. Amer. med. Ass.219, 1165 (1972)
Griffin, F.M.: Hepatitis B antigenemia in apparently healthy blood donors. J. Amer. med. Ass.226, 753 (1973)
Gudat, F., Bianchi, L., Sonnabend, W., Thiel, G., Aenishaenslin, W., Stalder, G.A.: Pattern of core and surface expression in liver tissue reflects state of specific immune response in hepatitis B. Lab. Invest.32, 1 (1975)
Helske, T.: Carriers of Hepatitis B antigen and transfusion hepatitis in Finland. Scand. J. Hemat. Suppl.22, 65 (1974)
Hess, G., Nielsen, J.O., Arnold, W., Knolle, J., Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H.: “e” and anti-“e” in HbsAg-positive and-negative inflammatory liver disease and asymptomatic HBsAg-carriers. In Vorbereitung
Hoofnagle, J.H., Markerson, J.A., Daniles, C.A., Gerety, R.J., Notkins, A.L., Barker, L.F.: The lack of association between rheumatoid factor and hepatitis B antigen. Amer. J. med. Sci.268, 23 (1974)
Hopf, U., Arnold, W., Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H., Förster, E., Bolte, J.P.: Studies on the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory liver diseases. I. Membrane-fixed IgG on isolated hepatocytes from patients. Clin. exp. Immunol.22, 1 (1975)
Ichida, F., Sasaki, H., Sekine, T., Inagaki, T.: Clinico-pathological studies of the liver in asymptomatic carriers of Australia Antigen (HBAg). Acta Hepato-Gastroenterol.22, 13 (1975)
Iwarson, S., Magnius, L., Lindholm, A., Lundin, P.: Subtypes of hepatitis B antigen in blood donors and posttransfusion hepatitis: clinical and epidemiological aspects. Brit. med. J. I, 84 (1973)
Kaboth, U., Schober, A., Arndt, H.J., Vido, J., Selmair, M., Gallasch, E., Vermo, P., Thomssen, R., Creutzfeldt, W.: Australia (SH)-Antigen-Befunde bei Leberkranken und Blutspendern. Dtsch. med. Wschr.95, 2157 (1970)
Kliman, A.: Australia antigen in volunteer and paid blood donors. New Engl. J. Med.284, 109 (1971)
Klinge, O., Kaboth, U., Arnold, R.: Histologische Leberuntersuchungen bei gesunden Australia (SH)-Antigen- und Antikörper-Trägern. Dtsch. med. Wschr.95, 2583 (1970)
Klinge, O., Altmann, H.W.: Morphologic toxischer Hepatosen. Münch. med. Wschr.113, 1529 (1971)
Klinge, O., Kaboth, U., Winckler, K.: Feingewebliche Befunde an der Leber klinisch gesunder Australia-Antigen (HB-Ag)-Träger. Virch. Arch. Abt. A Path. Anat.361, 359 (1973)
Kohler, P.F., Dubois, R.S., Merrill, D.A., Bowes, W.A.: Prevention of chronic neonatal hepatitis B virus infection with antibody to the hepatitis B surface antigen. New Engl. J. Med.291, 1378 (1974)
Krugman, S., Giles, J.P., Hammond, J.: Viral hepatitis Type B (MS-2 Strain). Studies on active immunization. J. Amer. med. Ass.217, 41 (1971)
Krugman, S., Hoofnagle, J.H., Gerety, R.J., Kaplan, P.M., Gerin, J.L.: Viral hepatitis Typ B; DNA Polymerase activity and antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. New Engl. J. Med.290, 1331 (1974)
Magnius, L.O., Epsmerk, J.A.: New specificities in Australia-antigen positive sera distinct from the le Bouvier determinants. J. Immunol.109, 1017 (1972)
Magnius, L.O., Lindholm, A., Lundin, P., Iwarson, S.: A new antigen-antibody system. Clinical significance in long-term carriers of hepatitis B surface antigen. J.Amer. med. Ass.231, 356 (1975)
Merrill, D.A., Dubois, R.S., Kohler, P.F.: Neonatal onset of the hepatitis-associated antigen carrier state. New Engl. J.Med.287, 1280 (1972)
Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H., Arnold, W., Knolle, J., Hess, G.: Immunreaktionen gegenüber HBsAg, HBcAg und „e“-Antigen bei akuter Virushepatitis sowie lebergesunden und leberkranken HBsAg-Trägern. Z. Gastroenterol.14, (1976) im Druck
Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H., Baumann, W., Arnold, W., Freudenberg, J.: Immunological aspects in chronic active hepatitis in children. In: Advances in Liver diseases in children. D. Alagille Hsg. Paris 1976
Mosley, J.W.: The HBV carrier — a new kind of leper. New Engl. J. Med.292, 477 (1975)
Naccarato, R., Fagiolo, U., Farini, R., Chiaramonte, M.: Immunological study of HB-Ag carriers. Klin. Wschr.53, 489 (1975)
Nielsen, J.O., Dietrichson, O., Elling, P., Christoffersen, P.: Incidence and meaning of persistence of Australia antigen in patients with acute viral hepatitis: development of chronic hepatitis. New Engl. J. Med.285, 1156 (1971)
Nielsen, J.O., Nielsen, M.H., Reinicke, V.: Absence of Dane particles in Au-antigen carriers with a histologically normal liver. LancetII, 934 (1972)
Nielsen, J.O., Nielsen, M.H., Elling, P.: Differential distribution of australia-antigen-associated particles in patients with liver diseases and normal carriers. New Engl. J. M.288, 484 (1973)
Nielsen, J.O., Le Bouvier, G.L., Copenhagen Hepatitis Acuta Program: Subtypes of Australia antigen among patients and healthy carriers in Copenhagen. New Engl. J. Med.288, 1257 (1973)
Nielsen, J.O., Reinicke, V., Dietrichson, O., Andersen, V., Thomsen, M., Andersen, E.: Immunological studies of Australia antigen carriers with and without liver diseases. Clin. exp. Immunol.15, 9 (1973)
Nielsen, J.O., Dietrichson, O., Juhl, E.: Incidence and meaning of the “e” determinant among B-antigen positive patients with acute and chronic liver diseases. LancetII, 913 (1974)
Pesendorfer, F., Krassnitzky, O., Wewalka, F.: Immunelektrophoretischer Nachweis von „Hepatitis-Associated-Antigen“ (Au/SH-Antigen). Klin. Wschr.48, 58 (1970)
Petersen, P., Christoffersen, P., Elling, P., Juhl, E., Dietrichson, O., Faber, V., Iversen, K., Nielsen, J.O., Poulsen, H.: Acute viral hepatitis: A survey of 500 patients, clinical biochemical, immunological and morphological features at time of diagnosis. Scand. J. Gastroent.9, 607 (1974)
Reinicke, V., Dybkjaer, E., Poulsen, H., Banke, O., Lyloff, K., Nordenfelt, E.: A study of Australia-antigen-positive donors and their recipients, with special reference to liver histology. New Engl. J. Med.286, 867 (1972)
Ringertz, O.: Epidemiology of serum hepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol.3, 305 (1974)
Russell, R.J., Goldberg, D.M., Allan, J.G., Mac Sween, R.N.H., Wallace, J.: A study of hepatic disease in Australia antigen and antibody-positive blood donors. Amer. J. dig. Dis.19, 113 (1974)
Scheffé, H.: A method for judging all contrasts in the analysis of variance. Biometrika40, 87 (1953)
Schober, A., Thomsen, R., Kaboth, U., Worch, R.: Nachweis inapparenter Infektionen im Rahmen eines Ausbruchs von übertragbarer Gelbsucht mit positivem Australia-(SH)-Antigen-Befund. Dtsch. med. Wschr.95, 2582 (1970)
Schober, A., Thomssen, R., Kaboth, U.: Serologische Subtypen des Hepatitis-B-Antigens (Australia-Antigen). Hepatitis-B-Epidemie des Subtyps Y bei regional vorherrschendem Subtyp D. Dtsch. med. Wschr.97, 1579 (1972)
Schweitzer, J.L., Dunn, A.E.G., Peters, R.L., Spears, R.L.: Viral hepatitis B in neonates and infants. Amer. J. Med.55, 762 (1973)
Shattock, A.G., Gorry, H.F.M.: Hepatitis B antigen (HBAg) in the Republic of Ireland: distribution of ad and ay subtypes. Ir. J. med. Sci.143, 214 (1974)
Simon, J.B., Patel, S.K.: Liver disease in asymptomatic carriers of hepatitis B antigen. Gastroenterology66, 1020 (1974)
Singleton, J.W., Fitch, R.A., Merrill, D.A., Kohler, P.F., Rettberg, W.A.H.: Liver disease in Australia-antigen-positive blood-donors. LancetII, 785 (1971)
Vittal, S.B.V., Dourdourekas, D., Shobassy, N., Gerber, M., Telischi, M., Szanto, P.B., Steigman, F., Clowdus, B.F.: Asymptomatic hepatic disease in blood donors with hepatitis B antigenemia. Amer. J. clin. Path.62, 649 (1974)
Vyas, G.N.: Evidence against recessive inheritance of susceptibility to the chronic carrier state for hepatitis B antigen. Nature248, 159 (1974)
Wewalka, F.: Epidemiology of hepatitis B antigen. In: The Liver and its diseases (F. Schaffner, S. Sherlock, C.M. Leevy Hsgb.). Stuttgart (Thieme) 1974
Woolf, J.L., Boyes, B.E., Jones, D.M.: Asymptomatic liver disease in hepatitis B antigen carriers. J. clin. Path.27, 348 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Professor Dr. P. Schölmerich zum 60. Geburtstag gewidmet
Mit Unterstützung der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft, Schwerpunkt Virushepatitisforschung, Me 244/8 und Me 244/9
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knolle, J., Born, M., Hess, G. et al. Die Charakterisierung des klinisch gesunden Hepatitis-B-Antigen (HBsAg)-Trägers. Klin Wochenschr 54, 567–578 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01619572
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01619572